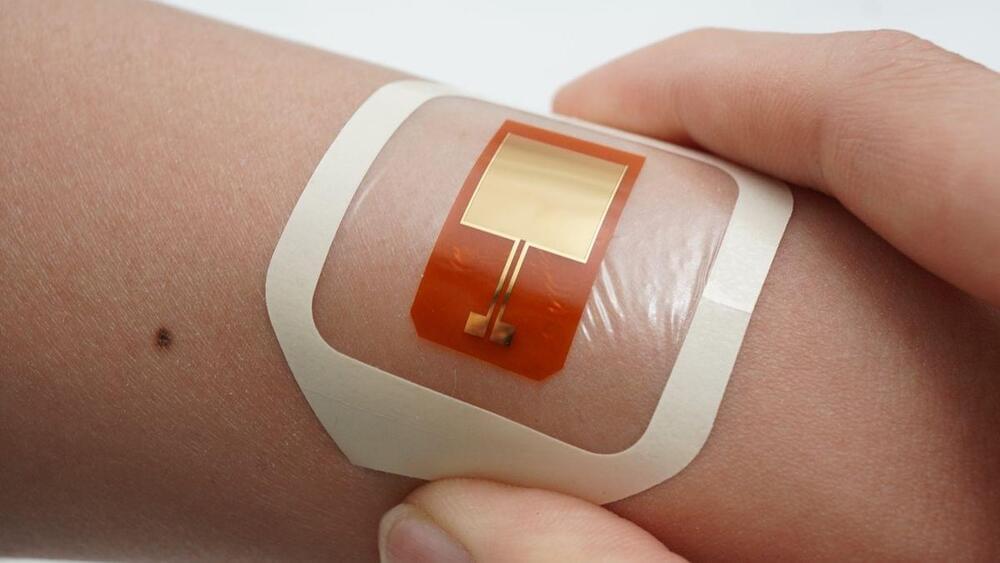
Early experiments suggest a patch that delivers harmless electric currents into the skin can thwart certain bacterial infections. However, it has not yet been tested in humans.

BIOHACKER Bryan Johnson who’s shelling out millions in his quest for immortality has revealed the exact steps he follows to reverse his hair loss and get rid of greys.
The tech-tycoon, 47, claimed he’s been able to grow a full head of hair despite being “genetically bald” through a mix of supplements, red light therapy and customised hair oil.
At one time, Bryan was best known for founding the payments company Braintree — but nowadays he’s making headlines for his very expensive quest to turn back the clock and become 18 again.
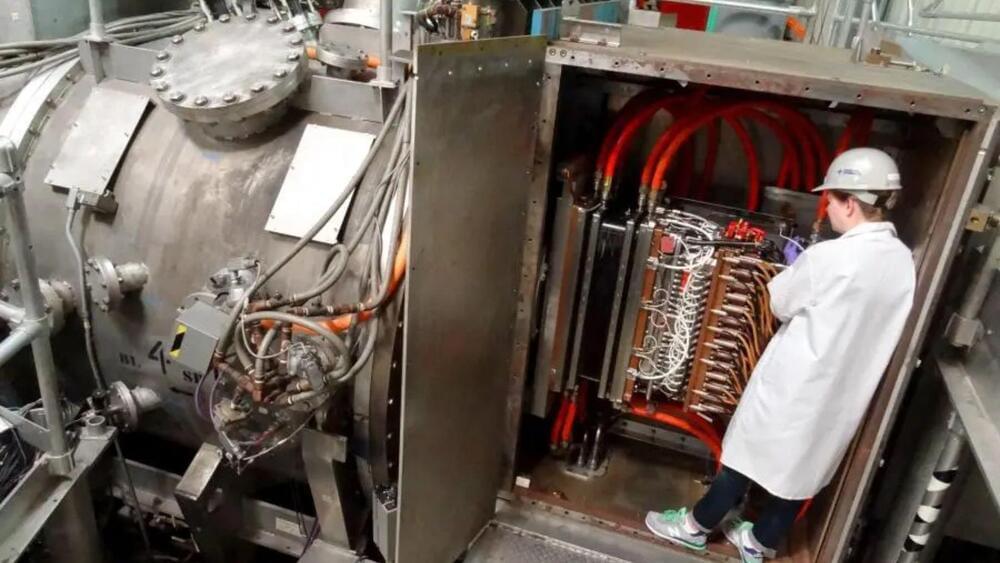
A cornerstone of the US fusion research program, the DIII-D National Fusion Facility, has accomplished a major achievement. The nuclear fusion facility has completed its 200,000th experimental cycle.
“While completing 200,000 shots is impressive in its own right, this achievement is far more than a mere number,” said Dr Richard Buttery, Director of the DIII-D National Fusion Facility.
Nuclear fusion has long been hailed as the “holy grail” of clean energy. It is the process of nuclear fusion itself that powers the sun and stars. Unlike nuclear fission, which splits atoms and generates radioactive waste, fusion involves combining lighter atoms to form heavier ones.

The reason? While sunny regions naturally provide enough light to grow crops, areas with colder winters often need grow lights and greenhouses part of the year. This increases energy consumption, logistical headaches, and ultimately, food costs.
In their paper, Jiao and colleagues argue for a new method that could dramatically revamp farming practices to reduce land use and greenhouse gas emissions.
Dubbed “electro-agriculture,” the approach uses solar panels to trigger a chemical reaction that turns ambient CO2 into an energy source called acetate. Certain mushrooms, yeast, and algae already consume acetate as food. With a slight genetic tweak, we could also engineer other common foods such as grains, tomatoes, or lettuce to consume acetate.
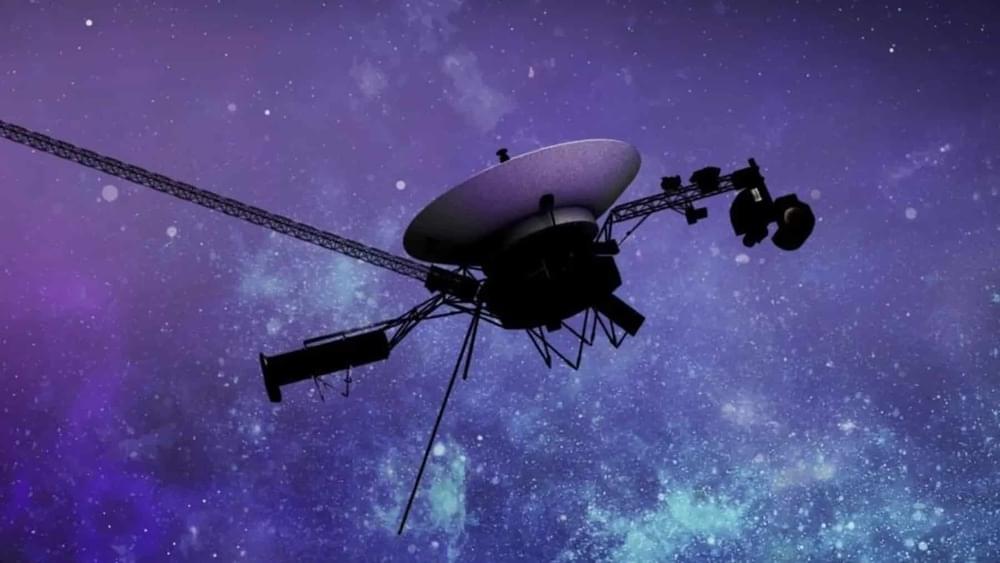

Considering the future: What Voyager 2 has in store
According to Miller (2024), even though this instrument has been deactivated, engineers anticipate that Voyager 2 will have at least one operable instrument for exploration through the 2030s. The spacecraft continues to operate and transmit data. NASA is also hoping that the spacecraft continues to provide valid information about the interstellar medium too.
The seamless continuation of activities was made possible by the confirmation that the instrument was operating normally. In 2018, it was confirmed that Voyager 2 had crossed the heliosphere’s border and entered interstellar space thanks in large part to the plasma science instrument. Significant changes in atoms, particles, and magnetic fields that are detectable by the instruments of the Voyager probes define this barrier.
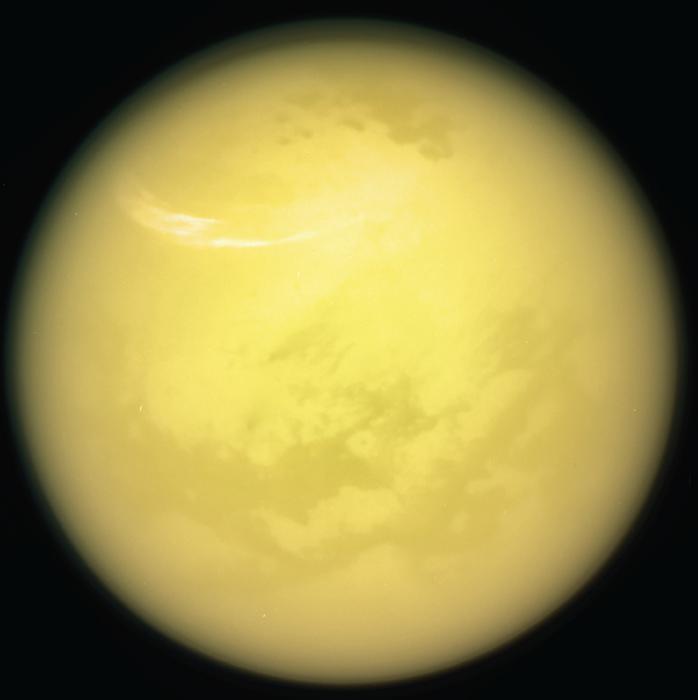


Dr. Lauren Schurmeier: “The methane clathrate crust warms Titan’s interior and causes surprisingly rapid topographic relaxation, which results in crater shallowing at a rate that is close to that of fast-moving warm glaciers on Earth.”
How does Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, have such a methane-rich atmosphere? This is what a recent study published in The Planetary Science Journal hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated how methane that resides with Titan’s crust could be responsible for the lack of depth in Titan’s impact craters, which could explain why Titan’s atmosphere has so much methane, as well. This study holds the potential to help researchers better understand the formation and evolution of Titan and whether it could host life as we know it.
For the study, the researchers used computer models to simulate the formation and evolution of impact craters on Titan, of which only approximately 90 have been identified via satellite imagery from NASA’s Cassini spacecraft.
“This was very surprising because, based on other moons, we expect to see many more impact craters on the surface and craters that are much deeper than what we observe on Titan,” said Dr. Lauren Schurmeier, who is a research associate in the Hawai‘i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) and lead author of the study. “We realized something unique to Titan must be making them become shallower and disappear relatively quickly.”
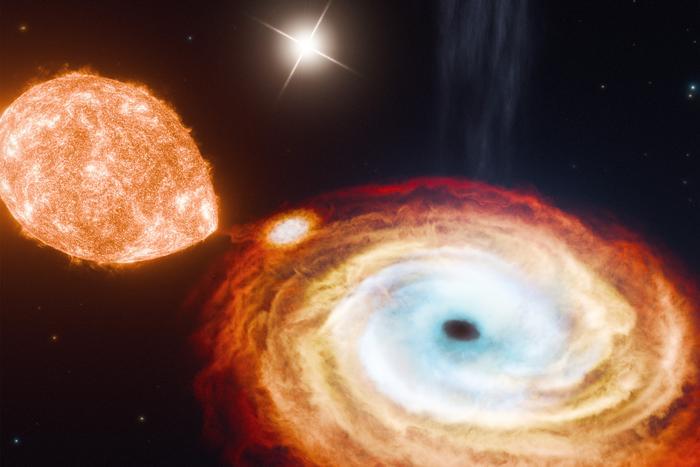

Black holes are some of the most mysterious and awe-inspiring celestial objects in science, and while pairs of black holes or a black hole orbiting another object like a star, known as binary black holes, have been confirmed to exist, what about triple systems? This is what a recent study published in Nature hopes to address as a team of researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) announced the discovery of a “black hole triple”, meaning three black holes are orbiting each other simultaneously. This study holds the potential to help researchers better understand the formation and evolution of black holes and what this can teach us about the universe, overall.
For the study, the researchers examined the binary black hole system V404 Cygni, which consists of a central black hole being orbited by two stars, with one orbiting in 6.5 days while the other takes approximately 70,000 years to complete one orbit. It is this second object that has scientists scratching their heads, as it is confounding how an object so far away can be influenced by a black hole’s gravity. While black holes are often created from a supernova, or the collapse and explosion of a large star, this means the explosion should have pushed away the farther star in this system. Therefore, the team postulates this black hole was formed by what’s known as a “direct collapse”, which is a smaller and gentler process when a star collapses in on itself as opposed to producing an outward explosion.
“We think most black holes form from violent explosions of stars, but this discovery helps call that into question,” said Dr. Kevin Burdge, who is a Pappalardo Fellow in the MIT Department of Physics and lead author of the study. “This system is super exciting for black hole evolution, and it also raises questions of whether there are more triples out there.”
Yes, it’s your Stargate partner-in-whine here to talk about my inability to relax and just give in to a fatty future…instead forcing myself on this horrible devices while I learn… today’s weapon of choice is the Smooth Fitness CE 74.4 Elliptical machine of horror…join me!