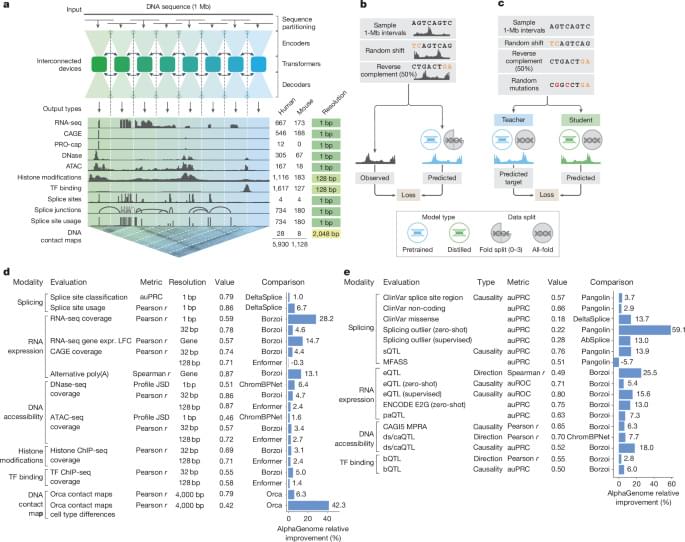
What makes it special is its versatility. Where older models might only predict how a mutation affects gene activity, AlphaGenome forecasts thousands of biological outcomes simultaneously—whether a variant will alter how DNA folds, change how proteins dock onto genes, disrupt the splicing machinery that edits genetic messages, or modify histone “spools” that package DNA. It’s essentially a universal translator for genetic regulatory language.
AlphaGenome is a deep learning model designed to learn the sequence basis of diverse molecular phenotypes from human and mouse DNA (Fig. 1a). It simultaneously predicts 5,930 human or 1,128 mouse genome tracks across 11 modalities covering gene expression (RNA-seq, CAGE and PRO-cap), detailed splicing patterns (splice sites, splice site usage and splice junctions), chromatin state (DNase, ATAC-seq, histone modifications and transcription factor binding) and chromatin contact maps. These span a variety of biological contexts, such as different tissue types, cell types and cell lines (see Supplementary Table 1 for the summary and Supplementary Table 2 for the complete metadata). These predictions are made on the basis of 1-Mb of DNA sequence, a context length designed to encompass a substantial portion of the relevant distal regulatory landscape. For instance, 99% (465 of 471) of validated enhancer–gene pairs fall within 1 Mb (ref. 12).
AlphaGenome uses a U-Net-inspired2,13 backbone architecture (Fig. 1a and Extended Data Fig. 1a) to efficiently process input sequences into two types of sequence representations: one-dimensional embeddings (at 1-bp and 128-bp resolutions), which correspond to representations of the linear genome, and two-dimensional embeddings (2,048-bp resolution), which correspond to representations of spatial interactions between genomic segments. The one-dimensional embeddings serve as the basis for genomic track predictions, whereas the two-dimensional embeddings are the basis for predicting pairwise interactions (contact maps). Within the architecture, convolutional layers model local sequence patterns necessary for fine-grained predictions, whereas transformer blocks model coarser but longer-range dependencies in the sequence, such as enhancer–promoter interactions.