Fed up with service dead zones? The free beta test launches early next year — here’s how to join.


World renowned neurophysiologist and computational neuroscientist Christof Koch joins Brian Greene to discuss how decades of experimental and theoretical investigation have shaped his understanding of consciousness and the brain — and how recent psychedelic experiences have profoundly reshaped his perspective on life and death.
This program is part of the Big Ideas series, supported by the John Templeton Foundation.
Participant: Christof Koch.
Moderator: Brian Greene.
00:00 — Introduction.
00:34 — Participant Introduction.
03:19 — Examining The Mystery Of Consciousness.
09:00 — Approaching Consciousness As A Physicist.
17:54 — Crafting Theories About Consciousness.
26:19 — A Brief Look Into The Causal Powers Of Consciousness.
43:12 — The Question Of Free Will.
51:46 — Introspection As A Tool For Examining The Mind.
01:22:52 — Credits.
SUBSCRIBE to our youtube channel and \.


Just as humans can use the taps of Morse Code or the patterns of smoke signals to communicate precise messages, infants show a remarkable flexibility to interpret nonlinguistic signals to aid their learning.
But what conditions are required for babies to elevate new nonlinguistic signals in this way? And how early can they do so?
Sandra Waxman, the study’s senior author, and her colleagues discovered that infants as young as six months old were able to harness nonlinguistic signals for learning, a surprising finding because at this age, babies are just beginning to acquire their own language.
The evidence revealed the conditions under which babies conferred communicative status to the novel tone signals and then recruited them to successfully complete a learning task. Infants’ success did not depend on whether the signals were produced by humans, or in a give-and-take interchange between individuals. Instead, what mattered was cross-modal temporal synchrony, in other words, if the method of signal delivery included synchronized sound and movement.
Six-month-old infants use cross-modal synchrony to identify novel communicative signals. Sci Rep 14, 27859 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-78801-9
DDW Editor Reece Armstrong speaks to Ellie Mahjubi, Vice President, Protein and cell analysis at Thermo Fisher Scientific, about how spatial biology is impacting drug discovery and development research.
RA: What’s the future and potential for spatial biology?
EM: Technological advancements in spatial biology are providing unprecedented insights into single cells within their spatial context, facilitating the analysis of cell types, functional states, cell interaction networks, as well as tissue microenvironments and architecture. These innovations promise to significantly advance basic research and enhance our understanding of human health and disease.
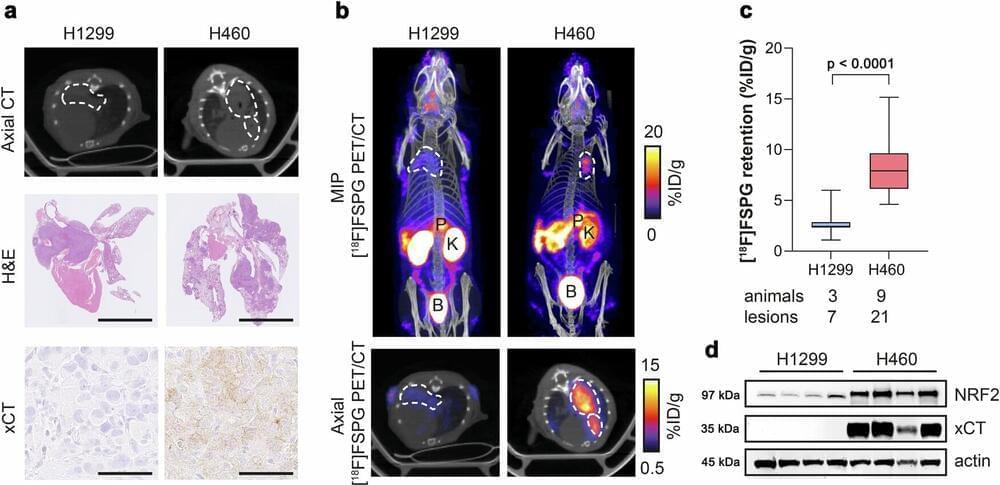
Researchers have used a chemical compound to light up treatment-resistant cancers on imaging scans, in a breakthrough that could help medical professionals better target and treat cancer.
The authors at King’s College London say that using the radiotracer—an injected compound used in PET scans—could help inform doctors that a patient’s aggressive cancer will not respond to chemotherapy before treatment is given. This would prevent patients receiving unnecessary treatment and provide them with alternative options that will give them the best chance of beating the disease.
The paper, “Imaging NRF2 activation in non-small cell lung cancer with positron emission tomography” published in Nature Communications, shows therapy-resistant non-small cell lung cancer tumors “lit up like a Christmas tree” on PET scans when the radiotracer was injected.
If humans want to survive long-term — millions of years into the future and beyond — we will have to grapple with existential threats to civilization and life itself. But we are more empowered than any species in history. This film is a journey far into the future to explore the extreme challenges we will face, and a vision into how far humanity might go to reinvent our planet.
Coming Spring 2025.

TSMC has revealed additional details about its “2nm N2” technology, disclosing massive advancements in yield rates and performance metrics.
TSMC’s “N2 Nanosheet” Implementation Has Brought A Huge Rise In Node Performance, Showing Immense Potential
The Taiwan giant’s 2nm process is one of the most anticipated developments in the market, mainly since the node is expected to bring in gigantic leaps in performance and efficiency results. The process is likely to come under mass production by H2 2025, and we now have information about the performance of 2nm when stacked against previous-gen counterparts, credit to the Taiwan giant’s briefing at the IEEE International Electron Device Meeting (IEDM) in San Francisco, where 2nm “nanosheets” were the highlight of the briefing.

Sign up for the Morning Brief email newsletter to get weekday updates from The Weather Channel and our meteorologists.
A powerful earthquake, possibly the strongest in years, has devastated the island nation of Vanuatu, killing at least 14 people. More than 200 are reported injured according to a post on X by Katie Greenwood, Fiji-based head of the Red Cross in the Pacific.
The 7.3-magnitude jolt rocked the region on Tuesday sending tremors through homes, businesses and critical infrastructure. Witnesses described buildings collapsing, roads blocked by landslides and hospitals stretched thin as reports of injuries — and unconfirmed casualties — surfaced.
NASA briefing on lunar lander from Firefly.
NASA holds a virtual audio-only media teleconference to highlight the NASA science flying onboard Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission 1 as part of the agency’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign. Participants include:
• Joel Kearns, deputy associate administrator for exploration, Science Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters.
• Ryan Watkins, program scientist, Exploration Science Strategy and Integration Office, NASA Headquarters.
• Jason Kim, CEO, Firefly Aerospace