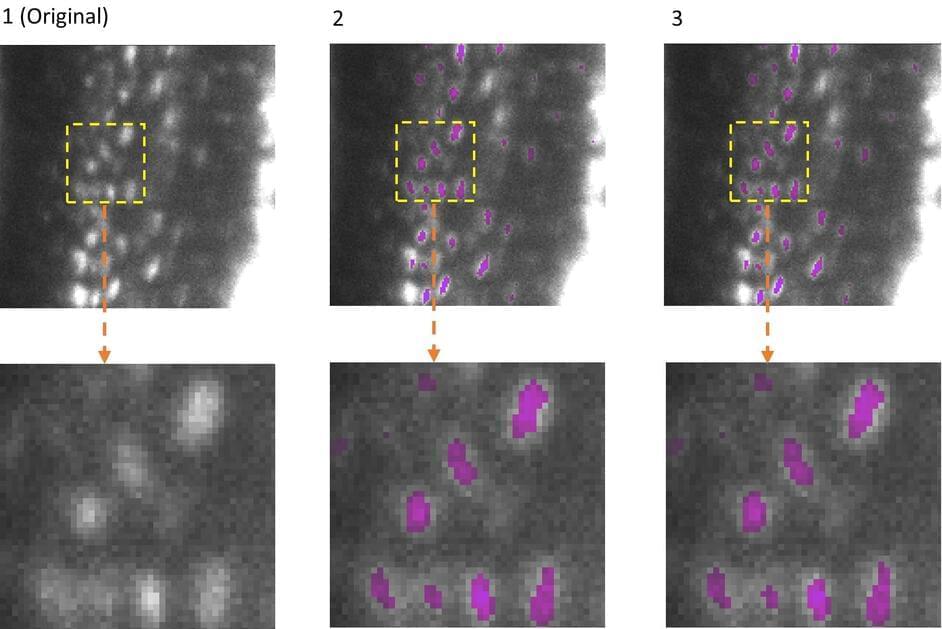
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become an indispensable component in the analysis of microscopic data. However, while AI models are becoming better and more complex, the computing power and associated energy consumption are also increasing.
Researchers at the Leibniz-Institut für Analytische Wissenschaften (ISAS) and Peking University have therefore created a free compression software that allows scientists to run existing bioimaging AI models faster and with significantly lower energy consumption.
The researchers have presented their user-friendly toolbox, called EfficientBioAI, in an article published in Nature Methods.