The agricultural production of food comes with substantial greenhouse gas emissions and impacts on the environment. Dietary fats, a staple of human diet, might be produced chemosynthetically with a fraction of the detrimental effects on the environment.
There is no “outside.” No other system. The universe is not on a computer. It is the computer. It is the thing performing the computation. It doesn’t need anyone watching it. It doesn’t need a server farm or a control panel. It simply is what it is: a system that processes information according to its own rules.
In other words, when we talk about the universe as a quantum computer, we’re not saying it’s pretending to be real. We’re saying this is what real is.
1:19 Reality as Code.
8:35 What Is a Quantum Computer, Anyway?
13:37 Evidence and Models That Support the Quantum Universe Idea.
20:04 What Would It Mean If the Universe Is a Quantum Computer?
26:14 Could We Simulate the Universe from Within It?
32:37 The Dark Implications.
39:53 Is This the Best Description We’ll Ever Get?
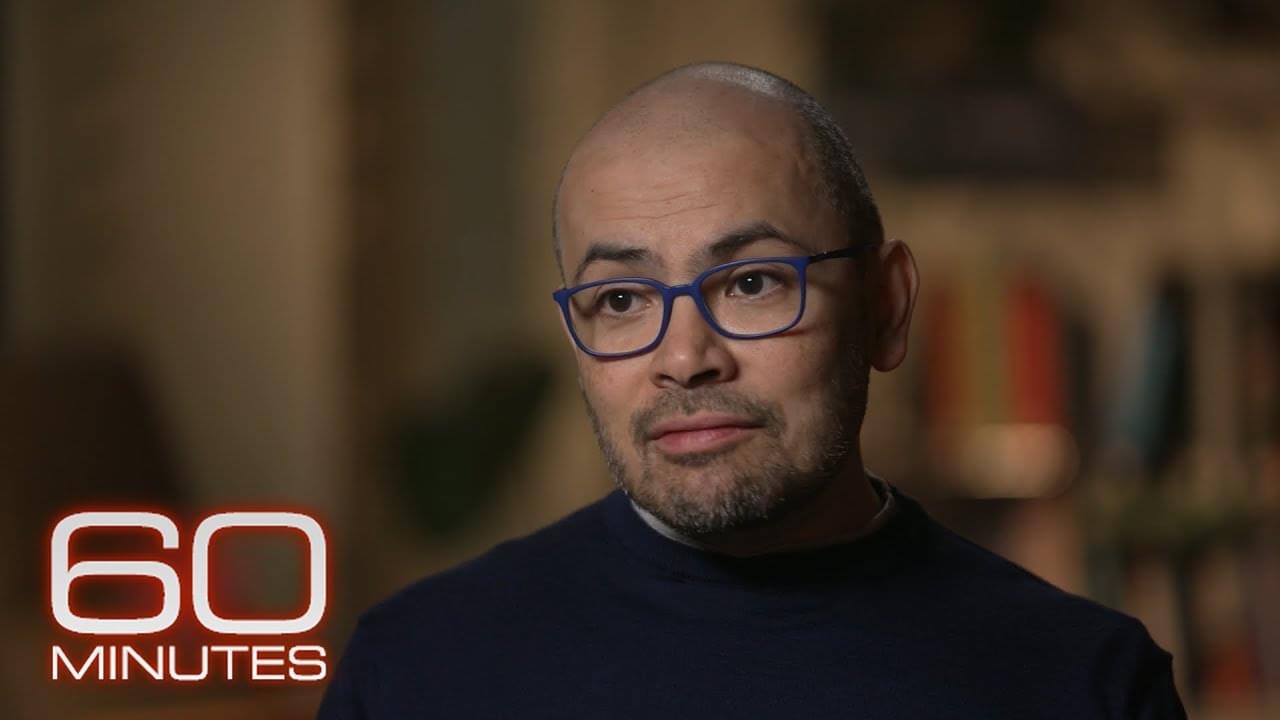
At Google DeepMind, researchers are chasing what’s called artificial general intelligence: a silicon intellect as versatile as a human’s, but with superhuman speed and knowledge.
Microplastics and much smaller nanoplastics enter the human body in various ways, for example through food or the air we breathe. A large proportion is excreted, but a certain amount remains in organs, blood, and other body fluids.
In the FFG bridge project Nano-VISION, which was launched two years ago together with the start-up BRAVE Analytics, a team led by Harald Fitzek from the Institute of Electron Microscopy and Nanoanalysis at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) and an ophthalmologist from Graz addressed the question of whether nanoplastics also play a role in ophthalmology.
The project partners have now been able to develop a method for detecting and quantifying nanoplastics in transparent body fluids and determining their chemical composition. The research is published in the journal Analytical Chemistry.
Resumen del artículo: La preocupación por el aparente aumento de los problemas de salud mental en adolescentes y jóvenes se ha intensificado considerablemente en los últimos años, siendo común en l…
AI Singularity Shock: Tech Titans Predict Unstoppable Intelligence Explosion Within 12 Months, Sparking Global Fear and Frenzy
Posted in robotics/AI, singularity | Leave a Comment on AI Singularity Shock: Tech Titans Predict Unstoppable Intelligence Explosion Within 12 Months, Sparking Global Fear and Frenzy
IN A NUTSHELL 🤖 The concept of singularity involves AI reaching a level of intelligence that surpasses that of humans. 🚀 Recent advancements in large language models and computing power have sparked debates about the possibility of achieving singularity soon. 🧠 Experts face technical and philosophical challenges, questioning whether AI can truly replicate human intelligence.
A Chinese research team has developed the world’s smallest and lightest known untethered terrestrial-aerial microrobot capable of transforming into various desired shapes, expected to replace humans in performing a wide range of tasks in complex and hazardous environments.
The robot measuring 9 centimeters in length and 25 grams in weight can operate flexibly on land and in the air with a top speed of up to 1.6 meters per second on the ground, according to the research team from Tsinghua University.
The research team has recently developed a thin-film-shaped small-scale actuator that enables microrobots to continuously transform their shape and “lock” into specific configurations — much like a Transformer — enhancing their ability to adapt to different environments.
Google DeepMind CEO Demis Hassabis, one of the only people in the world with a Nobel Prize for work on artificial intelligence, shares what’s next for the world of AI.
Physicists have successfully played a mind-bending “quantum game” using a real-world quantum computer, in which lasers shuffle around ions on a chip to explore the strange behavior of qubits. By creating a special, knotted structure of entangled particles, the team demonstrated that today’s quant