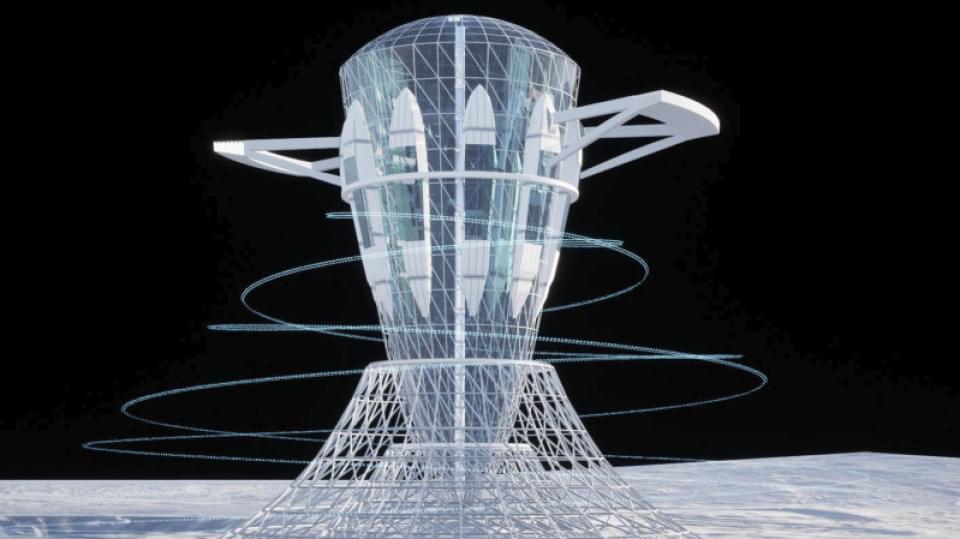
A Japanese university and construction company have partnered on research to develop a lunar habitat capable of generating artificial gravity, enabling people to live on the Moon under conditions similar to those on Earth.
Kyoto University and Kajima Corp. aim to construct a ground-based prototype of the “Neo Lunar Glass,” a paraboloid structure that generates gravity through rotation, by the 2030s.
The technology is expected to address concerns about the adverse effects of prolonged exposure to microgravity on the human body, including bone and muscle loss.