The rise of artificial intelligence, cloud platforms, and data processing is driving a steady increase in global data center electricity consumption. While running computer servers accounts for the largest share of data center energy use, cooling systems come in second—but a new study by researchers at the National Laboratory of the Rockies (NLR), formerly known as NREL, offers a potential solution to reduce peak energy consumption.
Published in Applied Energy, a techno-economic analysis led by Hyunjun Oh, David Sickinger, and Diana Acero-Allard—researchers in NLR’s energy storage and computational science groups—has demonstrated a system to cool data centers more efficiently and cost-effectively.
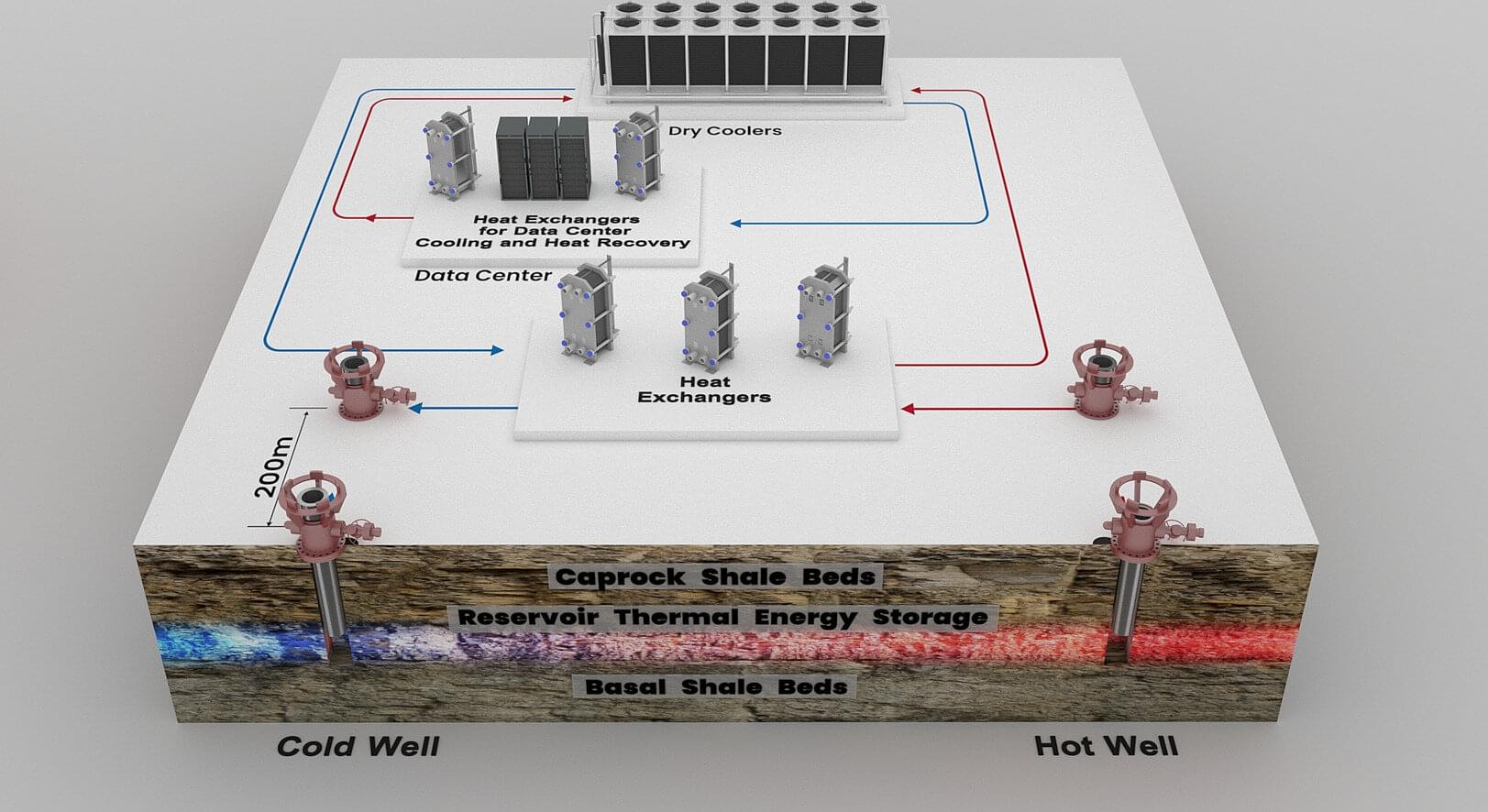
The approach, called reservoir thermal energy storage (RTES), stores cold energy underground then uses it to cool facilities during peak-demand periods.