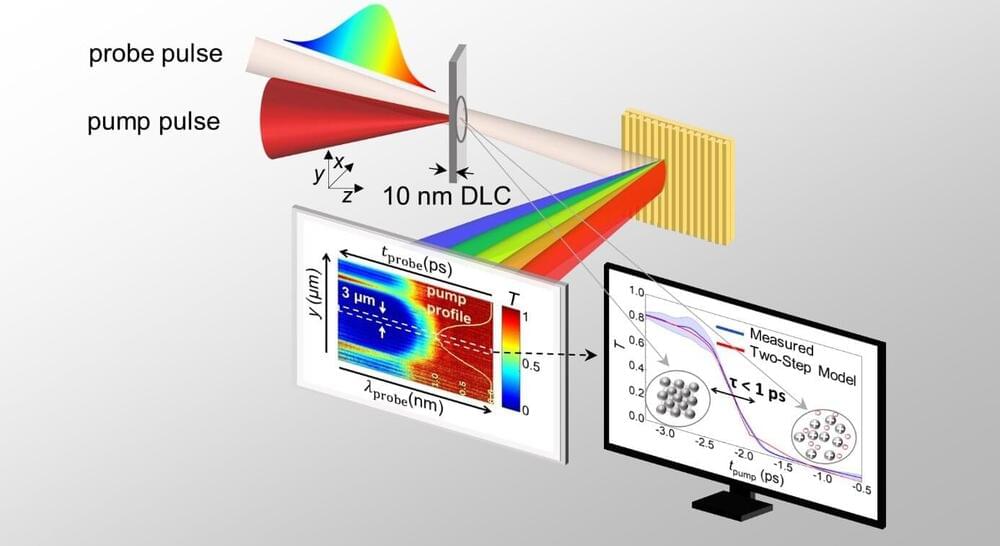
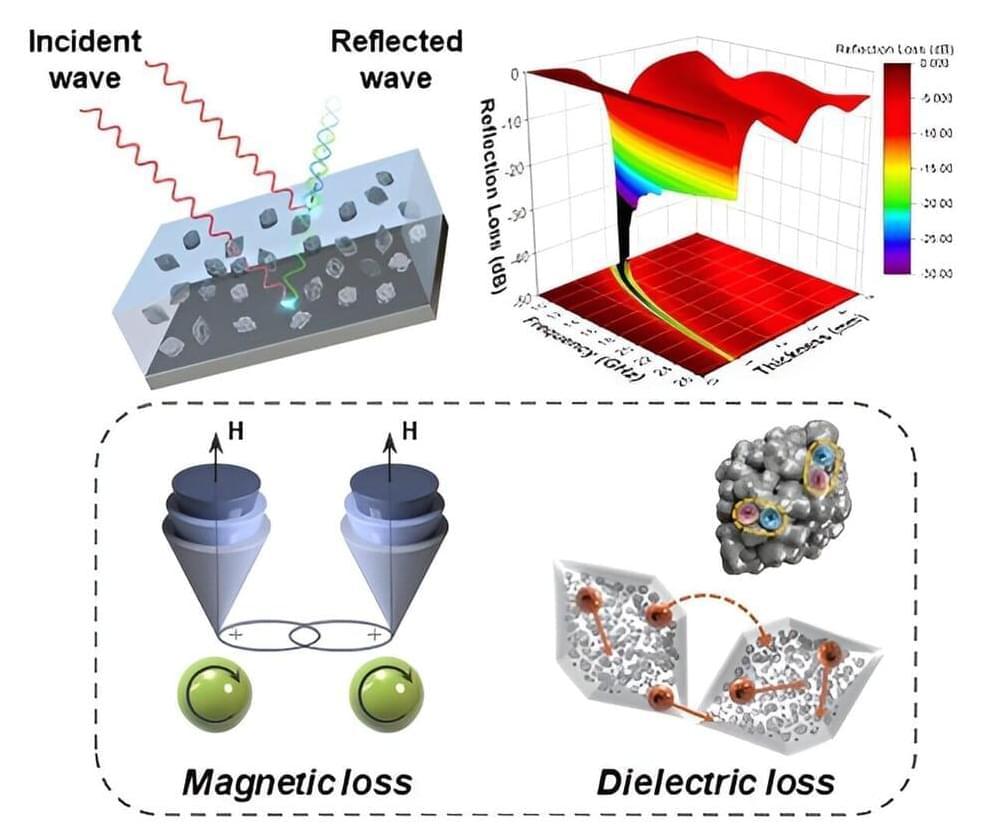
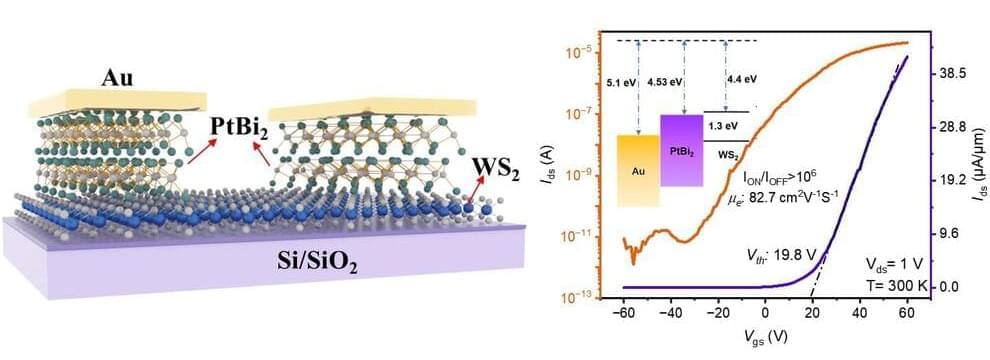
The interaction of solids with high-intensity ultra-short laser pulses has enabled major technological breakthroughs over the past half-century. On the one hand, laser ablation of solids offers micromachining and miniaturization of elements in medical or telecommunication devices. On the other hand, accelerated ion beams from solids using intense lasers may pave the way for new opportunities for cancer treatment with laser-based proton therapy, fusion energy research, and analysis of cultural heritage.