face_with_colon_three Year 2012
Elevated land-based islands could protect people living in low-lying areas from tsunamis – and archipelagos of them could form entire towns.

face_with_colon_three Year 2012
Elevated land-based islands could protect people living in low-lying areas from tsunamis – and archipelagos of them could form entire towns.

When you press your fingernails together, do you see a tiny diamond-shaped window of light?
If you can’t see this ‘diamond gap’, you could have finger clubbing, which can be a sign of lung cancer. Finger clubbing is seen in 35% of people with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and in 4% of those with small cell lung cancer.
Finger clubbing is when the ends of your fingers swell up, and it happens in stages. First, the base of the nail becomes soft and the skin next to the nail bed becomes shiny. Next, the nails begin to curve more than normal when looked at from the side. Finally, the ends of the fingers may get larger and swell; it’s thought to be caused by fluid collecting in the soft tissues of the fingers.

Vi arbetar för att få upp webbplatsen så fort som möjligt. Försök igen senare eller kontakta oss genom något av följande sätt :
Kontakta Karolinska Institutet
Telefon: 08–524 800 00, bemannad vardagar 08.00−16.30 fax: 08–31 11 01.
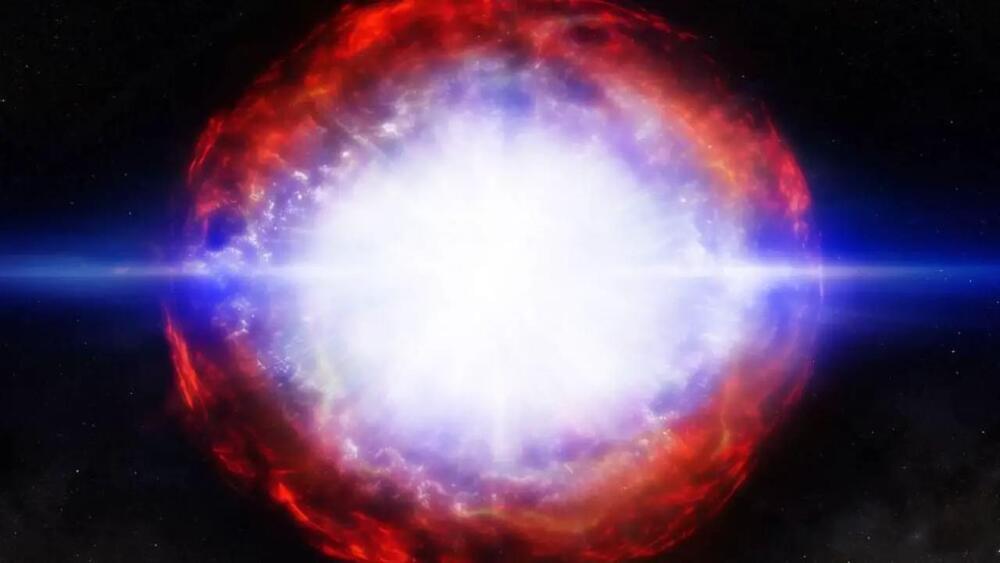

Cosmic Radiation: A Supernova’s Deadly Reach
Around 2.6 million years ago, a supernova erupted just 150 light-years from Earth, creating a dazzling display in the sky. But its most significant impact may have occurred years later when a wave of cosmic radiation reached Earth, triggering a marine extinction event. Researchers led by Adrian Melott of the University of Kansas propose that this cosmic catastrophe may have contributed to the disappearance of marine giants, including the Megalodon. Their findings were published in Astrobiology.

The Search for Quantum Gravity
Physics faces a profound crisis as it struggles to unify two foundational theories: general relativity and quantum mechanics. While general relativity explains gravity and large-scale phenomena, quantum mechanics governs the microscopic world of particles. Despite their individual successes, these theories conflict, prompting the need for a unified framework known as quantum gravity.
One promising approach is string theory, which posits that particles are actually vibrating strings in up to 11 dimensions. However, its lack of testable predictions has spurred alternative ideas, such as loop quantum gravity. This theory envisions space and time as a network of minuscule loops, challenging the notion of time as a fundamental construct. Remarkably, loop quantum gravity suggests time might not exist at all.
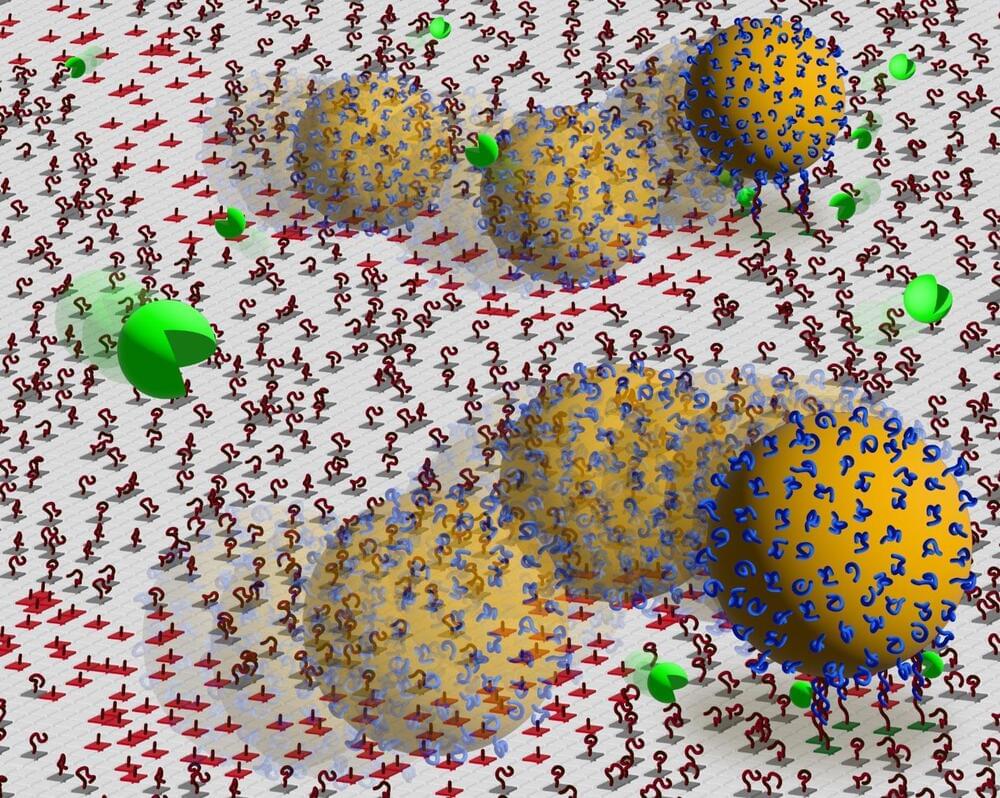
Researchers leverage their understanding of molecular motors to improve nanoscale.
The term “nanoscale” refers to dimensions that are measured in nanometers (nm), with one nanometer equaling one-billionth of a meter. This scale encompasses sizes from approximately 1 to 100 nanometers, where unique physical, chemical, and biological properties emerge that are not present in bulk materials. At the nanoscale, materials exhibit phenomena such as quantum effects and increased surface area to volume ratios, which can significantly alter their optical, electrical, and magnetic behaviors. These characteristics make nanoscale materials highly valuable for a wide range of applications, including electronics, medicine, and materials science.
NEW MEXICO (KRQE) – The world’s largest integrated quantum computing company announced plans to expand into New Mexico.
Quantinuum’s new location will be a research and development hub aimed at advancing photonics technologies. The company is headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado. “I am thrilled to welcome Quantinuum to New Mexico, launching a new industry for our state that builds on our proud foundation of innovation,” said New Mexico Governor Michelle Lujan Grisham in a news release.
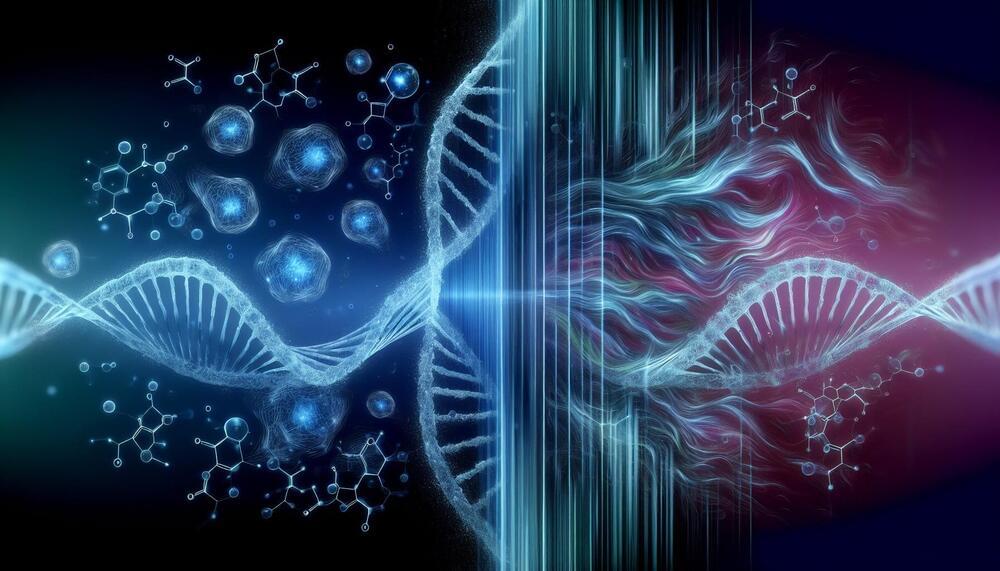

Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have published results that shed new light on an old question: what causes aging at the molecular level? Their findings, published in Nature Aging, describe a never-before-seen link between the two most accepted explanations: random genetic mutations and predictable epigenetic modifications. The latter, also known as the epigenetic clock theory, has been widely used by scientists as a consistent, quantitative measure of biological aging.
However, the new research suggests that the process may not be so simple.
“Major research institutions and companies are betting on turning back the epigenetic clock as a strategy to reverse the effects of aging, but our research suggests that this may only be treating a symptom of aging, not the underlying cause,” said co-corresponding author Trey Ideker, Ph.D., a professor at UC San Diego School of Medicine and UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering.