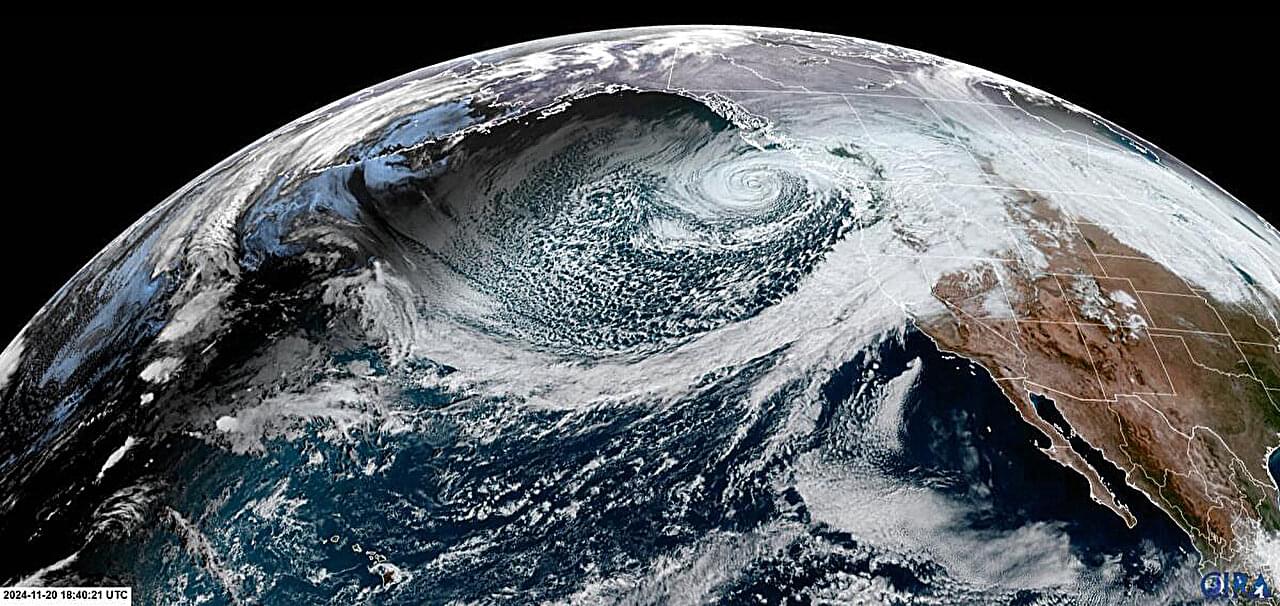
Alaska’s glaciers are melting at an accelerating pace, losing roughly 60 billion tons of ice each year. About 4,000 kilometers to the south, in California and Nevada, records for heat and dryness are being shattered, creating favorable conditions for wildfire events.
One major factor contributing to climate change in both regions is the northward shift of winter storm tracks across the North Pacific Ocean. These storms transport heat and moisture from Earth’s warmer regions toward the pole; when their tracks shift northward, more heat and moisture reach Alaska, while natural ventilation of the southwestern United States is reduced, driving temperatures upward.
In a new study published in Nature, Dr. Rei Chemke of the Weizmann Institute of Science’s Earth and Planetary Sciences Department and Dr. Janni Yuval of Google Research show that the storms’ northward shift is occurring much faster than climate models have predicted. Moreover, using a new metric based on sea-level pressure—a parameter measured consistently for decades—the researchers found that this shift is not part of natural climate variability but rather a clear consequence of climate change.