W/ ambroise odonnat of huawei noah’s ark lab and inria.
Speakers: Ambroise Odonnat

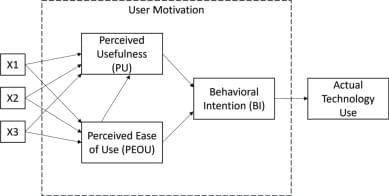
The rise of generative AI has been a major disruptive force in academia. Academics are concerned about its impact on student learning. Students can use generative AI technologies, such as ChatGPT, to complete many academic tasks on their behalf. This could lead to poor academic outcomes as students use ChatGPT to complete assessments, rather than engaging with the learning material. One particularly vulnerable academic activity is academic writing. This paper reports the results of an active learning intervention where ChatGPT was used by students to write an academic paper. The resultant papers were then analysed and critiqued by students to highlight the weaknesses of such AI-produced papers. The research used the Technology Acceptance Model to measure changing student perceptions about the usefulness and ease of use of ChatGPT in the creation of academic text.

Go to https://historicmail.com/DROID and check out with code DROID to get 10% off on their Christmas Sale on your gifts and help support the channel. Thanks to Historic Mail for sponsoring this video!
Machines so tiny they would be far smaller than a human blood cell, this is the promise of nanotechnology, and they already exist but how are they even made and will they be scarier than A.I. Experts say that we are just at the beginning of the nanobot revolution and what they promise could little short of miraculous. In this video we look at how we got here and what the current state of the art is.
To give one off tips and donations please use the following :
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/curiousdroid.
Patreon : https://www.patreon.com/curiousdroid — For longer term channel support.
Paypal.me : https://paypal.me/curiousdroid — For 1 off direct tips and thank you payments.
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/curiousdroid.
Quote: “We are like butterflies who flutter for a day and think it’s forever” : Carl Sagan.

The Principle that Tackles “TIME TRAVEL” Paradox: Enter “NOVIKOV self-consistency principle: The Novikov Principle — Time Travel and CausalityGreetings, curio…


Researchers, led by the University of Melbourne’s Professor Laura Mackay, a Laboratory Head and Immunology Theme Leader at the Peter Doherty Institute of Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute), in collaboration with Pfizer, have discovered new insights into possible future treatments for breast cancer.
A new dual-target drug that has been shown to supercharge cancer-fighting immune cells in mice may support a new treatment approach for patients, potentially paving the way for improved outcomes in breast cancer care.
Breast cancer is the fifth most common cause of cancer death in Australia, with more than 20,000 Australians diagnosed per year. Over 1,000 of those diagnosed are young Australian women under 40. There is an urgent need to discover more effective treatments for breast cancer.
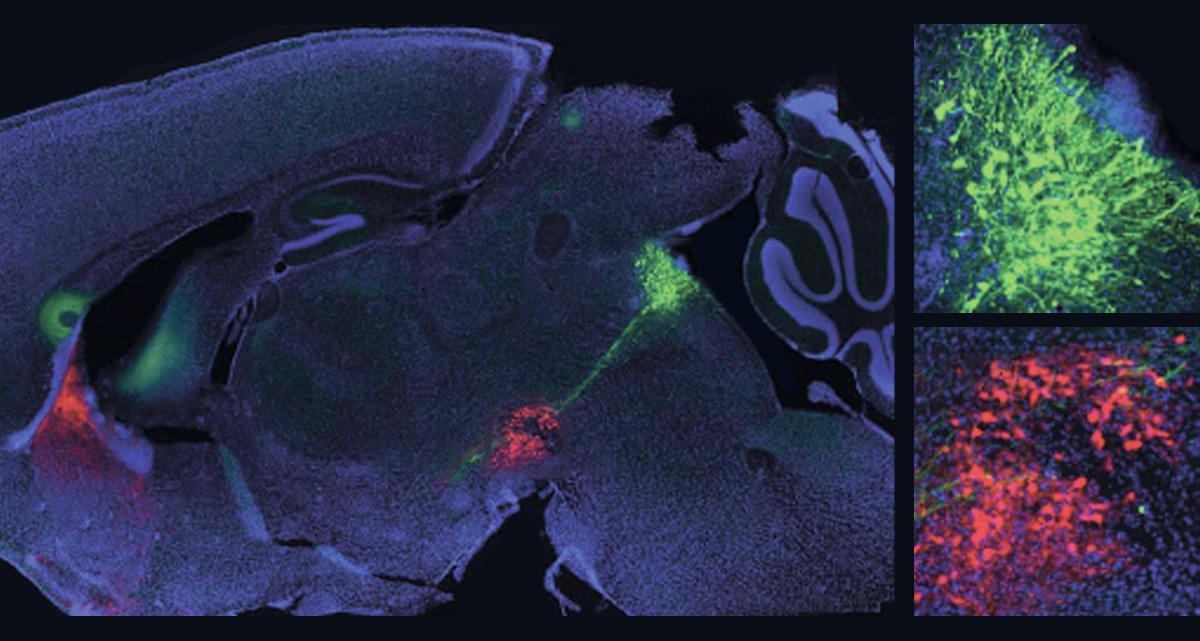
Mice learn best when the opponent opposing forces of dopamine and serotonin work together, a new study shows, helping to resolve long-standing questions about the neuromodulators’ relationship.
In the intricate dance of learning and motivation, two key brain chemicals—dopamine (DA) and serotonin (5HT)—play opposing yet deeply interconnected roles. Scientists have long speculated how these neuromodulators work together to shape our ability to form new associations, but testing these theories directly has been a challenge.
Now, researchers have developed a new mouse model that allows them to simultaneously study both dopamine and serotonin neurons in the brain. Their experiments focused on the nucleus accumbens (NAc), a region known for processing rewards. By monitoring neural activity, they found that receiving a reward boosts dopamine signals while simultaneously suppressing serotonin signals.
To understand how this dynamic affects learning, the team used optogenetics—a technique that uses light to control brain activity. They found that disrupting dopamine or serotonin alone caused only mild learning impairments. However, when both signals were suppressed together, the mice struggled significantly to learn from rewards. On the flip side, artificially recreating both dopamine and serotonin responses helped the mice learn more effectively than manipulating either signal alone.
These findings reveal that dopamine and serotonin work in opposition to control reinforcement and learning. Instead of acting in isolation, they create a delicate balance that shapes how we associate actions with rewards—providing new insights into how the brain learns and adapts.
Mice learn fastest and most reliably when they experience an increase in dopamine paired with an inhibition of serotonin, a new study shows.
While most animals reproduce sexually, some species rely solely on females for parthenogenetic reproduction. Even in these species, rare males occasionally appear. Whether these males retain reproductive functions is a key question in understanding the evolution of reproductive strategies.
A new study published in Ecology by a research team led by Assistant Professor Tomonari Nozaki from the National Institute for Basic Biology, Professor Kenji Suetsugu from Kobe University, and Associate Professor Shingo Kaneko from Fukushima University provides insight into this question. The researchers focused on the rare males of Ramulus mikado, a stick insect species in Japan, where parthenogenesis is predominant. Their analysis of male reproductive behavior reveals new findings.