How would atoms behave near a supermassive object? We know how atoms behave in extremely weak gravity like that at the Earth’s surface: They can be excited from a lower energy level to a higher one when an electron absorbs a photon or a nucleus absorbs a gamma ray, and so on. But what if the atom is in a strong gravitational field such as one near a supermassive, rotating black hole or rotating neutron star?
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Scientists unlock the secrets of how a key protein converts DNA into RNA
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have uncovered new insights into the fundamental mechanisms of RNA polymerase II (Pol II), the protein responsible for transcribing DNA into RNA. Their study shows how the protein adds nucleotides to the growing RNA chain. The results, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, have potential applications in drug development.
Novel encoding mechanism unveiled for particle physics
In the development of particle physics, researchers have introduced an innovative particle encoding mechanism that promises to improve how information in particle physics is digitally registered and analyzed. This new method, focusing on the quantum properties of constituent quarks, offers unprecedented scalability and precision. It paves the way for significant advancements in high-energy experiments and simulations.
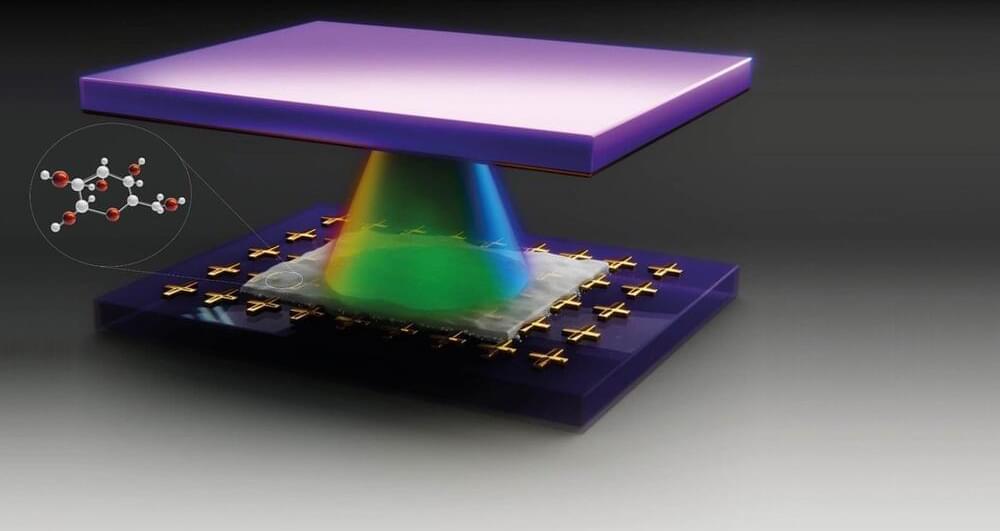
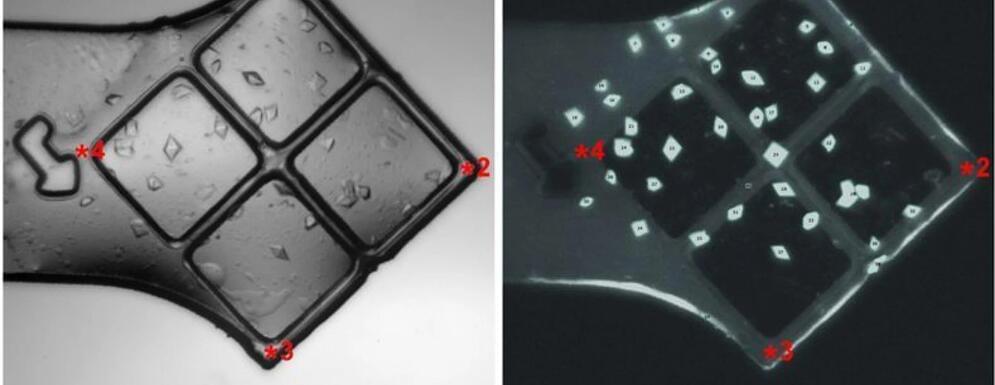
Quantum Alchemy: Scientists Fuse Light and Sugar To Create New States of Matter
Researchers have developed a technique to trap light within an organic material, forming a hybrid quantum state that gives rise to novel physical and chemical properties.
An international team of researchers led by the University of Ottawa has gone back to the kitchen cupboard to create a recipe that combines organic material and light to create quantum states.
Professor Jean-Michel Ménard, leader of the Ultrafast Terahertz Spectroscopy group at the Faculty of Science, coordinated with Dr. Claudiu Genes at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light (Germany), and with Iridian Spectral Technologies (Ottawa) to design a device which can efficiently modify properties of materials using the quantum superposition with light.
‘It’s insane’: Man with brain chip designs 3D objects
Neuralink assists second person ‘control cursor with mind’

Unitree’s $16,000 Humanoid Robot Is Ready for Mass Production
Unitree’s humanoid robot just got a mass production upgrade. The G1 will now feature stronger performance, the “ultimate appearance,” and is now more in line with mass production requirements according to Unitree.
Mashable is your source for the latest in tech, culture, and entertainment.
Follow us:
Check out https://mashable.com/
Facebook: / mashable.
Twitter: / mashable.
Instagram: / mashable.
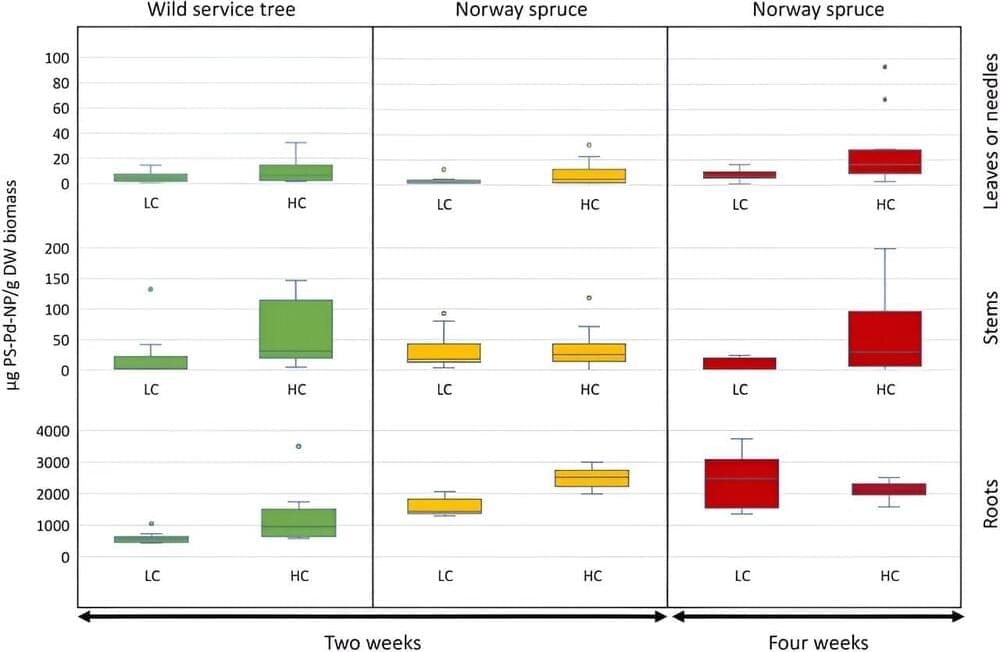
Nanoplastics put stress on trees and impair photosynthesis
And, if its in trees, guess where else it is, Crisis Yet? or nah.
It is well known that more and more plastic waste is ending up in soil and bodies of water. Researchers are particularly concerned about tiny micro-and nano-sized particles. It remains unclear how and to what extent they are able to enter living organisms—and what effect they may have on metabolism.

German emergency dispatchers get AI assistant to translate calls and suggest questions
Serious Question, does anyone in here know people who made said AI or run named company? would be interested in system described.
Artificial intelligence is being tested at the Integrated Control Center in Ludwigshafen to save precious time during emergency calls. For example, a computer voice translates for callers who speak a foreign language.
According to an SWR report, the Integrated Control Center in Ludwigshafen is using artificial intelligence (AI) to speed up emergency call handling. Until now, it took valuable minutes when callers only spoke a foreign language. Dispatchers had to quickly find a colleague who could translate, which cost time and caused stress, says Manuel Fischer, head of the integrated rescue service department.