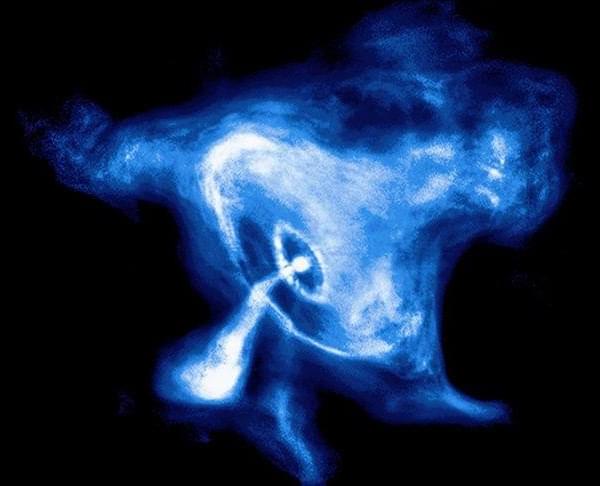
You can see shockwaves rippling through the remnants.
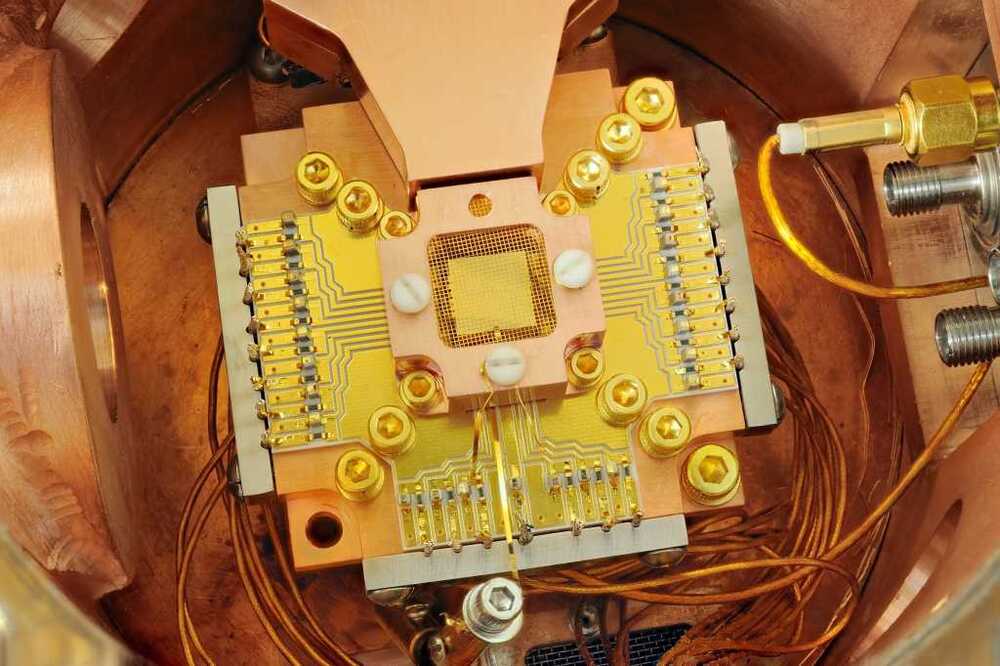
Some Google Chrome users report having issues connecting to websites, servers, and firewalls after Chrome 124 was released last week with the new quantum-resistant X25519Kyber768 encapsulation mechanism enabled by default.
Google started testing the post-quantum secure TLS key encapsulation mechanism in August and has now enabled it in the latest Chrome version for all users.
The new version utilizes the Kyber768 quantum-resistant key agreement algorithm for TLS 1.3 and QUIC connections to protect Chrome TLS traffic against quantum cryptanalysis.
Engineers at Georgia Tech have designed a process that converts carbon dioxide removed from the air into useful raw material that could be used for new plastics, chemicals, or fuels.
Their approach dramatically reduces the cost and energy required for these direct air capture (DAC) systems, helping improve the economics of a process the researchers said will be critical to addressing climate change.
The key is a new kind of catalyst and electrochemical reactor design that can be easily integrated into existing DAC systems to produce useful carbon monoxide (CO) gas. It’s one of the most efficient such design ever described in scientific literature, according to lead researcher Marta Hatzell and her team. They have published the details in Energy & Environmental Science.
While gen AI has captured the attention of virtually every CIO, quantum computing is priming to take center stage.
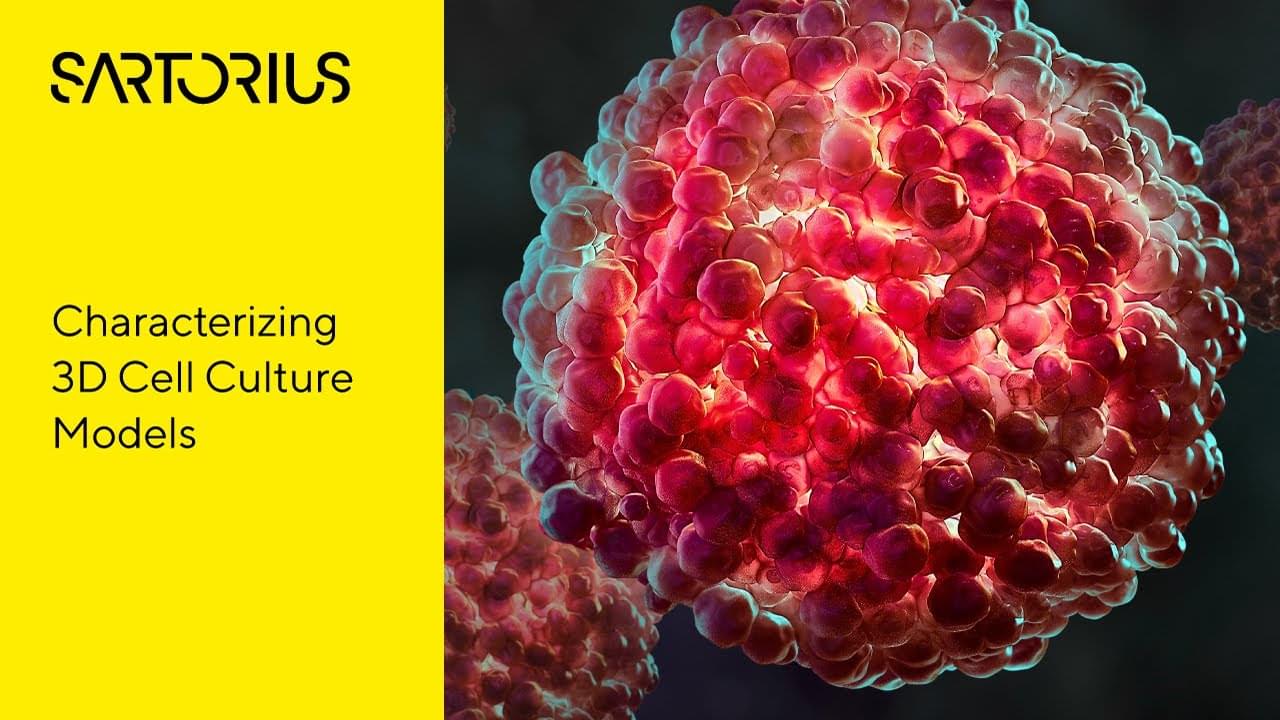
Recent advancements in our comprehension of human health and disease have been propelled by pioneering research utilizing in vitro 3D cell culture models, including both single-cell spheroids and multicellular organoids.
The refinement of these 3D cell culture models hinges on the capacity to visualize, measure, and track their development and expansion over time. Nonetheless, the methods employed to evaluate and scrutinize these intricate cell models are not without their challenges.
This video explores the challenges associated with characterizing organoids and introduces some solutions to these challenges.
Learn more about our solutions: https://www.sartorius.com/en/applicat…
Follow us on LinkedIn: / incucyte-live-cell-analysis-systems.
#organoids #3dcells #cellculture #3dcellculture #drugdiscovery
Dive into RNNs, the backbone of time series, understand their mathematics, implement them from scratch, and explore their applications.
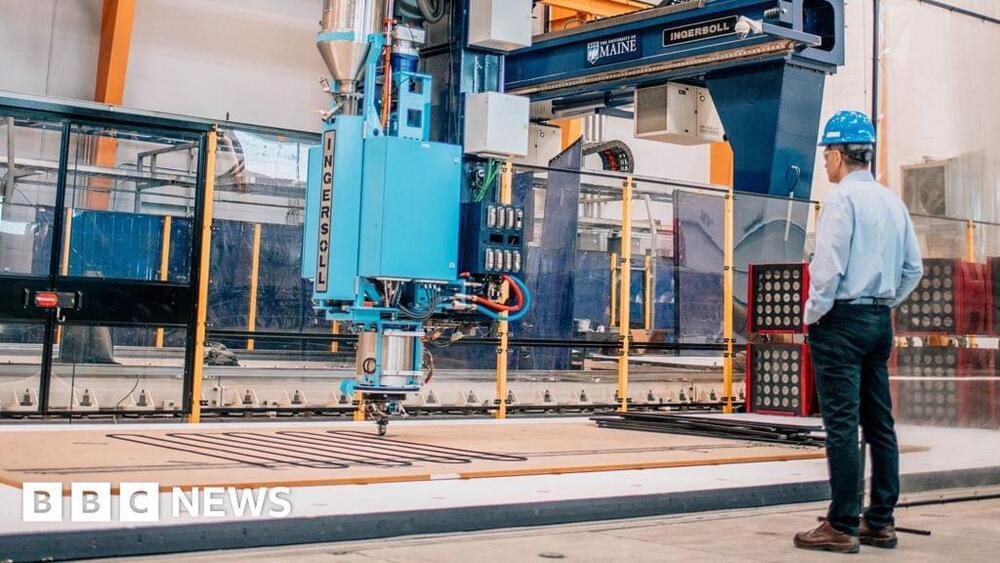
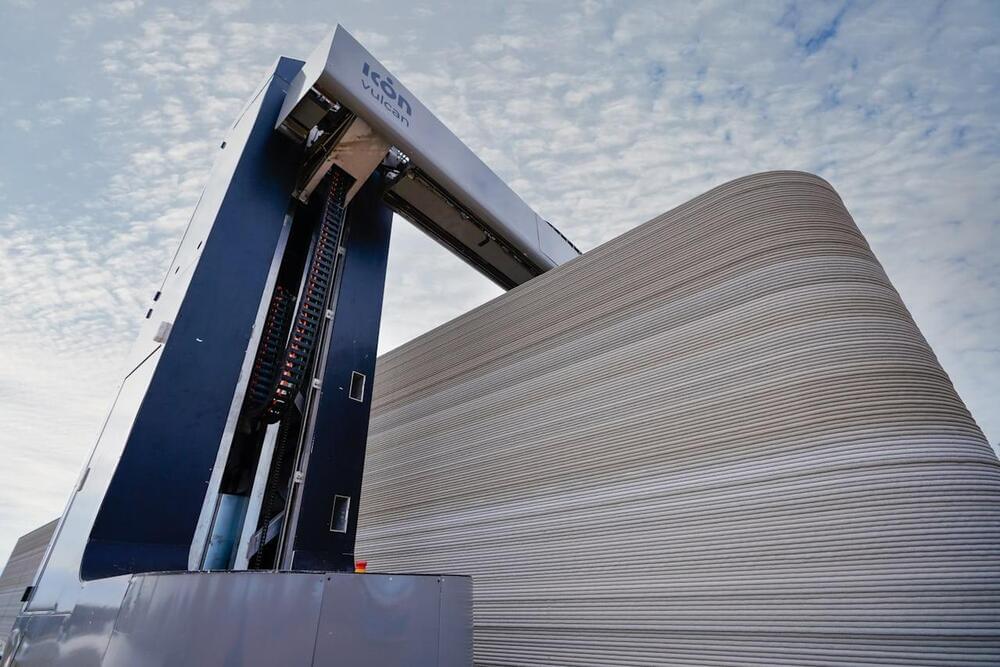
It’s hoped giant device will be able to print homes, bridges, boats and wind turbines.
When facing a predator, single cells sometimes unite to defend themselves, paving the way for more complex multicellular life forms to evolve.
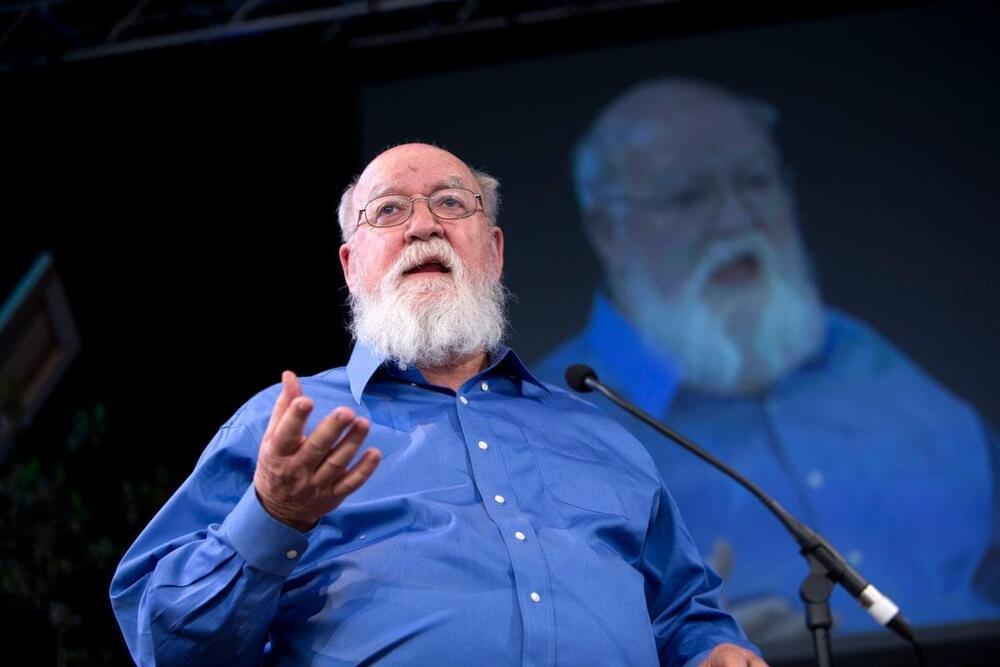
Is consciousness nothing more than an illusion? That idea defined the work of Daniel Dennett (1942–2024)
By John Horgan
Philosopher Daniel Dennett died a few days ago, on April 19. When he argued that we overrate consciousness, he demonstrated, paradoxically, how conscious he was, and he made his audience more conscious.
Generally, it’s advised not to compare apples to oranges. However, in the field of topology, a branch of mathematics, this comparison is necessary. Apples and oranges, it turns out, are said to be topologically the same since they both lack a hole – in contrast to doughnuts or coffee cups, for instance, which both have one (the handle in the case of the cup) and, hence, are topologically equal.
In a more abstract way, quantum systems in physics can also have a specific apple or doughnut topology, which manifests itself in the energy states and motion of particles. Researchers are very interested in such systems as their topology makes them robust against disorder and other disturbing influences, which are always present in natural physical systems.
Things get particularly interesting if, in addition, the particles in such a system interact, meaning that they attract or repel each other, like electrons in solids. Studying topology and interactions together in solids, however, is extremely difficult. A team of researchers at ETH led by Tilman Esslinger has now managed to detect topological effects in an artificial solid, in which the interactions can be switched on or off using magnetic fields. Their results, which have just been published in the scientific journal Science, could be used in quantum technologies in the future.