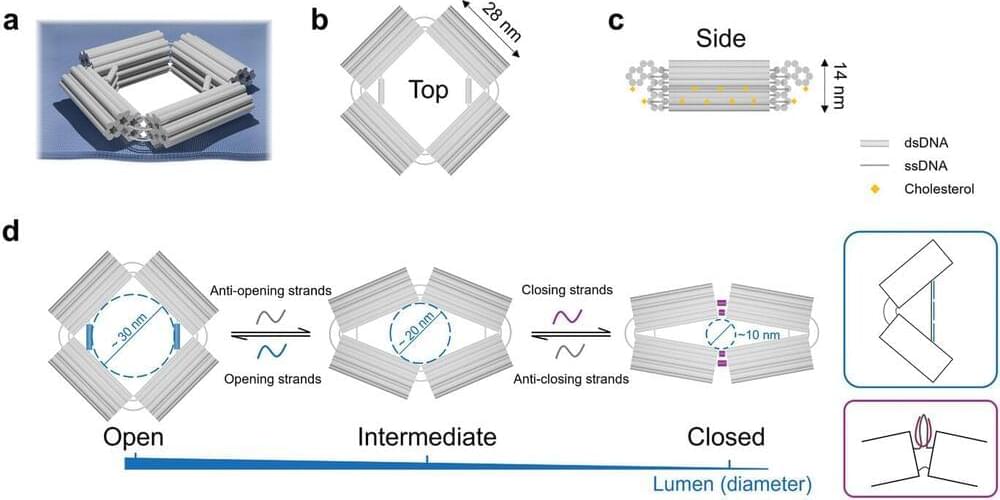
Researchers create DNA-based nanopores that switch between three sizes, allowing selective molecule transport across membranes for potential drug delivery and biosensing applications.

A novel way of making superheavy elements could soon add a new row to the periodic table, allowing scientists to explore uncharted atomic realms.
By Max Springer
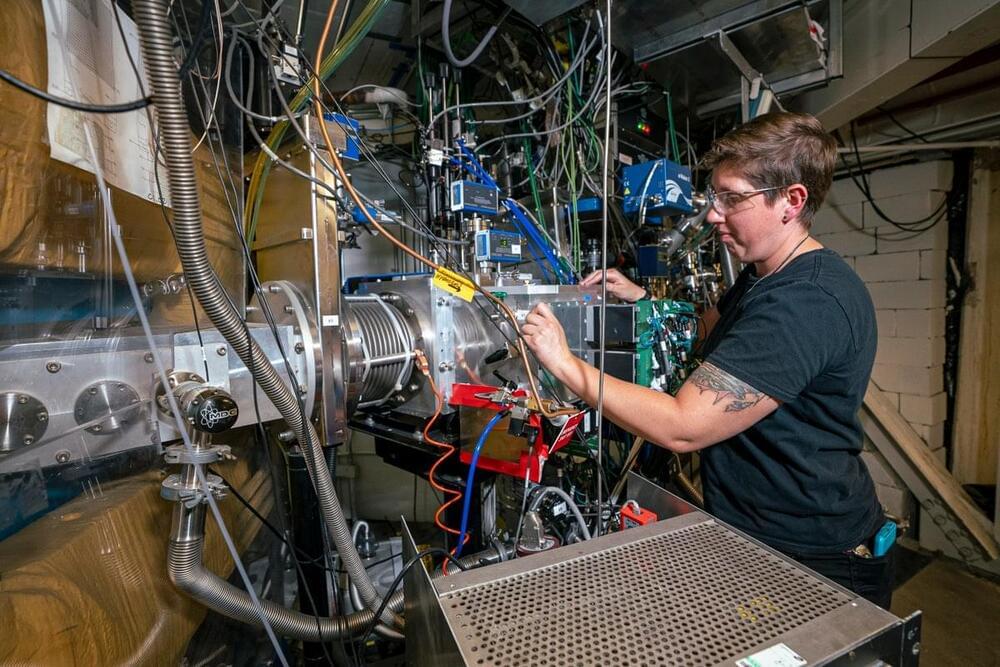
In a scientific breakthrough, an international research team from Germany’s Forschungszentrum Jülich and Korea’s IBS Center for Quantum Nanoscience (QNS) developed a quantum sensor capable of detecting minute magnetic fields at the atomic length scale. This pioneering work realizes a long-held dream of scientists: an MRI-like tool for quantum materials.
The research team utilized the expertise of bottom up single-molecule fabrication from the Jülich group while conducting experiments at QNS, utilizing the Korean team’s leading-edge instrumentation and methodological know how, to develop the world’s first quantum sensor for the atomic world.
The diameter of an atom is a million times smaller than the thickest human hair. This makes it extremely challenging to visualize and precisely measure physical quantities like electric and magnetic fields emerging from atoms. To sense such weak fields from a single atom, the observing tool must be highly sensitive and as small as the atoms themselves.

The first 150 people to join Planet Wild clicking this link or adding my code ISAAC7 later will get their first month for free https://planetwild.com/r/isaacarthur/.…
If you want to get to know them better first, check out their video about restoring barren land under powerlines into thriving ecosystems: https://planetwild.com/r/isaacarthur/.…
We often try to distinguish between what is alive and what is a machine, and note that machines can’t reproduce or fix themselves, but that may soon change.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Credits:
Self-Repairing Machines.
Episode 457; July 25, 2024
Produced, Narrated \& Written: Isaac Arthur.
Editor:
Lukas Konecny.
Graphics:
Jeremy Jozwik.
Ken York.
Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images.
Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator.
0:00 Intro.
0:17 Susan.
3:03 Fundamentals.
10:52 Sensing and Diagnostics.
14:19 Advanced Materials.
21:56 Robotics.
24:11 Artificial Intelligence

Teleology the return of Aristotle?
The scientific story of who we are is a reductionist, gene-centric model that forfeits natural phenomena like purpose due to its association with intelligent design and a transcendent, intelligent designer. Noble is neutral on religious matters. Yet he sees compelling evidence that purpose may be fundamental to life. He’s determined to debunk the current scientific paradigm and replace the elevated importance of genes with something much more controversial. His efforts have enraged many of his peers but gained support from the next generation of origins-of-life researchers working to topple the reign of gene-centrism. If successful, the shift could not only transform how we classify, study and treat disease, but what it means to be alive.
One of the earliest biomedical computer programmers, Noble created the first model for a working human heart in 1960 on a vacuum tube computer. The project led to his discovery that heartbeats are emergent properties—new phenomena—arising from feedback loops, transforming our understanding of heart function and underpin treatments for heart conditions that we use today. His research on the heart’s pacemaker demonstrates a prioritization of the organism as a whole over its genes alone. “Several genes could individually be knocked out but the process continues,” says Noble. These genes are responsible for heart rhythm, yet other mechanisms can take over to get the job done.
In the 1960s, Noble served as the dissertation examiner for the then-unknown Richard Dawkins—a prominent figure in the New Atheism movement—would go on to author the 1976 classic The Selfish Gene that popularized the gene-centric theory of evolution. Gene-centrism says evolution acts on genes, not individual organisms. We are merely vessels for our genes that are driving evolution by Darwinian natural selection. Noble’s analysis suggests that evolution acts on the organism as a whole, with the organism harnessing randomness and variation to create and heal itself—on purpose. In this re-evaluation, Noble believes that purpose, creativity, and innovation are fundamental to evolution. He argues that we experience these processes as drives, but they are not purely subjective. They also progress non-consciously in other parts of our body. These natural processes harness randomness and unpredictability—stochasticity—to survive, make decisions, and thrive. “Stochasticity is the center of creativity in organisms,” says Noble.

The study found that black holes in old, inactive galaxies have grown significantly in mass over the last 9 billion years, suggesting they interact with the expanding universe.
If black hole mass development happened only through accretion or merging, the masses of these black holes would be anticipated to remain relatively constant. However, if black holes gain mass by interacting with the expanding cosmos, these passively developing elliptical galaxies might disclose this process.
The researchers discovered that the further back in time they examined, the smaller the black holes were in mass compared to their masses today. These changes were significant: black holes were 7 to 20 times bigger now than they were 9 billion years ago, leading the researchers to hypothesize cosmic coupling.

Many astronauts who have viewed the earth from space recall experiencing the “overview effect.” This is a profound positive shift in perspective and involves experiencing a sense of awe and a new understanding of the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
Astronauts are often overwhelmed with emotion while taking in the beauty and vastness of our planet from their unique vantage point. They describe a deep sense of wonder and appreciation for the planet and the universe.
From space, astronauts can see Earth as a single, unified ecosystem without borders. This evokes an increased drive to protect our fragile ecosystem and inspires a recognition of the common humanity shared by all people.

Tesla CEO Elon Musk confirmed a number of key details about the Robotaxi during the company’s Q2 2024 Update Letter and earnings call. These include the site of the Robotaxi’s production, as well as the manufacturing process that would be used on the vehicle.
It would not be an exaggeration to state that the Robotaxi unveiling on October 10, 2024 is poised to be Tesla’s most important event this year. And considering Elon Musk’s noticeable focus on Full Self Driving (FSD), it was no surprise when several questions during the Q2 2024 earnings call were focused on the Robotaxi.
As per Tesla’s Q2 2024 Update Letter, its plans for new vehicles, including more affordable models, are still on track for the start of production in the first half of 2025. These vehicles will utilize aspects of its next-generation and current platforms, and they could be produced on the same manufacturing lines as the company’s current vehicle line-up. As for the Robotaxi, however, Tesla was clear.
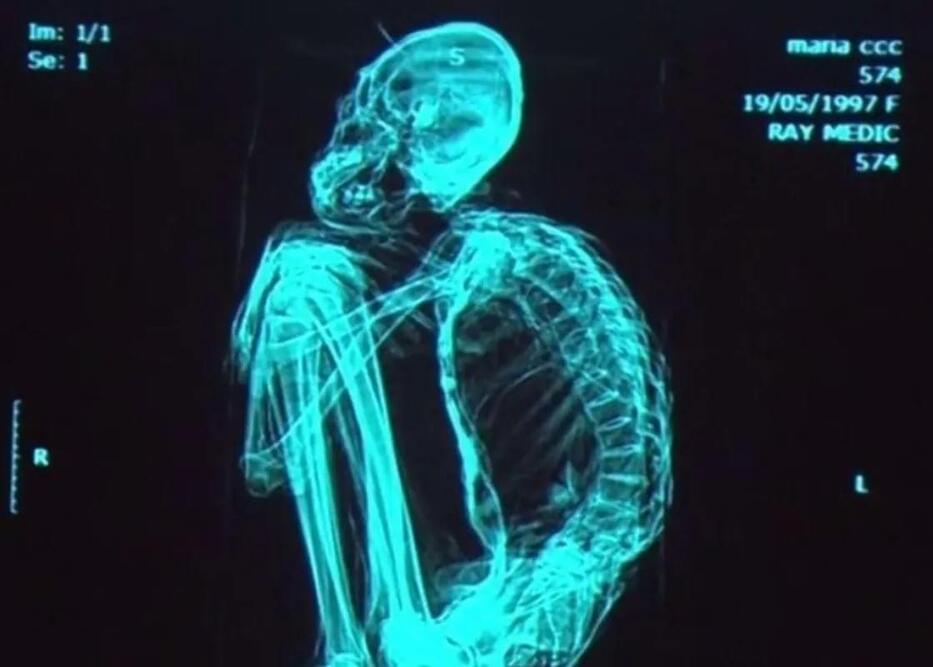
The Nazca Mummies have to be amongst the most controversial topics in recent human history, they have been “debunked” multiple times since they were first discovered by Archeologist Thierry Jamin from Peru’s Inkarri institute. Given that this case needed more eyes from the international community, Thierry and Peruvian journalist Jois Mantilla agreed to associate themselves with Mexican journalist Jaime Maussan. What they wanted became a reality, but the movedidn’t come with not obstacles. Nearly seven years after the bodies were discovered from an undisclosed location in the Nazca region, there are still a majority of scientists and academia members who dismiss these bodies as fake. None of them have studied the specimens in person. So far, every scientist who comes close to these bodies and studies them has stated they are real bodies of once living beings.
Carbon 14 test results confirmed these specimens’ remains are from various times in the distant past, some are 1,000+ years old and others are between 1,500 and 2,000 years old. Despite the Carbon 14 test results, the x-rays, and other types of scans that show incredible evidence. There are still many from the mainstream scientific community who believe we won’t get to prove these bodies are real until we get resuls from an extensive DNA analysis that is taking place in lultiple places around the world. Because Jaime Maussan’s involvement did bring more eyes on these bodies, and multiple labs are already running tests on samples obtained directly from the two sources in Peru that have them.