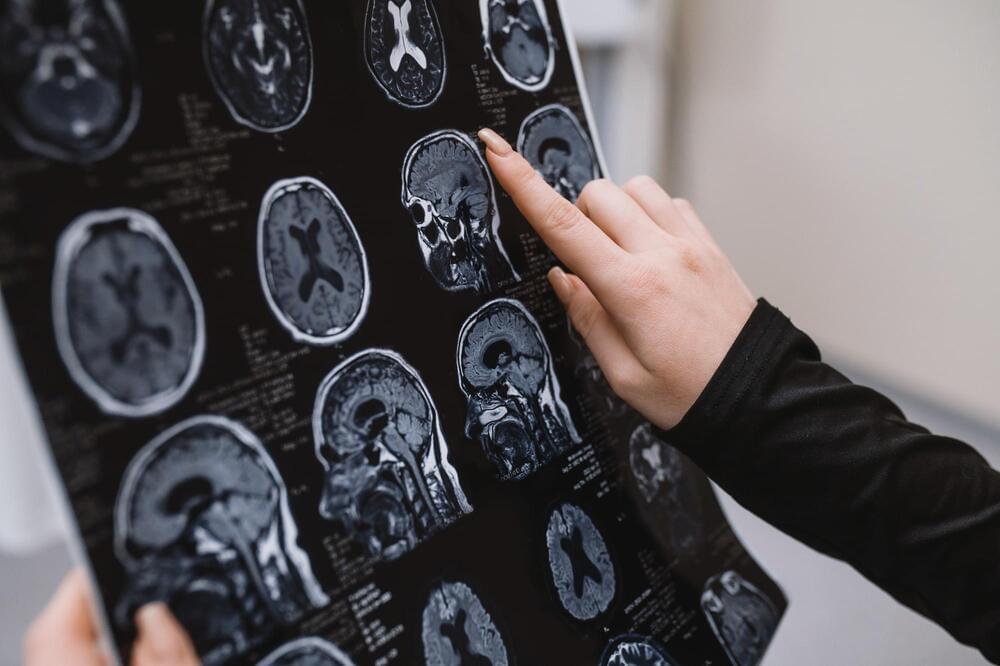
Researchers optimized portable low-field MRI with machine learning to improve brain morphometry and white matter hyperintensity detection, making Alzheimer’s diagnosis more accessible and cost-effective.


Photonic space-time crystals enhance light interaction and amplification, offering new applications in optical information processing.
Photonic space-time crystals are advanced materials designed to enhance the performance and efficiency of technologies like wireless communication and lasers. These crystals have a unique structure that is periodically arranged in three spatial dimensions and also changes over time, allowing precise control of light’s behavior. Researchers from the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), in collaboration with Aalto University, the University of Eastern Finland, and Harbin Engineering University in China, have demonstrated how these four-dimensional materials can be applied in real-world technologies. Their findings were published in Nature Photonics.
Photonic Time Crystals


Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a common, contagious virus that affects your respiratory system. It spreads easily and leads to cold-like symptoms such as a runny nose and cough.
Most people with RSV have mild symptoms that go away on their own in a week or two. But RSV can lead to serious complications, especially for babies, older adults, and people with certain conditions.
If you have RSV and you can’t breathe well or you’re dehydrated, you may need to go to the hospital. You may need IV fluids, oxygen, or ventilation (which helps with your air flow).

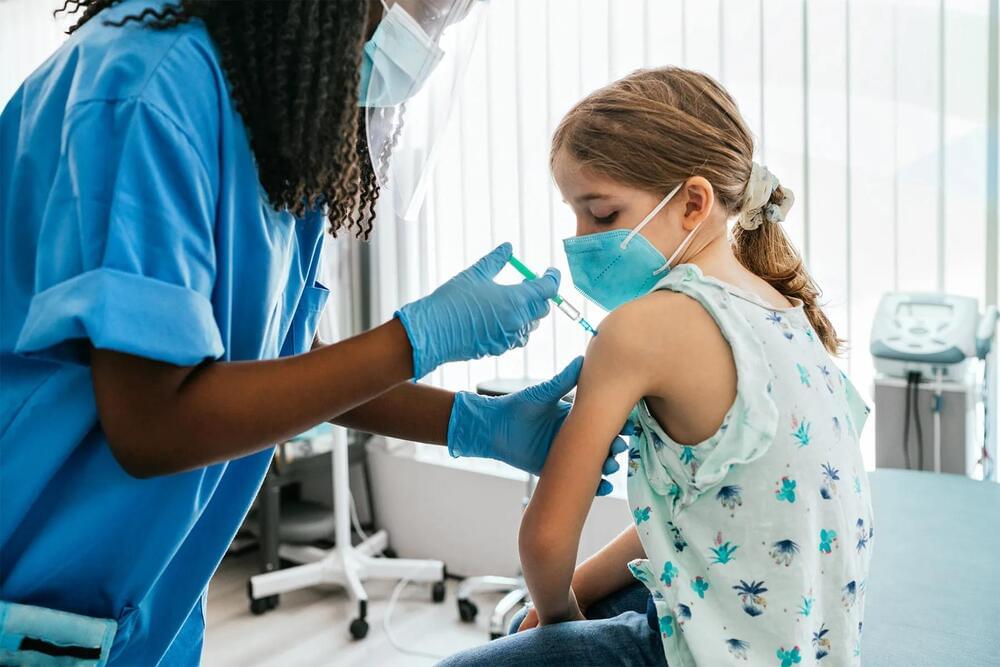
Just 37% of kids have gotten flu shots this year, according to new CDC data. That’s down seven percentage points, from 44% of kids getting shots by this same time last year.
The data concerns health officials, especially since a record number of children died of flu-related causes last year.
Ultimately, 55% of kids got vaccinated against the flu during the 2023–24 flu season, which was the lowest rate in 12 years, a CDC official told NBC News. Vaccination rates have fallen for a variety of childhood vaccines in recent years. The trend has been blamed on vaccine fatigue after the pandemic as well as misinformation about the safety of childhood shots.
By searching sparsely populated regions of the galaxy, astronomers have for the first time found the source of a kind of signal that has puzzled them for years.

A new photonic chip designed by MIT scientists performs all deep neural network computations optically, achieving tasks in under a nanosecond with over 92% accuracy.
This could revolutionize high-demand computing applications, opening the door to high-speed processors that can learn in real-time.
Photonic Machine Learning