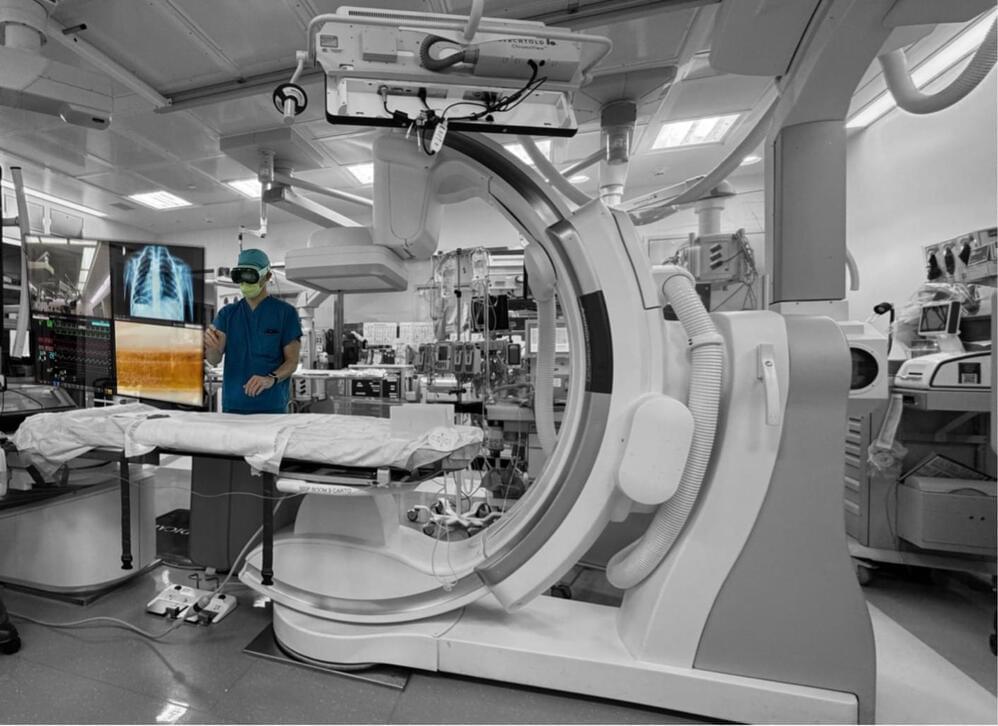
A team of Stanford Medicine doctors and biomedical engineers are among the first to integrate a new augmented reality tool into surgical practice. The technology, Apple Vision Pro, is a headset that provides a form of human-computer interaction — it allows its wearer to navigate their surroundings using real-time visual data in combination with virtual elements.
“The novel use of augmented reality in the operating room exemplifies Stanford Medicine’s mission of serving patients in a digitally driven, human-centered care environment,” said Lloyd Minor, dean of the School of Medicine and vice president of medical affairs at Stanford University. “Our health system has long stood at the vanguard for the use of digital technologies in medicine, and I’m proud that through initiatives like RAISE Health, we also define the safe, responsible and equitable use of these innovations.”
A cardiologist used the technology, with the patient’s informed consent, to successfully perform an ablation procedure this week at Stanford Hospital to treat atrial fibrillation.