The Sudan virus, a close relative of Ebola, has a fatality rate of 50% but remains poorly understood in terms of how it infects cells. Currently, no approved treatments exist. To address this critical gap in pandemic preparedness, researchers at the University of Minnesota and the Midwest Antiviral Drug Discovery (AViDD) Center investigated how this deadly virus attaches to human cells.
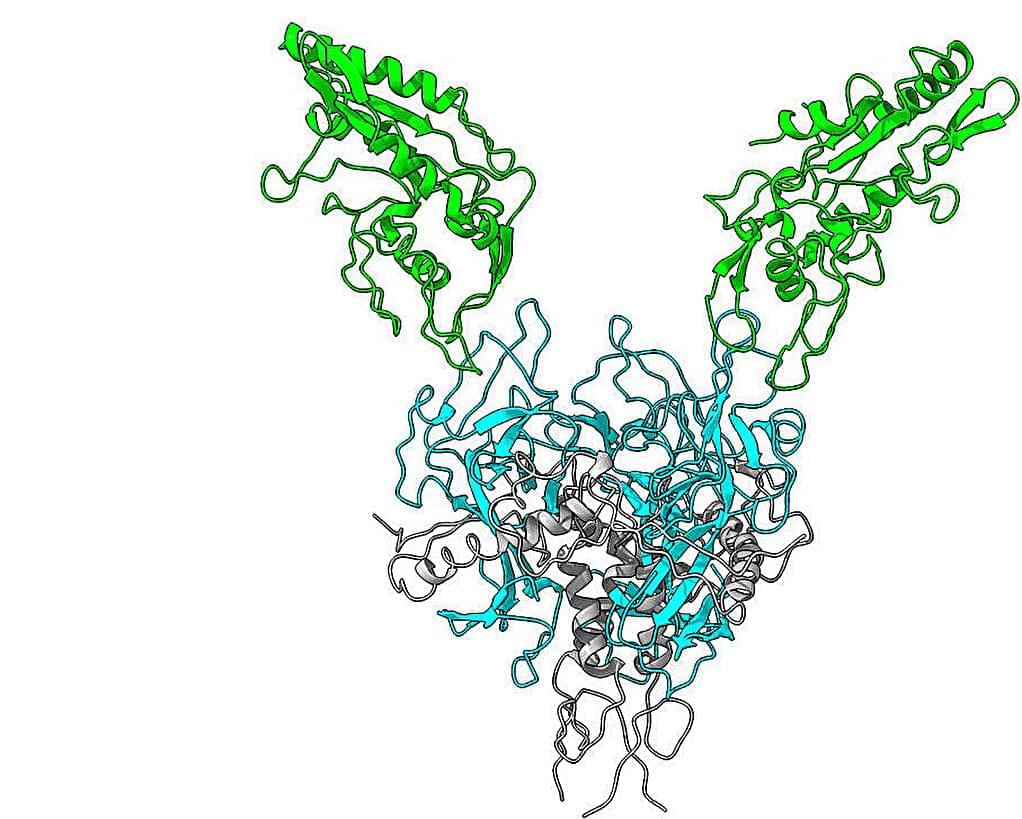
Like Ebola, the Sudan virus enters cells by binding to NPC1, a protein responsible for cholesterol transport. Using cryo-electron microscopy, the researchers mapped how the Sudan virus interacts with the human NPC1 receptor. Their findings revealed that four key amino acid differences in the receptor-binding proteins of Sudan and Ebola viruses enable the Sudan virus to bind to human NPC1 with nine times greater affinity than Ebola, which may contribute to its high fatality rate.
Building on this discovery, the team predicted the receptor-binding affinities of three other filoviruses closely related to Sudan and Ebola. They also examined how the Sudan virus binds to NPC1 receptors in bats, which are believed to be natural hosts of filoviruses. These findings provide crucial insights into the infection mechanisms and evolutionary origins of Sudan virus and related filoviruses, paving the way for potential treatments.