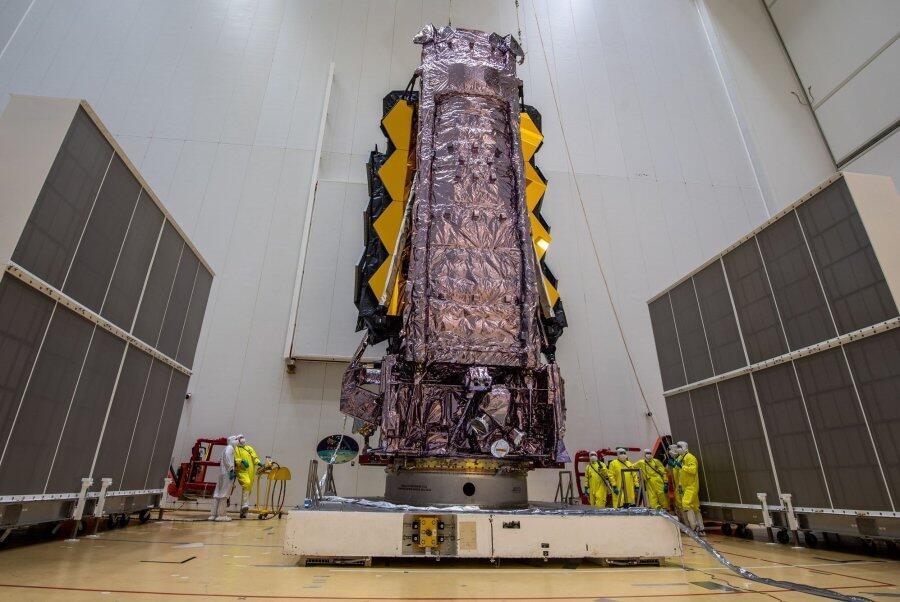
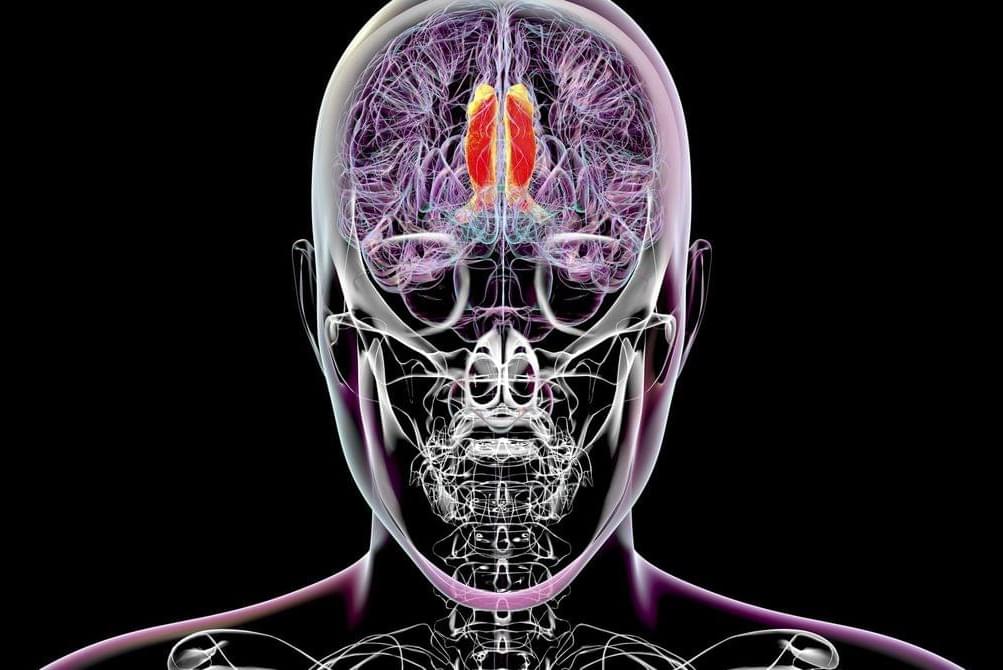
A new experiment suggests that the thalamus plays a key role in humans becoming consciously aware of stimuli their brain receives.
What do you think of when it comes to extra terrestrial life? Most popular sci-fi books and TV shows suggest humanoid beings could live on other planets. But when astronomers are searching for extra-terrestrial life, it is usually in the form of emissions from bacteria or other tiny organisms.
A new research paper in the Astrophysical Journal suggests that Cambridge scientists have managed to find this type of emission with a certainty of 99.7% from a planet called K2-18b, 124 light years away. They used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to analyze the chemical composition of the planet’s atmosphere and say they found promising evidence K2-18b could host life.
It’s an exciting breakthrough, but it doesn’t confirm alien life.
Scientists achieve record-shattering results after testing limitless energy device: ‘Experiments will continue with increased power’
Posted in nuclear energy, sustainability, transportation | Leave a Comment on Scientists achieve record-shattering results after testing limitless energy device: ‘Experiments will continue with increased power’
In a groundbreaking leap toward cleaner, more affordable energy, scientists in France held a fusion reaction steady for over 22 minutes — shattering the previous world record. If that number sounds insignificant, here’s why it’s a big deal: That is 1,337 seconds of controlled, blazing-hot plasma, the critical ingredient needed to power nuclear fusion, a nearly limitless energy source that does not rely on polluting fuels like gas, coal, or oil.
This milestone brings us one step closer to a dream energy future: one where our homes, cities, and electric cars are powered by a technology that mimics the sun — minus the radioactive waste and environmental damage of traditional nuclear power.
Nuclear fusion has the capability to solve a major problem with polluting energy sources. Right now, our power mostly comes from dirty energy that pollutes the air and contributes to extreme weather. While solar and wind energy are gaining momentum, fusion offers something different: the possibility of continuous, around-the-clock clean energy using hydrogen — the most common element in the universe — as fuel.
Major advancements in tech and science are brewing as the industry makes its way through the ‘International Year of Quantum.’
Quantum gravity is one of the biggest unresolved and challenging problems in physics, as it seeks to reconcile quantum mechanics, which governs the microscopic world, and general relativity, which describes the macroscopic world of gravity and space-time.
Efforts to understand quantum gravity have been focused almost entirely at the theoretical level, but Monika Schleier-Smith at Stanford University has been exploring a novel experimental approach — trying to create quantum gravity from scratch. Using laser-cooled clouds of atoms, she is testing the idea that gravity might be an emergent phenomenon arising from quantum entanglement.
In this episode of The Joy of Why podcast, Schleier-Smith discusses the thinking behind what she admits is a high-risk, high-reward approach, and how her experiments could provide important insights about entanglement and quantum mechanical systems even if the end goal of simulating quantum gravity is never achieved.
Europe’s flawed oversight of pesticides may be fueling a silent epidemic, warns Dutch neurologist Bas Bloem. His fight for reform pits him against industry, regulators — and time.
In this Perspective, the authors propose that patients with psoriatic arthritis and an inadequate response to therapy can be classified into two distinct subgroups, characterized by persistent inflammatory and non-inflammatory phenotypes, and discuss potential mechanisms underlying these phenotypes, as well as considerations for treatment strategies and trial design.
Sellers, Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, 415 Main St., Cambridge, Massachusetts, 2,142, USA. Phone: 617.714.7110; Email: [email protected].
Find articles by Chaturantabut, S. in: JCI | | Google Scholar
1Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA…
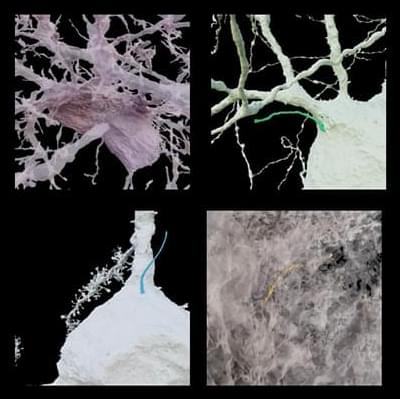
Many cells in our body have a single primary cilium, a micrometer-long, hair-like organelle protruding from the cell surface that transmits cellular signals. Cilia are important for regulating cellular processes, but because of their small size and number, it has been difficult for scientists to explore cilia in brain cells with traditional techniques, leaving their organization and function unclear.
In a new series of work, researchers at HHMI’s Janelia Research Campus, the Allen Institute, the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, and Harvard Medical School used super high-resolution 3D electron microscopy images of mouse brain tissue generated for creating connectomes to get the best look yet at primary cilia.
WASHINGTON — Blue Shepard launched six women, including a pop star and TV show host, on a suborbital flight of the company’s New Shepard vehicle April 14.
New Shepard lifted off at 9:30 a.m. Eastern from the company’s Launch Site One in West Texas after a problem-free countdown. The vehicle’s capsule, RSS Kármán Line, reached a peak altitude of 106 kilometers before landing 10 minutes and 21 seconds after liftoff.
The NS-31 mission, the company’s 11th crewed suborbital flight, flew a routine profile but with a unique complement of spaceflight participants. It was the company’s first mission to carry only women, and the first all-woman spaceflight of any kind since Valentina Tereshkova became the first woman in space on a solo flight in 1963.