Plus: Bytedance’s $7 billion loophole, AI-enabled robo-surgeons, the U.S. Treasury hack, and an IBM antitrust probe—in the latest edition of Fortune’s flagship tech newsletter.

When quantum electrodynamics, the quantum field theory of electrons and photons, was being developed after World War II, one of the major challenges for theorists was calculating a value for the Lamb shift, the energy of a photon resulting from an electron transitioning from one hydrogen hyperfine energy level to another.
The effect was first detected by Willis Lamb and Robert Retherford in 1947, with the emitted photon having a frequency of 1,000 megahertz, corresponding to a photon wavelength of 30 cm and an energy of 4 millionths of an electronvolt—right on the lower edge of the microwave spectrum. It came when the one electron of the hydrogen atom transitioned from the 2P1/2 energy level to the 2S1/2 level. (The leftmost number is the principal quantum number, much like the discrete but increasing circular orbits of the Bohr atom.)
Conventional quantum mechanics didn’t have such transitions, and Dirac’s relativistic Schrödinger equation (naturally called the Dirac equation) did not have such a hyperfine transition either, because the shift is a consequence of interactions with the vacuum, and Dirac’s vacuum was a “sea” that did not interact with real particles.
A new study shows that intelligence is best predicted by global brain connectivity, not just specific regions, indicating a more holistic neural basis for cognition. They examined fluid, crystallized, and general intelligence using fMRI data, finding that general intelligence had the strongest predictive power.
The human brain is the central organ that controls our body. It processes sensory information and enables us to think, make decisions, and store knowledge. Despite its remarkable capabilities, it is paradoxical how much remains unknown about this intricate organ.
Jonas Thiele and Dr. Kirsten Hilger, who leads the “Networks of Behavior and Cognition” research group at the Department of Psychology I at Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU), are dedicated to unraveling the mysteries of the brain. Their latest research has been published in the scientific journal PNAS Nexus.
Microgravity is known to affect muscles, bones, the immune system, and cognition, but its specific effects on the brain remain largely unexplored. To investigate this, scientists from Scripps Research partnered with the New York Stem Cell Foundation to send tiny clusters of brain cells, known as “organoids,” to the International Space Station (ISS). These organoids were derived from stem cells and designed to mimic certain aspects of brain development.
Remarkably, the organoids returned from their month-long stay in orbit still healthy. However, they exhibited accelerated maturation compared to identical organoids grown on Earth. The space-exposed cells progressed closer to becoming fully developed neurons and showed early signs of specialization. These findings, recently published in Stem Cells Translational Medicine, offer new insights into how space travel might influence neurological development and brain function.
“The fact that these cells survived in space was a big surprise,” says co-senior author Jeanne Loring, PhD, professor emeritus in the Department of Molecular Medicine and founding director of the Center for Regenerative Medicine at Scripps Research. “This lays the groundwork for future experiments in space, in which we can include other parts of the brain that are affected by neurodegenerative disease.”

M
The human brain is the central control organ of our body. It processes information received through the senses and enables us, among other things, to form thoughts, make decisions and store knowledge. Given everything our brain is capable of, it seems almost paradoxical how little we actually still know about it.
Among those who are on the trail of the most complex and complicated organ are Jonas Thiele and Dr. Kirsten Hilger, head of the “Networks of Behavior and Cognition” working group at the Department of Psychology I at the Julius Maximilian University of Würzburg (JMU). Their latest study was recently published in the journal PNAS Nexus: “Choosing explanation over performance: Insights from machine learning-based prediction of human intelligence from brain connectivity.”
To do this, the researchers used data sets from a large-scale data-sharing project in the USA — the Human Connectome Project. Using fMRI — an imaging method that measures changes in brain activity — over 800 people were examined, both at rest and while they were performing various tasks.
The team led by Würzburg researchers looked at various connections that reflect the strength of communication between brain regions and made predictions about the intelligence of the test subjects based on these observations.
“There are already many such predictive studies and they achieve quite good prediction results,” says Kirsten Hilger. However, the psychologist questions their deeper meaning, since the predictions would never be as accurate as the results of an intelligence test. “We therefore wanted to move away from pure predictions and instead better understand the basic processes in the brain. We hope that this will give us a better understanding of the neural code of individual differences in intelligence.”
Kirsten Hilger hopes that colleagues will follow suit and that more studies will be designed in the future that will improve the conceptual understanding of human cognition with a focus on interpretability.

In a groundbreaking study, researchers have developed optical spring tracking to enhance signal clarity in gravitational-wave detectors, such as aLIGO.
This innovation could dramatically increase our understanding of cosmic events like black hole mergers, potentially unlocking secrets of the universe’s formation.
Revolutionary advances in gravitational wave detection.

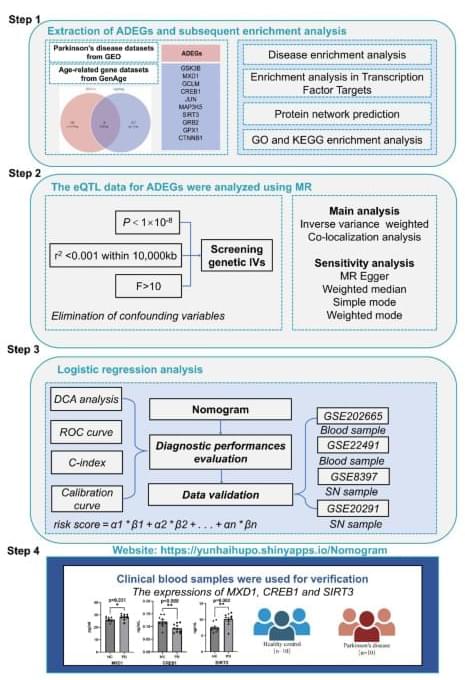
Wang, Z., Zhang, Z., Li, P. et al. Multi-omics analysis reveals the genetic aging landscape of Parkinson’s disease. Sci Rep 14, 31,167 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-82470-z.

Summary: A new “molecular lantern” technique allows researchers to monitor molecular changes in the brain non-invasively using a thin light-emitting probe. This innovative tool utilizes Raman spectroscopy to detect chemical changes caused by tumors, injuries, or other pathologies without altering the brain beforehand.
Unlike prior methods requiring genetic modifications, this approach analyzes natural brain tissue with high precision, offering significant potential for diagnosing and studying brain diseases. Future developments aim to integrate artificial intelligence to enhance diagnostic accuracy and explore diverse biomedical applications.