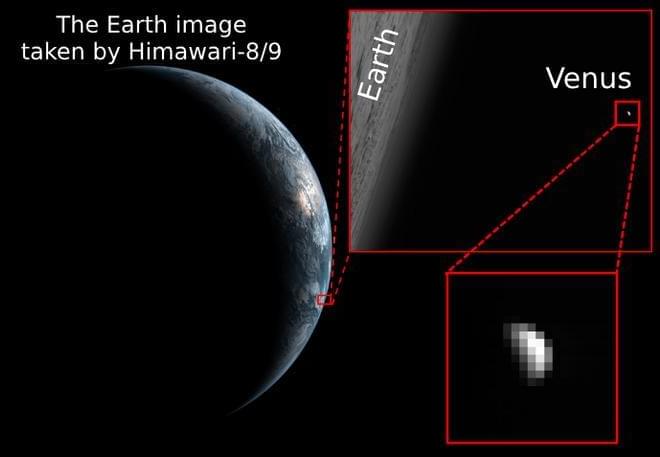
How can scientists study the meteorology of Venus from Earth since there are currently no missions to Venus? This is what a recent study published in Earth | Space


A history of Leibniz. Another Historic figure that did more then you or I ever will.




This week, my laundry machine broke. Bummer. Like any normal person, I dove into research mode, scrolling through endless product pages, feature lists, and discounts. After a while, one machine caught my attention. It was a Samsung model labelled “AI-enhanced”. (Not going to lie, it came with a solid discount, making it one of the cheapest among the top-rated options, but I was really excited about the AI feature)
In full honesty (this is not a sponsored post), it works great. From what I could observe, when you throw the clothes inside the machine, it weighs the clothes, and based on that, it selects the most suitable wash setting: water level, soap, temperature, and timing. Yes, it’s clever, efficient, and genuinely helpful. But it got me thinking: is that really AI, or just a well-designed automation?
In business, as in life, those who tell the most compelling story tend to succeed. We love to use fancy words, set expectations high, and hold attention long enough to turn curiosity into conversion. Labels matter. Language sells. That is where the “washing” comes in.