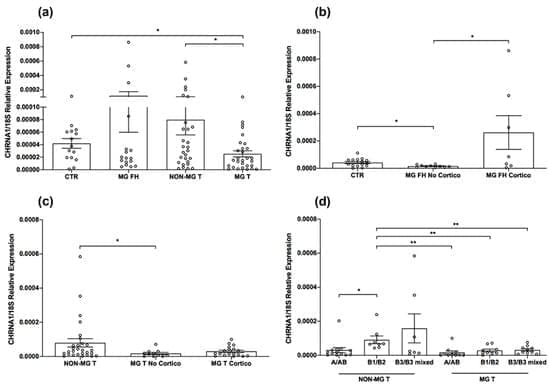
The thymus is widely recognized as an immunological niche where autoimmunity against the acetylcholine receptor (AChR) develops in myasthenia gravis (MG) patients, who mostly present thymic hyperplasia and thymoma. Thymoma-associated MG is frequently characterized by autoantibodies to the muscular ryanodine receptor 1 (RYR1) and titin (TTN), along with anti-AChR antibodies. By real-time PCR, we analyzed muscle—CHRNA1, RYR1, and TTN—and muscle-like—NEFM, RYR3 and HSP60—autoantigen gene expression in MG thymuses with hyperplasia and thymoma, normal thymuses and non-MG thymomas, to check for molecular changes potentially leading to an altered antigen presentation and autoreactivity.