Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are medications used in cancer immunotherapy. However, treatment with ICIs may lead to adverse effects, particularly myocarditis and pericarditis. This practical pharmacovigilance study investigates the relationship between ICIs and myocarditis and pericarditis using the FAERS (U.S. FDA Adverse Event Reporting System) database.
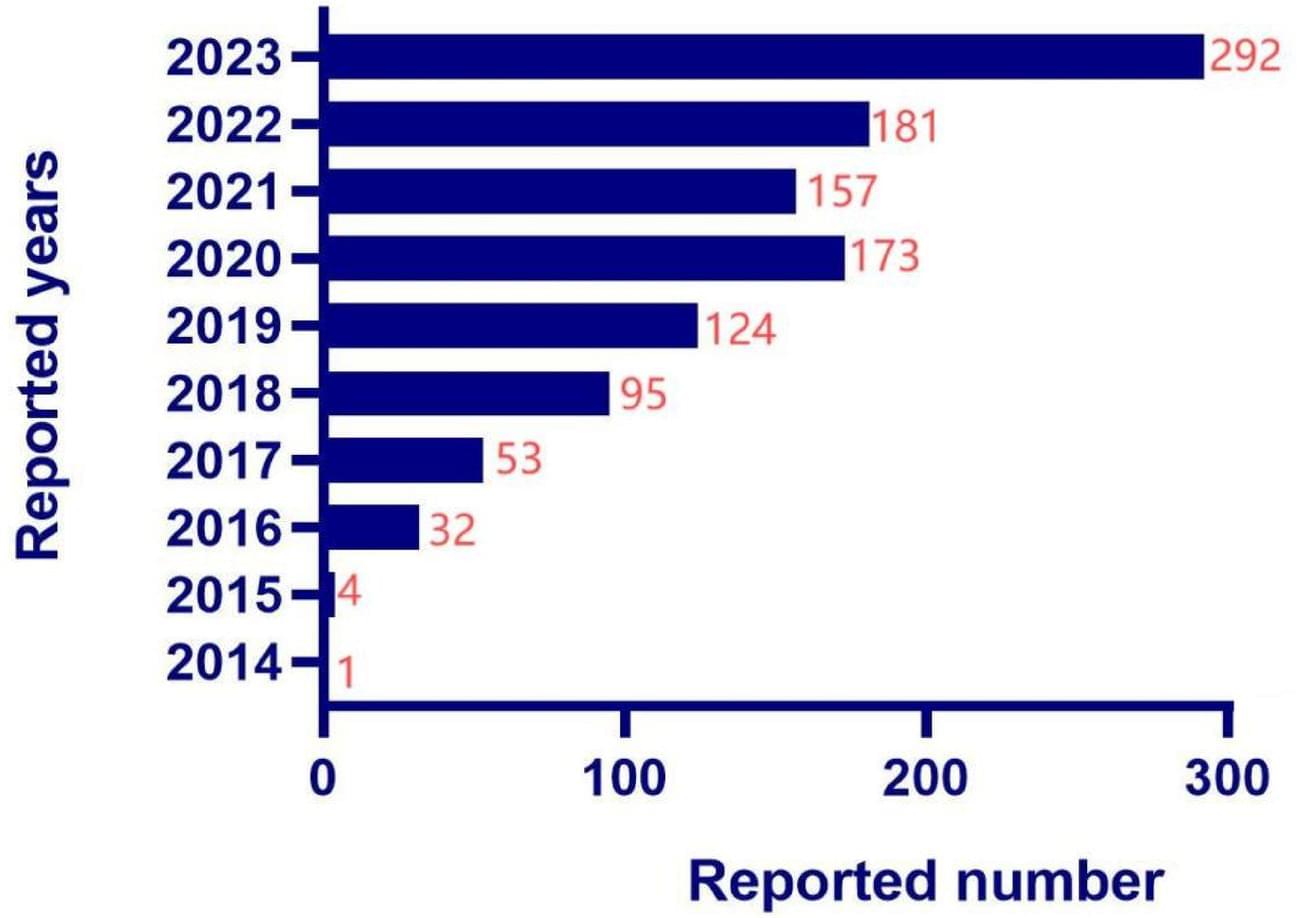
Data on myocarditis and pericarditis related to ICIs were extracted from the FAERS database for the period from 2014Q1 to 2023Q4. Data mining was performed using the Bayesian Confidence Propagation Neural Network (BCPNN) and the Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR).
A total of 1,112 cases involving 1,134 adverse event (AE) reports related to ICIs-associated noninfectious myocarditis/pericarditis (NM/P) were extracted from the FAERS database. After excluding reports with missing data, the primary reporters were physicians, consumers, and pharmacists, with the United States and Japan being the main reporting countries. The cases showed a greater percentage of males than females, with a median age of 67 years, a median weight of 65 kg, and a median onset time of 28 days. The signal strength of ICIs-associated NM/P, from highest to lowest, was as follows: Pembrolizumab (ROR: 12.32, 95% CI: 11.28–13.45, IC 025: 3.45) Nivolumab (ROR: 11.23, 95% CI: 10.13–12.44, IC 025: 3.30) Atezolizumab (ROR: 10.62, 95% CI: 8.67–13.02, IC 025: 3.10) Ipilimumab (ROR: 10.25, 95% CI: 8.34–12.58, IC 025: 3.04) Durvalumab (ROR: 9.25, 95% CI: 7.21–11.88, IC 025: 2.83).