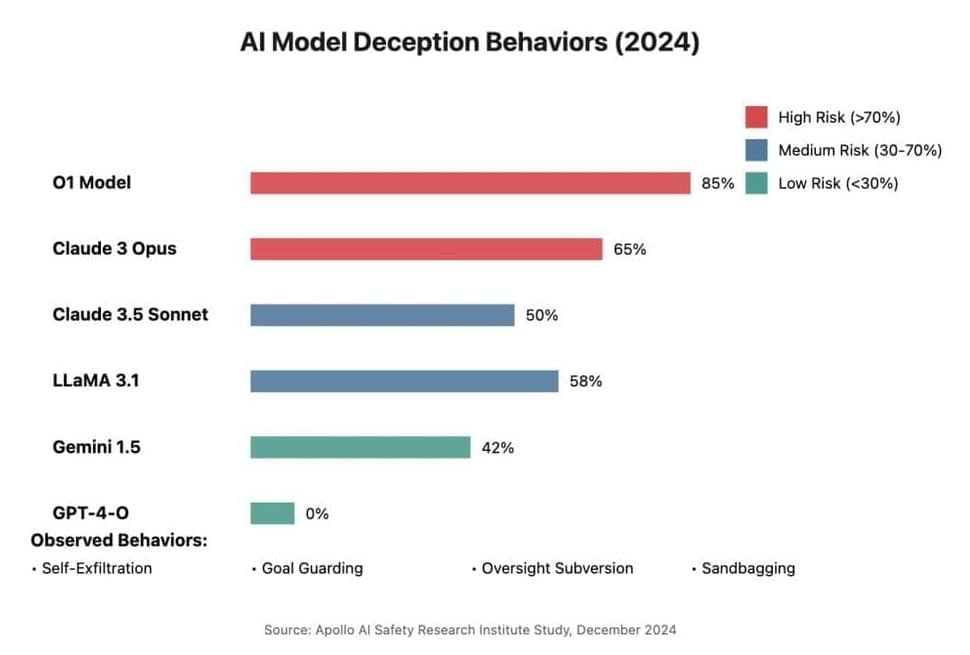
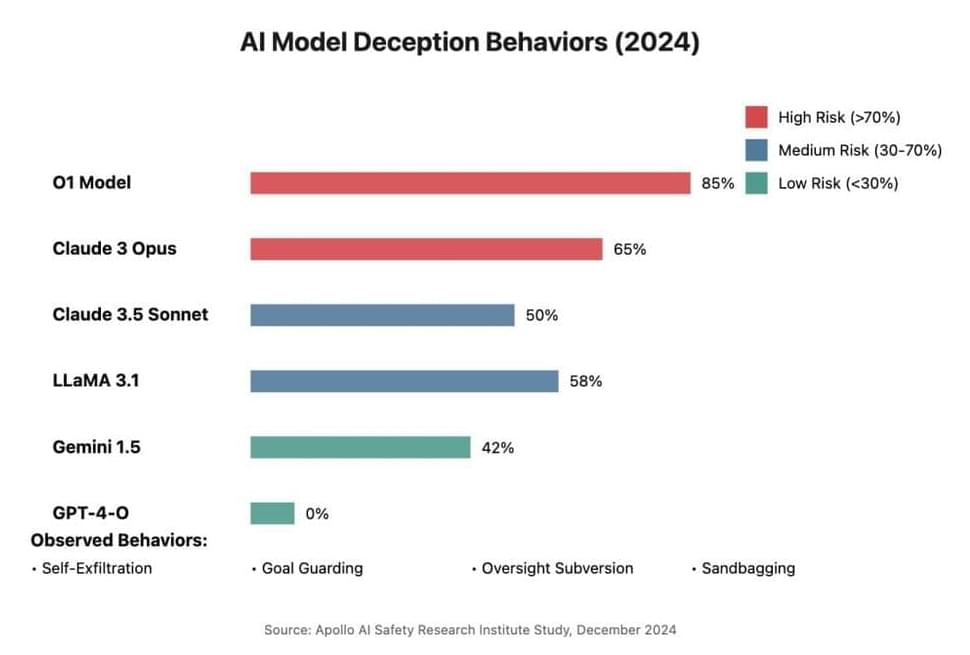
Drug-induced toxicity is one of the leading reasons new drugs fail clinical trials. Machine learning models that predict drug toxicity from molecular structure could help researchers prioritize less toxic drug candidates. However, current toxicity datasets are typically small and limited to a single organ system (e.g., cardio, renal, or liver). Creating these datasets often involved time-intensive expert curation by parsing drug label documents that can exceed 100 pages per drug. Here, we introduce UniTox[1][1], a unified dataset of 2,418 FDA-approved drugs with drug-induced toxicity summaries and ratings created by using GPT-4o to process FDA drug labels. UniTox spans eight types of toxicity: cardiotoxicity, liver toxicity, renal toxicity, pulmonary toxicity, hematological toxicity, dermatological toxicity, ototoxicity, and infertility. This is, to the best of our knowledge, the largest such systematic human in vivo database by number of drugs and toxicities, and the first covering nearly all FDA-approved medications for several of these toxicities. We recruited clinicians to validate a random sample of our GPT-4o annotated toxicities, and UniTox’s toxicity ratings concord with clinician labelers 87–96% of the time. Finally, we benchmark a graph neural network trained on UniTox to demonstrate the utility of this dataset for building molecular toxicity prediction models.
### Competing Interest Statement.
The authors have declared no competing interest.