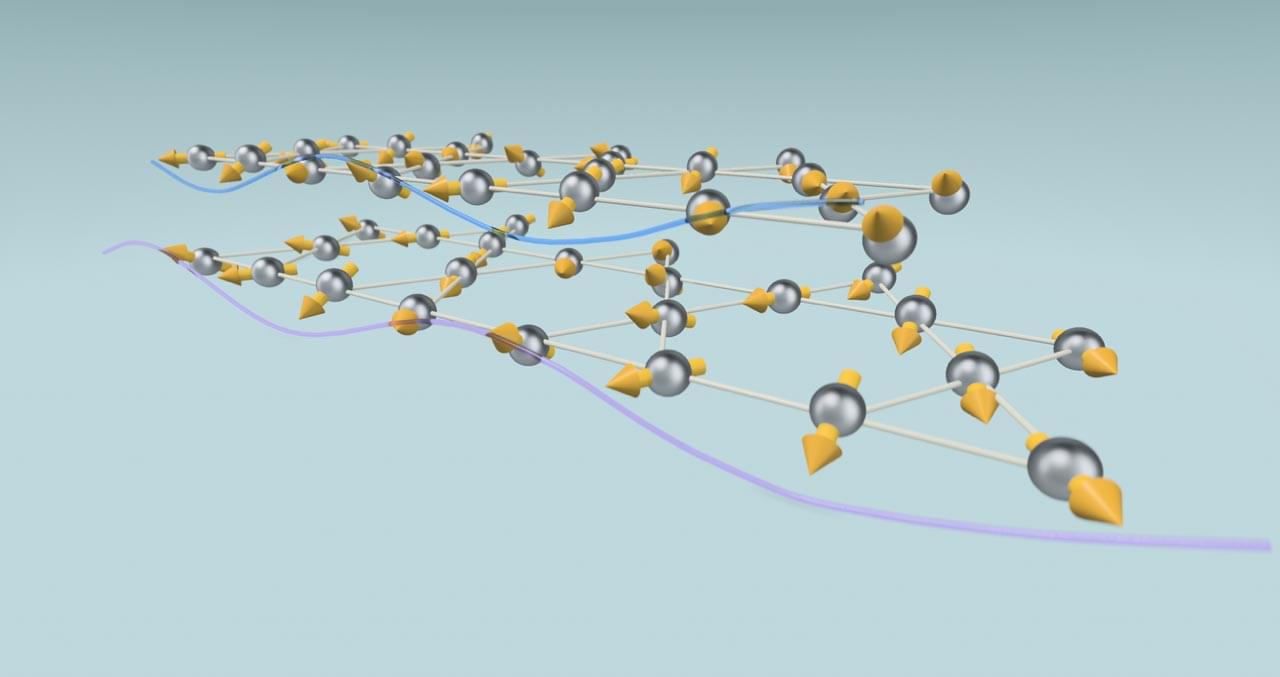
Research by physicists at The City College of New York is being credited for a novel discovery regarding the interaction of electronic excitations via spin waves. The finding by the Laboratory for Nano and Micro Photonics (LaNMP) team headed by physicist Vinod Menon could open the door to future technologies and advanced applications such as optical modulators, all-optical logic gates, and quantum transducers. The work is reported in the journal Nature Materials.
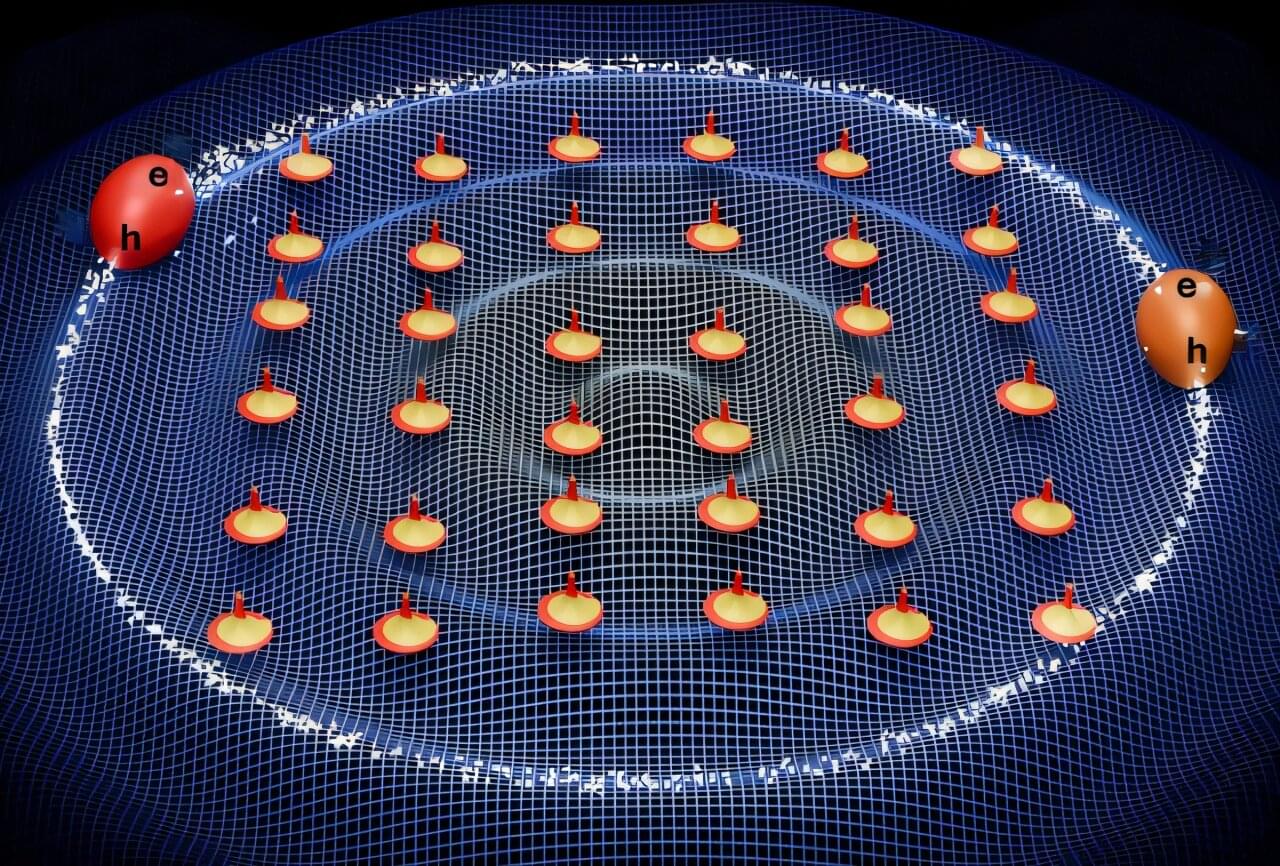
The researchers showed the emergence of interaction between electronic excitations (excitons—electron hole pairs) mediated via spin waves in atomically thin (2D) magnets. They demonstrated that the excitons can interact indirectly through magnons (spin waves), which are like ripples or waves in the 2D material’s magnetic structure.
“Think of magnons as tiny flip-flops of atomic magnets inside the crystal. One exciton changes the local magnetism, and that change then influences another exciton nearby. It’s like two floating objects pulling toward each other by disturbing water waves around them,” said Menon.