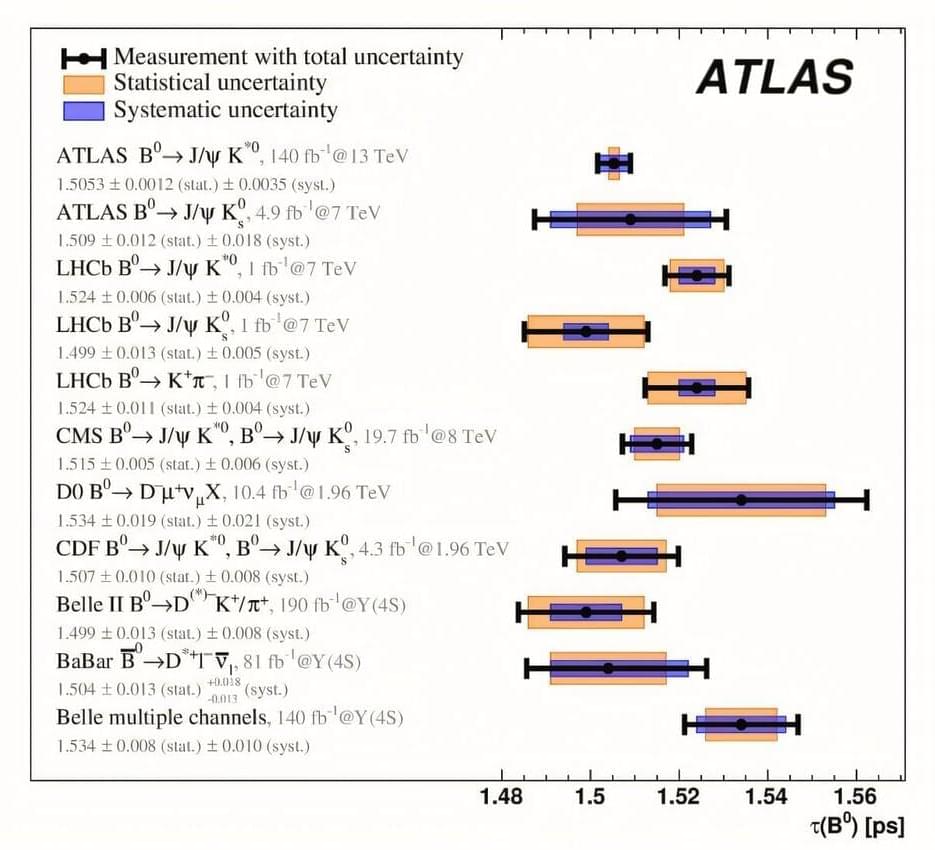
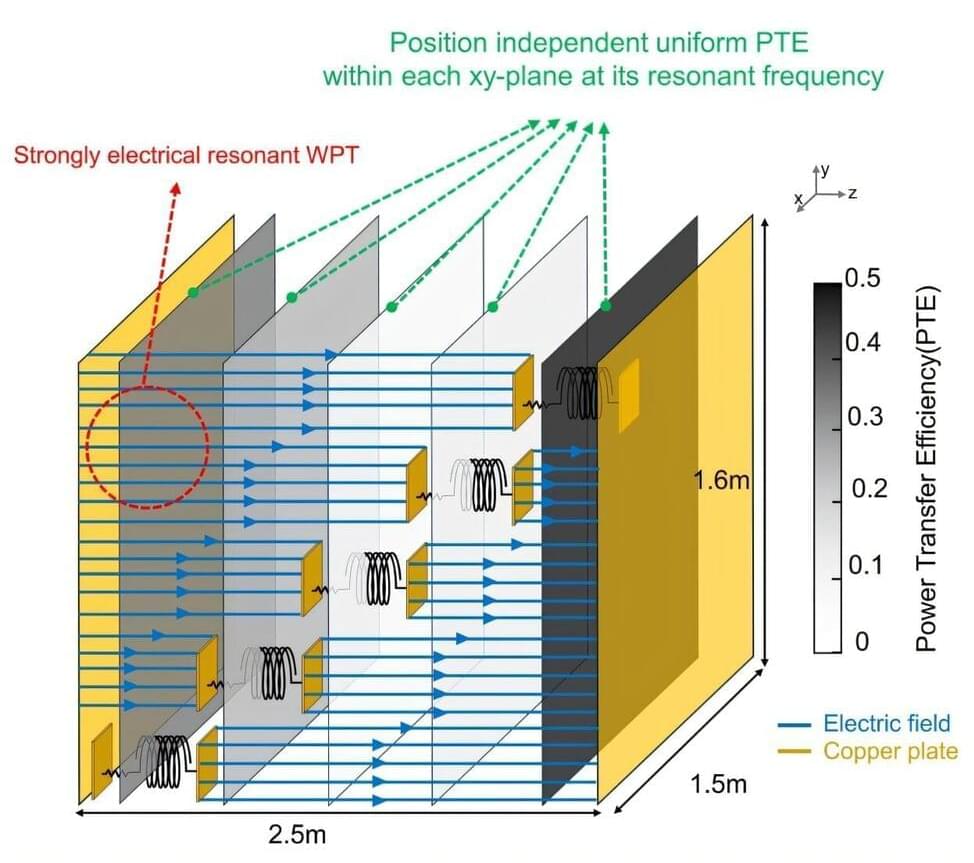
The ATLAS collaboration at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has released a new high-precision measurement of the lifetime of the electrically neutral beauty (B0) meson—a hadron composed of a bottom antiquark and a down quark.
Beauty (B) mesons are made up of two quarks, one of which is a bottom quark. Over the past decades, by studying B mesons, physicists have been able to examine rare and precisely predicted phenomena to gain insights into interactions mediated by the weak force and into the dynamics of heavy-quark bound states. The precise measurement of the B0 meson lifetime—the average time it exists before decaying into other particles—is of critical importance in this context.
The new ATLAS study of the B0 meson looked for the particle’s decay into an excited neutral kaon (K*0) and a J/ψ meson. The J/ψ meson subsequently decays into a pair of muons while the K*0 meson is studied through its decay into a charged pion and a charged kaon. The analysis is based on proton –proton collision data collected by the ATLAS detector during Run 2 of the LHC (2015–2018), amounting to an impressive data set of 140 inverse femtobarns (1 inverse femtobarn corresponds to approximately 100 trillion proton–proton collisions).