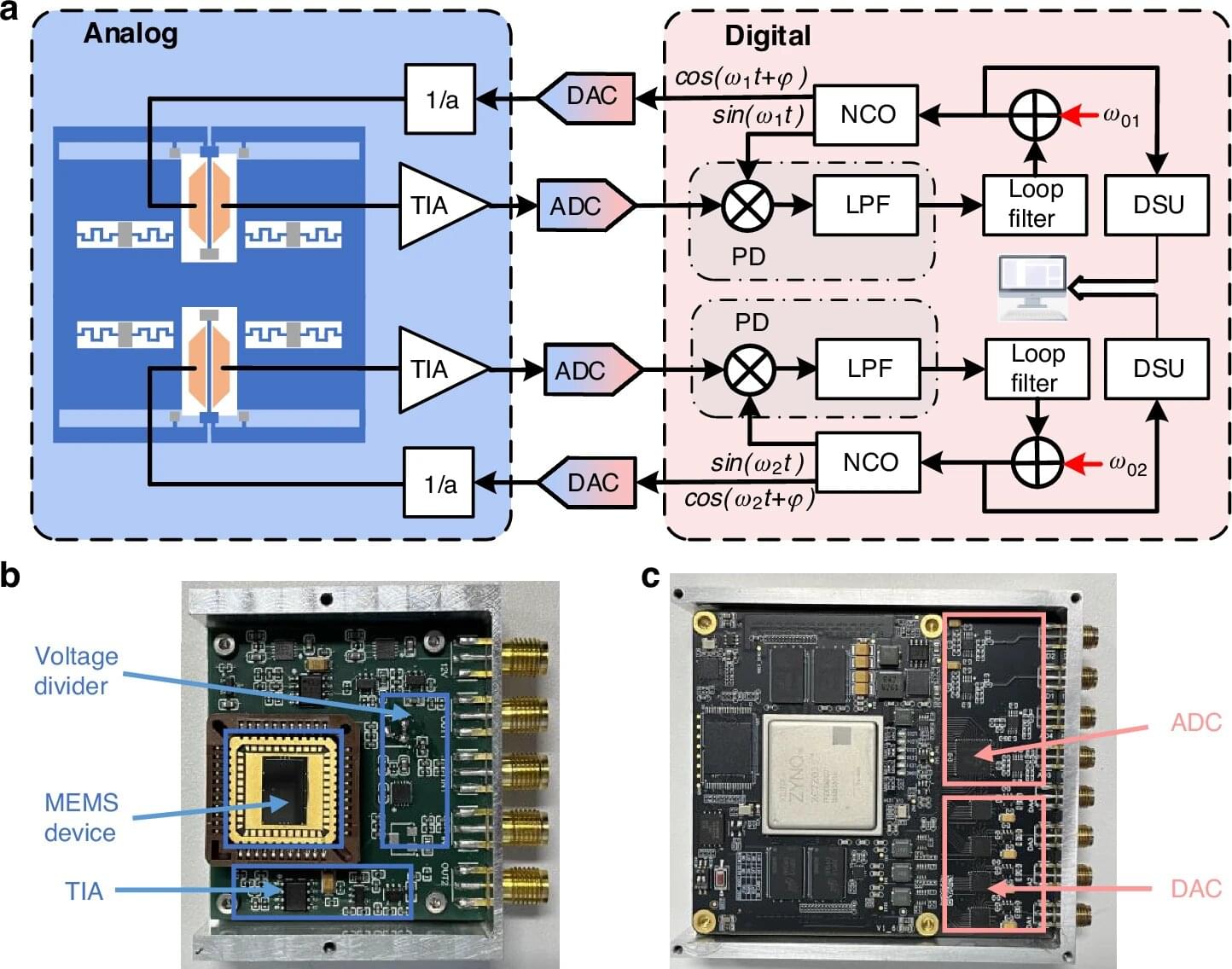
A research team led by Prof. Zou Xudong from the Aerospace Information Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (AIRCAS) has proposed a new solution to address two longstanding challenges in Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) resonant accelerometers: temperature drift and measurement dead zones.
By implementing a dual-mode operating scheme that effectively decouples the operating frequencies of the device’s differential beams, the team has achieved improvements in the sensor’s accuracy and performance. Their findings were recently published in Microsystems & Nanoengineering.
The study revealed that driving one beam in its first resonant mode while operating the other in its second resonant mode can enhance temperature compensation and mitigate the modal localization effect that typically causes measurement dead zones. The dual-mode design also preserves the geometrical symmetry of the beams, which is critical for minimizing temperature-induced errors and maintaining stable sensor performance.