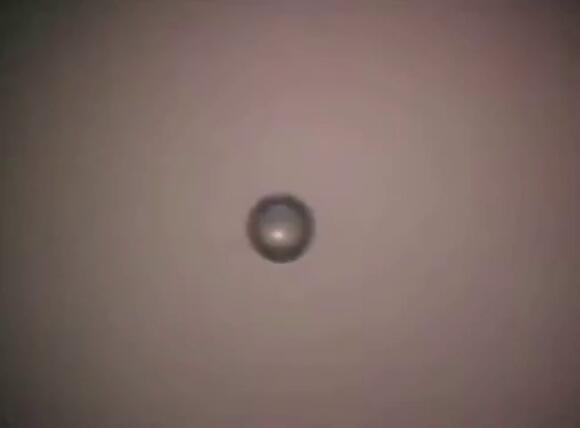
The fascinating phenomenon of sonoluminescence, where light is produced when an underwater bubble is collapsed by a sound wave, has sparked a vibrant discussion. Despite being a subject of scientific research and debate, the exact mechanisms behind sonoluminescence are still not fully understood.
One user pointed out that this phenomenon is also known as sonoluminescence, which occurs when a small gas bubble in a liquid is collapsed by intense sound waves, emitting a short burst of light. This can happen in a laboratory setting using a device that generates and focuses sound waves into a liquid.
Several theories have been proposed to explain how the light is produced. The Hot Spot Theory suggests that the bubble’s collapse causes the gas inside to heat up to extremely high temperatures, possibly hot enough to ionize the gas and produce a plasma, which then emits light.