It’ll certainly take some work.
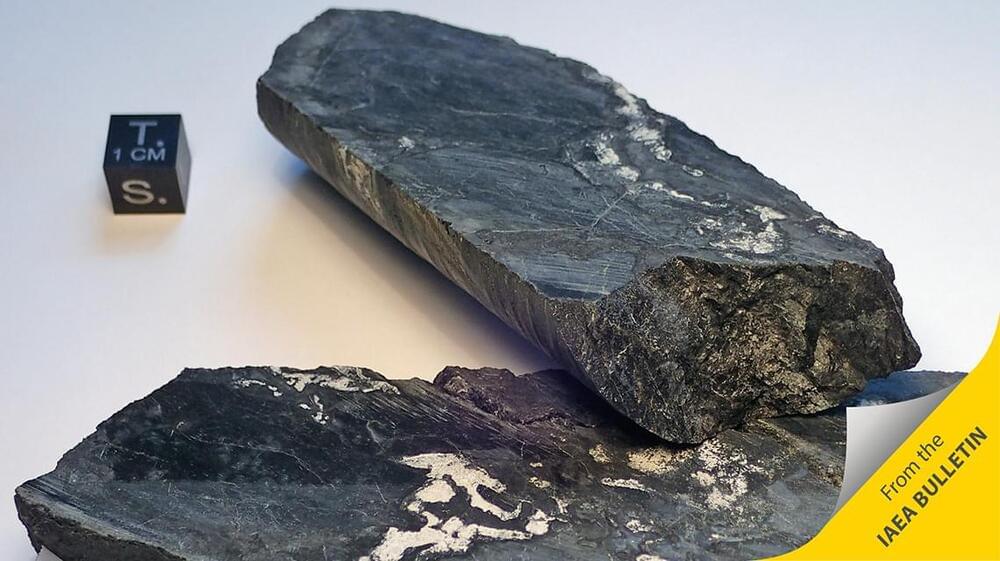



Physicist Francis Perrin sat at a nuclearfuel-processing plant down in the south of France, thinking to himself: “This cannot be possible.” It was 1972. On the one hand, there was a dark piece of radioactive natural uranium ore, extracted from a mine in Africa. On the other, accepted scientific data about the constant ratio of radioactive uranium in ore.
Examination of this high-grade ore from a mine in Gabon was found to contain a lower proportion of uranium-235 (U-235) — the fissile sort. Only a tiny bit less, but enough to make the researchers sit back and scratch their heads.

Computer science expert Kristian Hammond discusses Northwestern’s Center for Advancing Safety of Machine Intelligence and its efforts in making AI more responsible.
Computer scientist Kristian Hammond says the Center for Advancing Safety of Machine Intelligence is working to develop the kinds of guardrails that will help us use AI for a bigger and better impact on the world without compromising our well-being. Photo by Jonah Elkowitz.

Oxford Nanopore Technologies and Wasatch BioLabs have joined forces to develop a groundbreaking direct whole-methylome sequencing (dWMS) product. This collaboration addresses the limitations of traditional methylation sequencing methods, such as bisulfite sequencing and methylation microarrays.
By leveraging Oxford Nanopore’s advanced sequencing technology and Wasatch BioLabs’ proprietary methylation assays, the partners aim to offer a more comprehensive and accurate approach to studying epigenetic modifications. dWMS eliminates the need for harsh chemical treatments and PCR amplification, reducing biases and improving genome-wide coverage.
This innovative technology has the potential to revolutionize epigenetic research, providing valuable insights into the role of methylation in various biological processes and diseases. The collaboration between these two companies is poised to drive significant advancements in genomics and precision medicine.
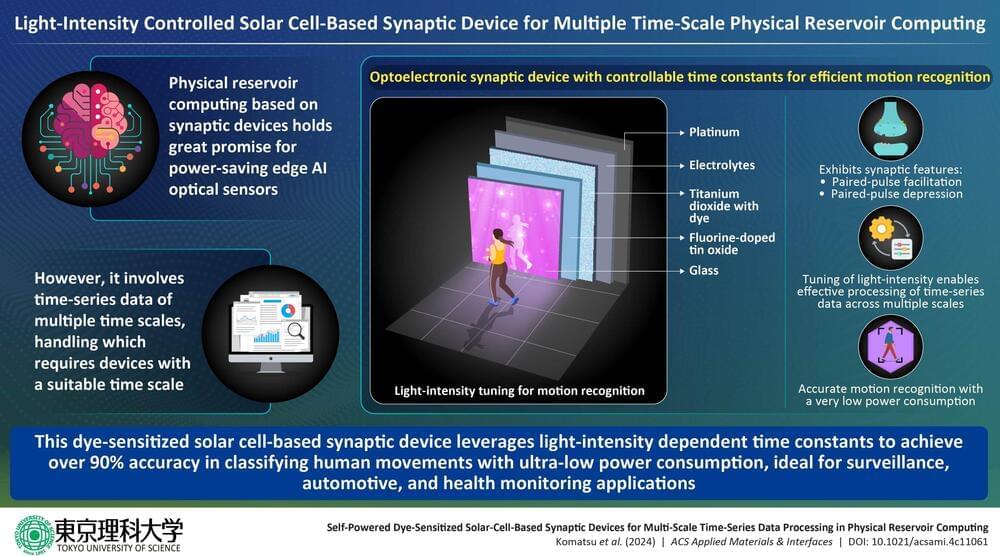
Researchers at Tokyo University of Science have developed a solar cell-based optoelectronic device that mimics human synapses for efficient edge AI processing.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming increasingly useful for the prediction of emergency events such as heart attacks, natural disasters, and pipeline failures. This requires state-of-the-art technologies that can rapidly process data. In this regard, reservoir computing, specially designed for time-series data processing with low power consumption, is a promising option.
It can be implemented in various frameworks, among which physical reservoir computing (PRC) is the most popular. PRC with optoelectronic artificial synapses (junction structures that permit a nerve cell to transmit an electrical or chemical signal to another cell) that mimic human synaptic elements are expected to have unparalleled recognition and real-time processing capabilities akin to the human visual system.
However, PRC based on existing self-powered optoelectronic synaptic devices cannot handle time-series data across multiple timescales, present in signals for monitoring infrastructure, natural environment, and health conditions.
Proxie by Cobot automates tasks, enabling teams to focus on high-value work. https://link.ie.social/1TJU7S
#Automation #CobotTech
Proxie is a more direct and practical solution in an industry where many companies gravitate toward super-advanced humanoid robots. Brad Porter explains that while humanoid robots represent an exciting frontier, their high costs and variable reliability pose significant barriers to widespread deployment.
“At Amazon, we looked a lot at humanoids,” Porter remarks. “Here are real problems to be solved with something more human capable, but jumping all the way to a humanoid is super complicated. The AI is not really there yet.”
Instead, Proxie is designed to efficiently handle the simpler, essential tasks humans prefer to avoid, reflecting a more immediate application of robotic technology in everyday operations. This approach aligns with industry trends where simplicity and reliability in automation are becoming increasingly important.



The LTV program involves companies taking responsibility for delivering lunar rovers to the Moon, with the possibility of commercial use outside of NASA’s requirements.
Lunar Outpost Executive Director Justin Cyrus said that the choice of Starship was due to SpaceX’s high level of technological advancement, the rapid pace of their work, and the quality of the organization. It’s a vehicle that we think will be able to provide reliable landing on the lunar surface, and we know that they can get it done on the timelines we need, Cyrus emphasized.
The Lunar Outpost Eagle rover is designed to be compatible with a variety of landing systems, but Starship is the prioritized choice. The company strives to remain flexible in its choice of technical solutions by evaluating the progress of the industry over time.

The V-score benchmarks classical and quantum algorithms in solving the many-body problem. The study highlights quantum computings potential for tackling complex material systems while providing an open-access framework for future research innovations.
Scientists aspire to use quantum computing to explore complex phenomena that have been difficult for current computers to analyze, such as the characteristics of novel and exotic materials. However, despite the excitement surrounding each announcement of “quantum supremacy,” it remains challenging to pinpoint when quantum computers and algorithms will offer a clear, practical advantage over classical systems.
A large collaboration led by Giuseppe Carleo, a physicist at the Swiss Federal Institute for Technology (EPFL) in Lausane and the member of the National Center for Competence in Research NCCR MARVEL, has now introduced a method to compare the performance of different algorithms, both classical and quantum ones, when simulating complex phenomena in condensed matter physics. The new benchmark, called V-score, is described in an article just published in Science.