Centenarians, once considered rare, have become commonplace.

Physicist and computer scientist Stephen Wolfram explores how simple rules can generate complex realities, offering a bold new vision of fundamental physics and the structure of the universe.
Stephen Wolfram is a British-American computer scientist, physicist, and businessman. He is known for his work in computer algebra and theoretical physics. In 2012, he was named a fellow of the American Mathematical Society. He is the founder and CEO of the software company Wolfram Research, where he works as chief designer of Mathematica and the Wolfram Alpha answer engine.
Watch more CTT Chats here: https://t.ly/jJI7e
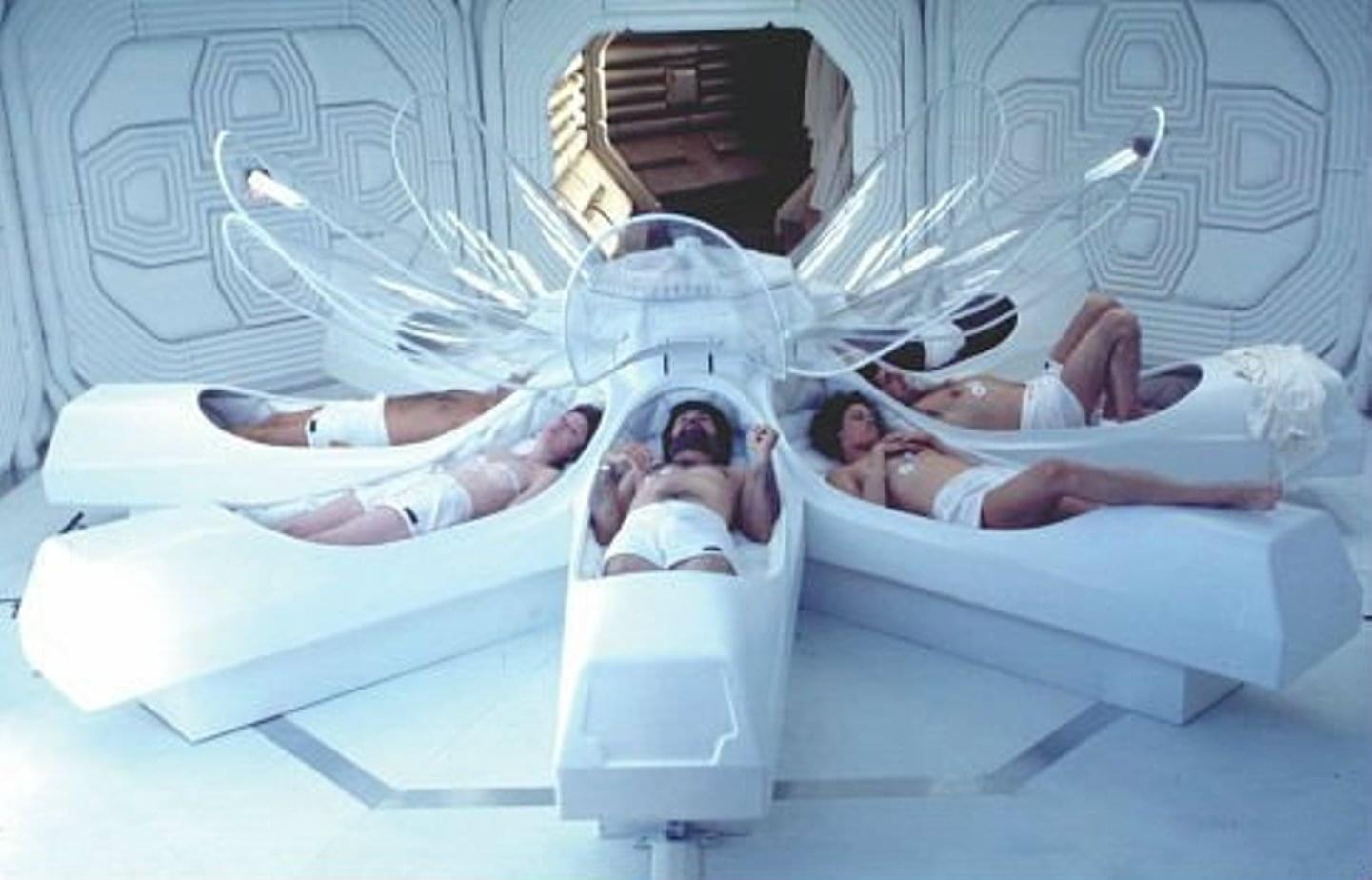

Veteran cryonicist and inventor of cryptographic hashing, Ralph Merkle, tells us how he came to decide that cryonics was a good idea. In his talk, Ralph discusses Information Theoretic Death, why information is so hard to destroy, and how advances in nano-tech might make cryonics revival possible.
Links:
• Cryosphere Discord server: https://discord.com/invite/ndshSfQwqz.
• Cryonics subreddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/cryonics/
#cryosphere

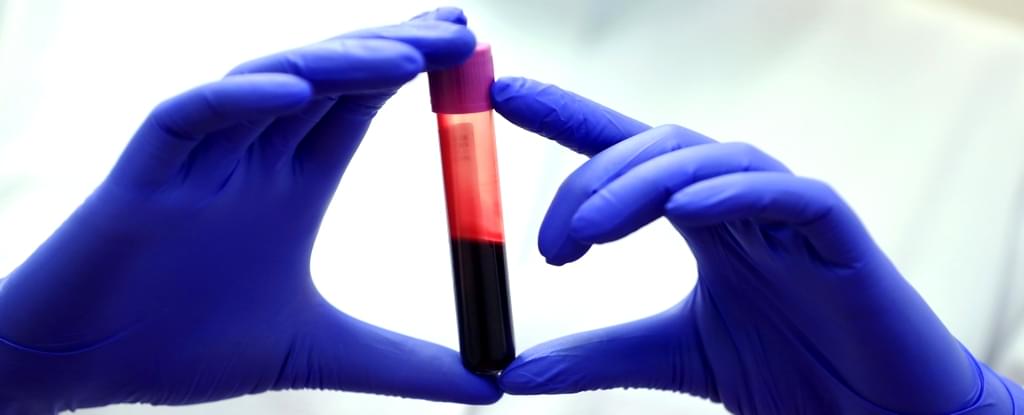
As a chronic condition, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can’t be cured, so treatment focuses on managing the disease and controlling its progression. Although current treatments help control RA symptoms in most people, they cannot prevent the onset of RA or painful flare-ups.
Now, researchers publishing in ACS Central Science have developed nanoparticles that could slow disease progression and reduce flare severity, based on results from tests with human blood and mice models with RA-like disease.
For a person diagnosed with RA, their immune system attacks tissue that makes up the joints, causing inflammation, swelling and pain. However, as the disease progresses, serious cartilage and bone damage can occur if left uncontrolled.

A study published in Cell Reports Medicine reports a scalable, data-driven computational framework for designing combinatorial immunotherapies, offering hope for patients with poor responses to current immunotherapies.
Immunotherapy, particularly immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), has revolutionized cancer treatment. Widespread resistance to ICB is a major challenge in clinical practice.
To enhance treatment efficacy and overcome resistance, combining ICB therapy with chemotherapy or targeted therapy has become an important research direction. However, candidate combinations rely on empirical selection from existing drugs, and it is difficult to discover new candidates.

Can artificial intelligence, robots and surveillance protect workers on the job? Yes, according to the latest report from the International Labour Organization. In this episode of the Future of Work podcast, ILO occupational safety and health expert Manal Azzi explains how AI and technology is being used as a safety net, and not a threat, for workers worldwide.
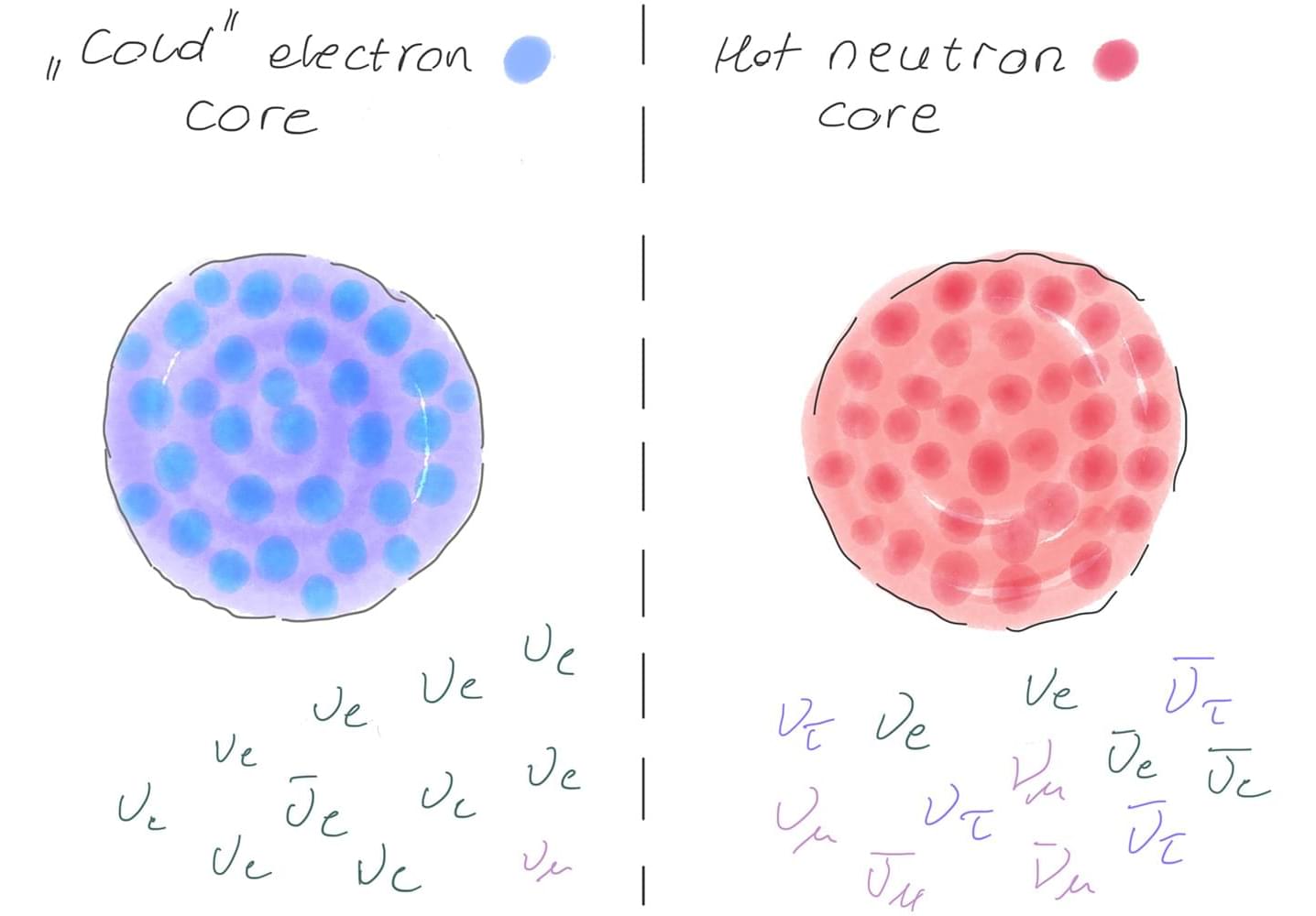
Neutrinos are cosmic tricksters, paradoxically hardly there but lethal to stars significantly more massive than the sun. These elementary particles come in three known “flavors”: electron, muon and tau. Whatever the flavor, neutrinos are notoriously slippery, and much about their properties remains mysterious. It is almost impossible to collide neutrinos with each other in the lab, so it is not known if neutrinos interact with each other according to the standard model of particle physics, or if there are much-speculated “secret” interactions only among neutrinos.
Now a team of researchers from the Network for Neutrinos, Nuclear Astrophysics, and Symmetries (N3AS), including several from UC San Diego, have shown, through theoretical calculations, how collapsing massive stars can act as a “neutrino collider.” Neutrinos steal thermal energy from these stars, forcing them to contract and causing their electrons to move near light speed. This drives the stars to instability and collapse.
Eventually the collapsing star’s density becomes so high that the neutrinos are trapped and collide with each other. With purely standard model interactions, the neutrinos will be mostly electron flavor, the matter will be relatively “cold,” and the collapse will likely leave a neutron star remnant. However, secret interactions that change neutrino flavor radically alter this scenario, producing neutrinos of all flavors and leading to a mostly neutron “hot” core that may lead to a black hole remnant.
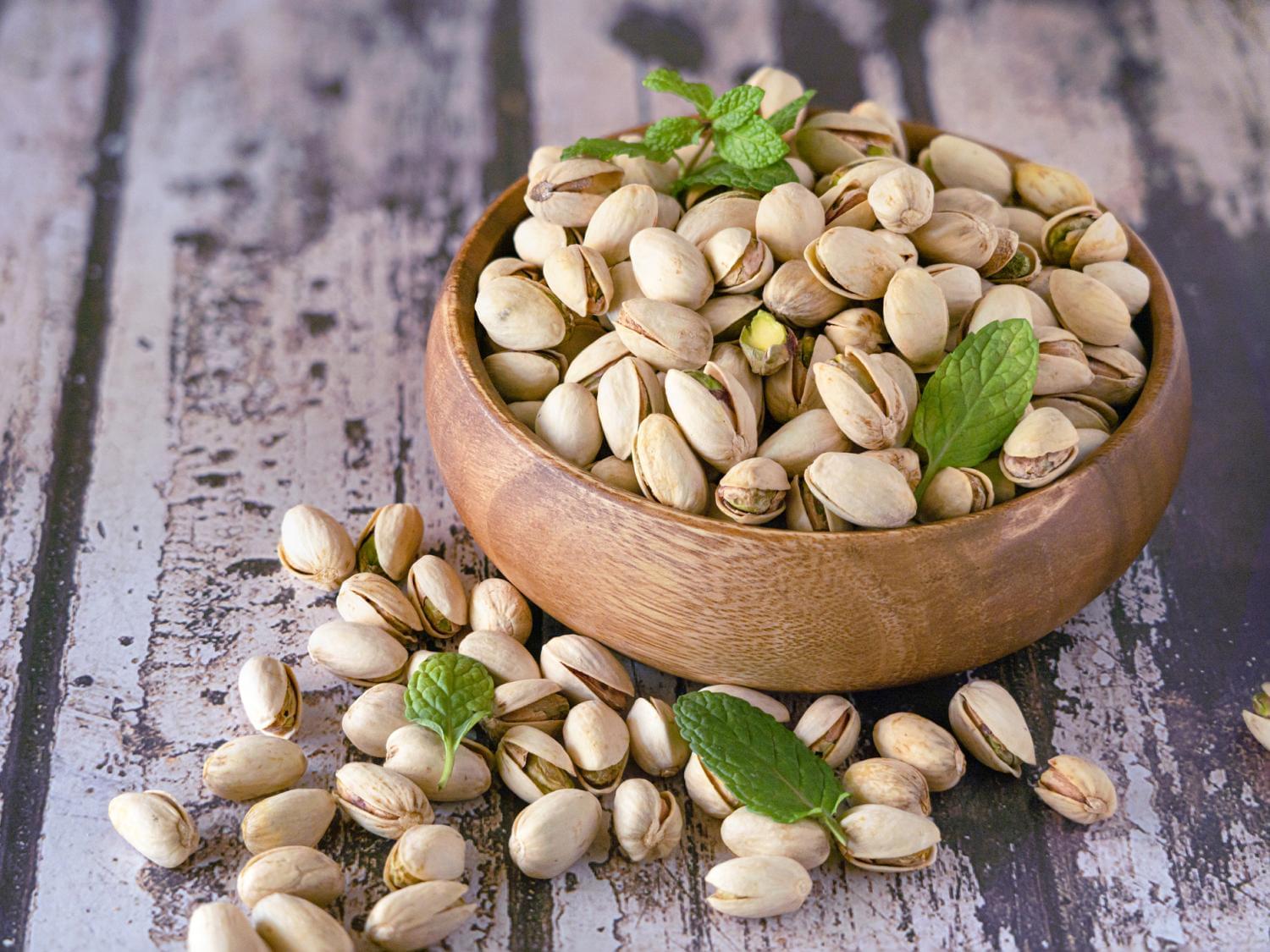

Eating pistachios every night for 12 weeks altered bacteria in the gut, according to new study. A new study reveals that swapping a typical nighttime carbohydrate snack for pistachios may beneficially alter gut bacteria in people with prediabetes. Conducted by Penn State researchers, the 12-week clinical trial found that pistachio consumption increased beneficial gut microbes like Roseburia and reduced harmful ones such as Blautia hydrogenotrophica. These microbiome changes could potentially support metabolic health and slow the progression to Type 2 diabetes. While more research is needed to confirm health outcomes, this study positions pistachios as a promising late-night snack with microbiome-boosting potential.
Prediabetes affects a third of people in the United States and most of them will develop Type 2 diabetes, yet effective dietary intervention strategies remain limited. Pistachios have shown promise in improving markers of diet quality, yet little is known about how they influence the gut microbiome — a key player in glucose regulation and inflammation.
A new study led by Kristina Petersen, associate professor of nutritional sciences at Penn State, determined that nighttime pistachio consumption affects gut bacteria in adults with prediabetes. Though the potential therapeutic implications of the findings remain unclear, according to Petersen, they may prove significant for people who are working to improve their metabolic health.