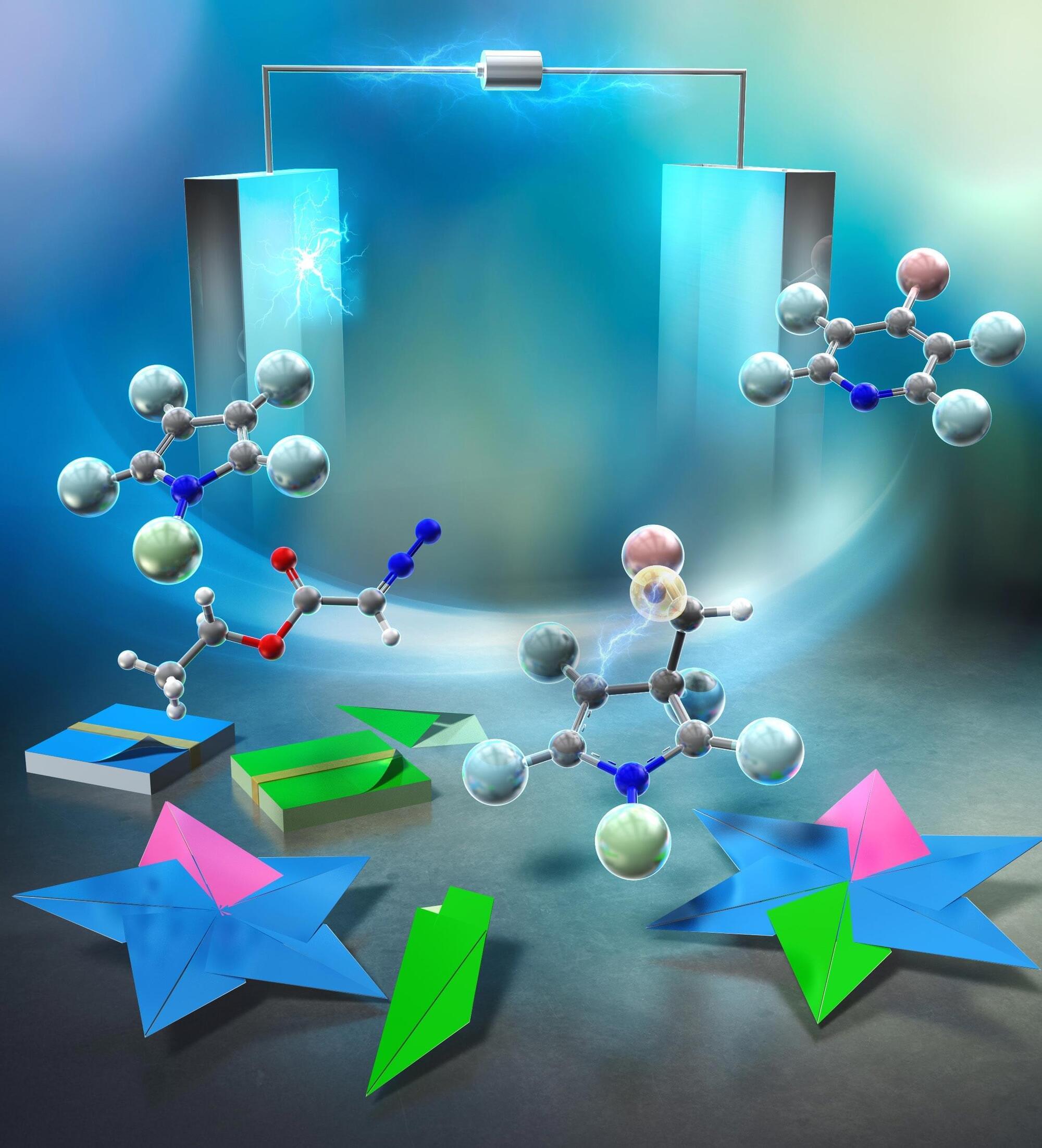
Optical sensors have undergone significant evolution, transitioning from discrete optical microsystems toward sophisticated photonic integrated circuits (PICs) that leverage artificial intelligence (AI) for enhanced functionality. This review systematically explores the integration of optical sensing technologies with AI, charting the advancement from conventional optical microsystems to AI-driven smart devices. First, we examine classical optical sensing methodologies, including refractive index sensing, surface-enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA), surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), surface plasmon-enhanced chiral spectroscopy, and surface-enhanced fluorescence (SEF) spectroscopy, highlighting their principles, capabilities, and limitations. Subsequently, we analyze the architecture of PIC-based sensing platforms, emphasizing their miniaturization, scalability, and real-time detection performance. This review then introduces the emerging paradigm of in-sensor computing, where AI algorithms are integrated directly within photonic devices, enabling real-time data processing, decision making, and enhanced system autonomy. Finally, we offer a comprehensive outlook on current technological challenges and future research directions, addressing integration complexity, material compatibility, and data processing bottlenecks. This review provides timely insights into the transformative potential of AI-enhanced PIC sensors, setting the stage for future innovations in autonomous, intelligent sensing applications.