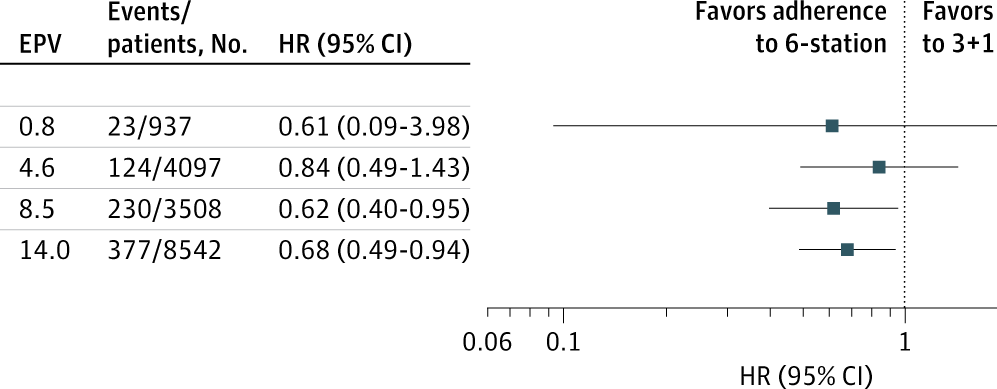
Guideline-adherent lymph node dissection provided a small survival benefit for patients with high-grade or no lepidic pattern LungAdenocarcinoma, but not for those with lepidic pattern alone.
Importance Lymph node dissection for early-stage lung adenocarcinoma is controversial. Histologic pattern subtyping reveals heterogeneity of lung adenocarcinoma, yet its association with lymph node involvement and dissection is understudied.
Objective To assess the association between guideline-adherent lymph node dissection, histologic pattern subtyping, and overall survival in patients with clinical T1N0M0 lung adenocarcinoma.
Design, Setting, and Participants This multicenter cohort study used data from the National Cancer Center LungReal database, a multicenter, electronic health records-based database for patients undergoing surgery for lung cancer, from January 2014 to December 2021, with the last follow-up in December 2022. Patients were categorized based on histologic pattern of adenocarcinoma into 2 groups: lepidic without high-grade pattern, and high-grade or no lepidic pattern. The data analysis was performed from April to November 2025.