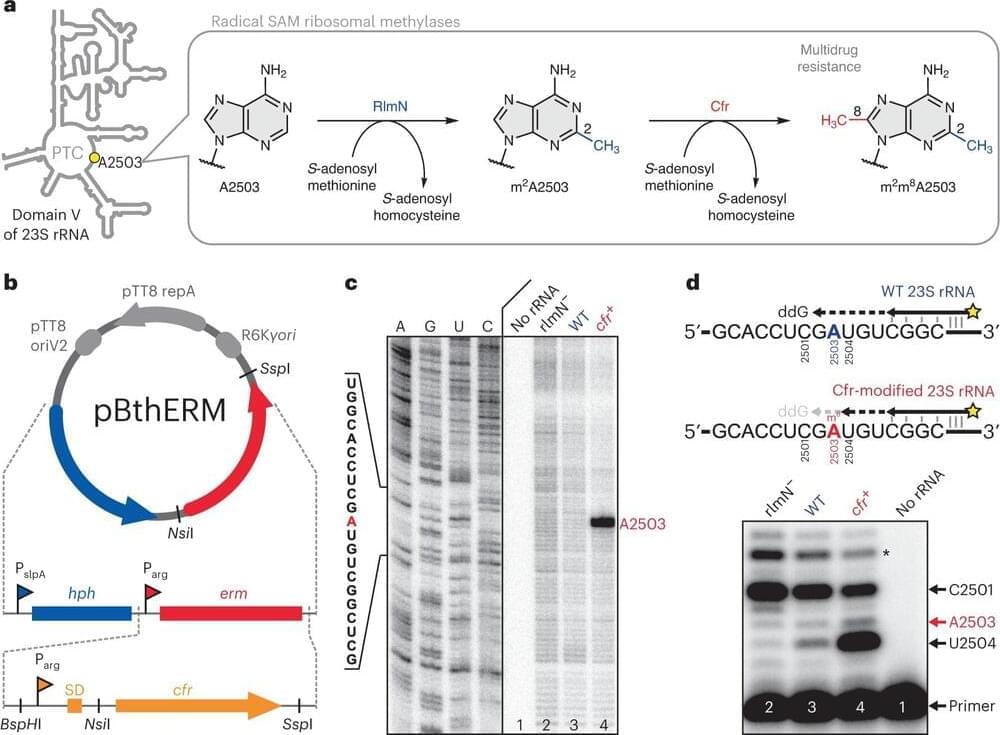
Scientists at the University of Illinois Chicago and Harvard University have developed an antibiotic that could give medicine a new weapon to fight drug-resistant bacteria and the diseases they cause.
The antibiotic, cresomycin, described in Science, effectively suppresses pathogenic bacteria that have become resistant to many commonly prescribed antimicrobial drugs.
The promising novel antibiotic is the latest finding for a longtime research partnership between the group of Yury Polikanov, associate professor of biological sciences at UIC, and colleagues at Harvard. The UIC scientists provide critical insights into cellular mechanisms and structure that help the researchers at Harvard design and synthesize new drugs.