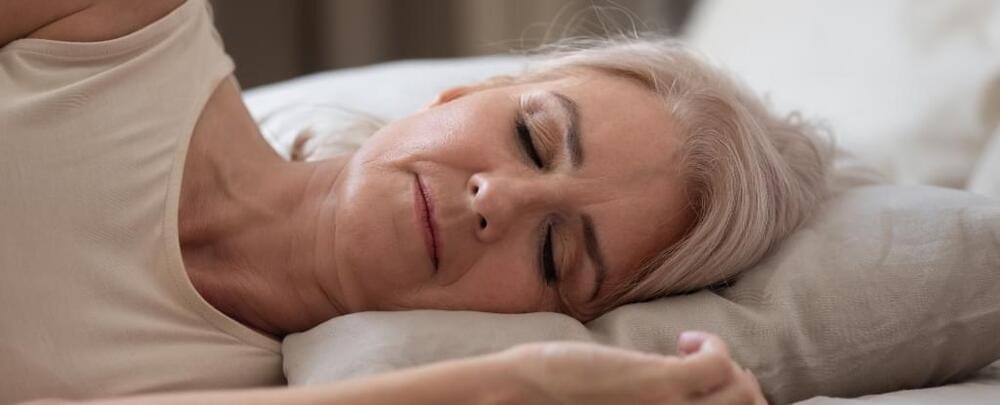
The risk of getting dementia may go up as you get older if you don’t get enough slow-wave sleep. Over-60s are 27 percent more likely to develop dementia if they lose just 1 percent of this deep sleep each year, a 2023 study found.
Slow-wave sleep is the third stage of a human 90-minute sleep cycle, lasting about 20–40 minutes. It’s the most restful stage, where brain waves and heart rate slow and blood pressure drops.
Deep sleep strengthens our muscles, bones, and immune system, and prepares our brains to absorb more information. Recently, research discovered that individuals with Alzheimer’s-related changes in their brain did better on memory tests when they got more slow-wave sleep.