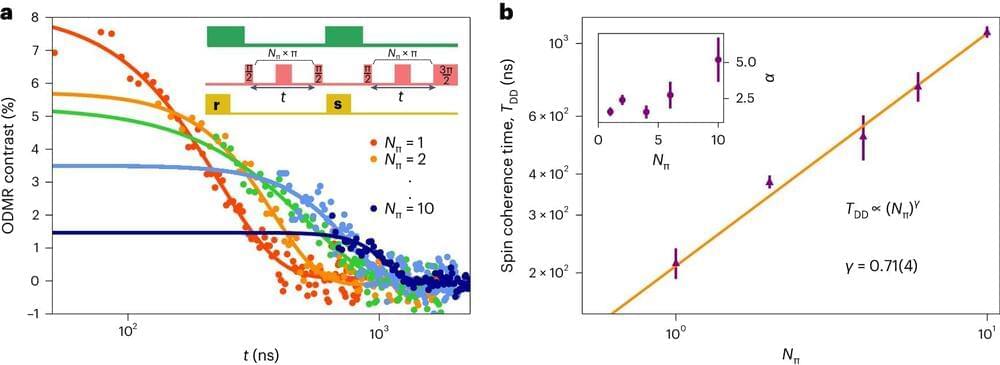
Scientists have discovered that a “single atomic defect” in a layered 2D material can hold onto quantum information for microseconds at room temperature, underscoring the potential of 2D materials in advancing quantum technologies.
The defect, found by researchers from the Universities of Manchester and Cambridge using a thin material called hexagonal boron nitride (hBN), demonstrates spin coherence—a property where an electronic spin can retain quantum information —under ambient conditions. They also found that these spins can be controlled with light.
Up until now, only a few solid-state materials have been able to do this, marking a significant step forward in quantum technologies.