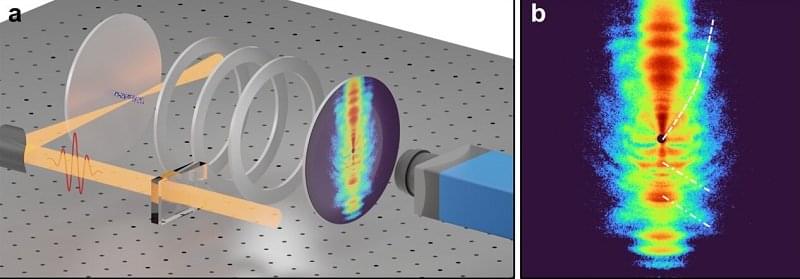
NASA has developed a new plasma rocket that could potentially reach Mars in just 2 months, cutting the travel time in half. In addition, the world is being warned to prepare for a possible geomagnetic storm, and a new fusion record has been set. These advancements in space technology and energy production have the potential to greatly impact our future.