NASA’s DAVINCI probe will be first in 21st century to brave Venus’ atmosphere as it descends from above the planet down to its surface.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
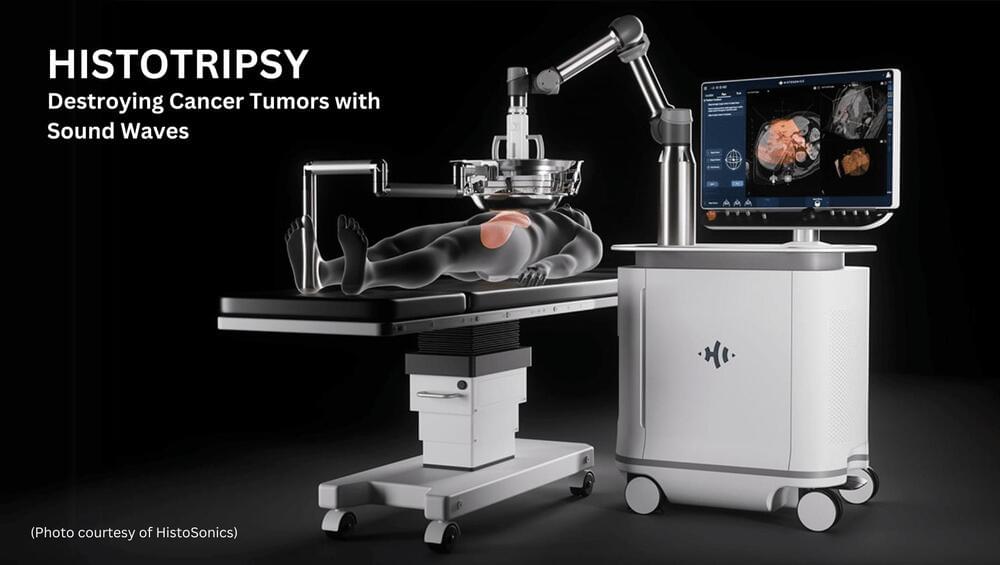
Histotripsy: Destroying cancer tumors with sound waves
“The future of medicine is the medicine of frequencies.” – Albert Einstein.
Imagine a future where cancerous tumors inside the body could be destroyed using only sound waves. Well… the future is now. And it’s called histotripsy.
Histotripsy is a non-invasive process that uses sound waves to completely eliminate cancer tumors. Like radiation therapy, doctors point an ultrasound device at your tumor and “zap it.” But unlike radiotherapy, there is no cancer-causing radiation or heat involved, tumors can be destroyed in one treatment, there is minimal damage to surrounding tissue, a low rate of complications, faster recovery time, and it has been shown to activate immune cells to identify and target any remaining cancer cells in the body.

Gameto Announces World’s First Live Birth Using Fertilo Procedure that Matures Eggs Outside the Body
IVF technology matures eggs in a culture of iPSC (induced stem cell)-derived ovarian cells.
A baby was born in their trial, marking “first ever human birth using using iPSC technology” company claims.
Gameto useds iPSCs, or induced pluripotent stem cells. Same as embryonic stem cell, except made by inducing (forcing) a skin cell or white blood from a donor cell to become a stem cell using a protein cocktail. Dont need embryo to start.
This is also the first demonstration of an end-to-end process by which a therapy developed from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) has the potential to improve IVF outcomes and advance women’s health. Co-culturing immature eggs with Gameto’s proprietary OSCs has shown promising results to date, with the potential for higher rates of egg maturation and embryo formation.
“This breakthrough represents a historic milestone in reproductive medicine,” said Dr. Luis Guzmán, Lead at Pranor Labs & Science, who oversaw the Fertilo-enabled IVF cycle that enabled the first live birth. “The ability to mature eggs outside the body with minimal hormonal intervention significantly reduces risks such as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome and alleviates the side effects caused by high hormone doses. Fertilo is a major advancement for women who cannot tolerate or do not want to undergo the burden of the traditional IVF protocol, bringing hope and new possibilities to a broader patient population.”
China: Ampace’s cylindrical lithium battery charges 80% in 10 minutes
A China-based firm has launched a novel energy storage device that tackles the 18650-battery power challenge. Introduced by Ampace, the latest JP30 cylindrical lithium battery is claimed to be capable of delivering breakthrough performance in a compact form.
Themed “Working Non-stop, compact and more powerful”, the new battery is the latest addition to the JP series.
Despite having a compact and sleek design in appearance, the battery offers ultra-high power performance.

Probiotic Delivers Anti-cancer Drug to the Gut
Oral immunotherapy shrinks gastrointestinal tumors in mouse study.
Immunotherapy is a promising treatment that recruits the immune system to help fight cancer, but it has had limited success in gastrointestinal cancers. Now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have engineered a probiotic that delivers immunotherapy directly to the gut to shrink tumors in mice, offering a potentially promising oral drug for hard-to-reach cancers.
The probiotic cancer treatment, described Nov. 20 in the journal Cell Chemical Biology, establishes a customizable drug delivery system that can be modified to potentially treat other gut diseases.

What bacteria taught me about metaphysics
Documentary filmmaker Hans Busstra shares with us, with the aid of amazing and scientifically accurate animations of the molecular world, the background story of his journey from imaging the hardcore science of molecular biology to the fundamental insights of metaphysics.

DeepMind Vice President sees AI on the brink of a fundamental shift towards autonomous agents
DeepMind’s Vice President of Drastic Research and Gemini co-tech lead Oriol Vinyals describes how artificial intelligence is moving from narrowly focused systems toward autonomous agents, and what challenges remain ahead.
Ad.
According to Vinyals, AI is going through a fundamental transformation away from highly specialized systems and toward autonomous agents. Speaking on a company podcast, he explained that early AI systems like AlphaStar, which focused on playing StarCraft, were just the beginning of this development.
A Genetic Immunity Modulator is Discovered
Infectious diseases can have very different effects on different people; some individuals may have virtually no symptoms from COVID-19, for example, while others are killed by the viral disease. Scientists have now learned more about one genetic mechanism that can lead to variations in immune responses in different people. The findings, which have been reported in Cell, describe a kind of tuner that can dial the immune response up or down, and has been encoded in human DNA for millions of years.
The human genome contains bits of ancient viruses known as retrotransposons, which were once able to move around the genome, like so-called jumping genes, but have since been brought under control. They are thought to compose a major part of the genome. Researchers have identified instances where retrotransposons can become active again, however, such as in some types of cancer. Now even more consequences of these trasnposons are being identified.