The Air Force Research Lab is working with the Space Warfighting Analysis Center and the Defense Innovation Unit to test space data transport concepts.


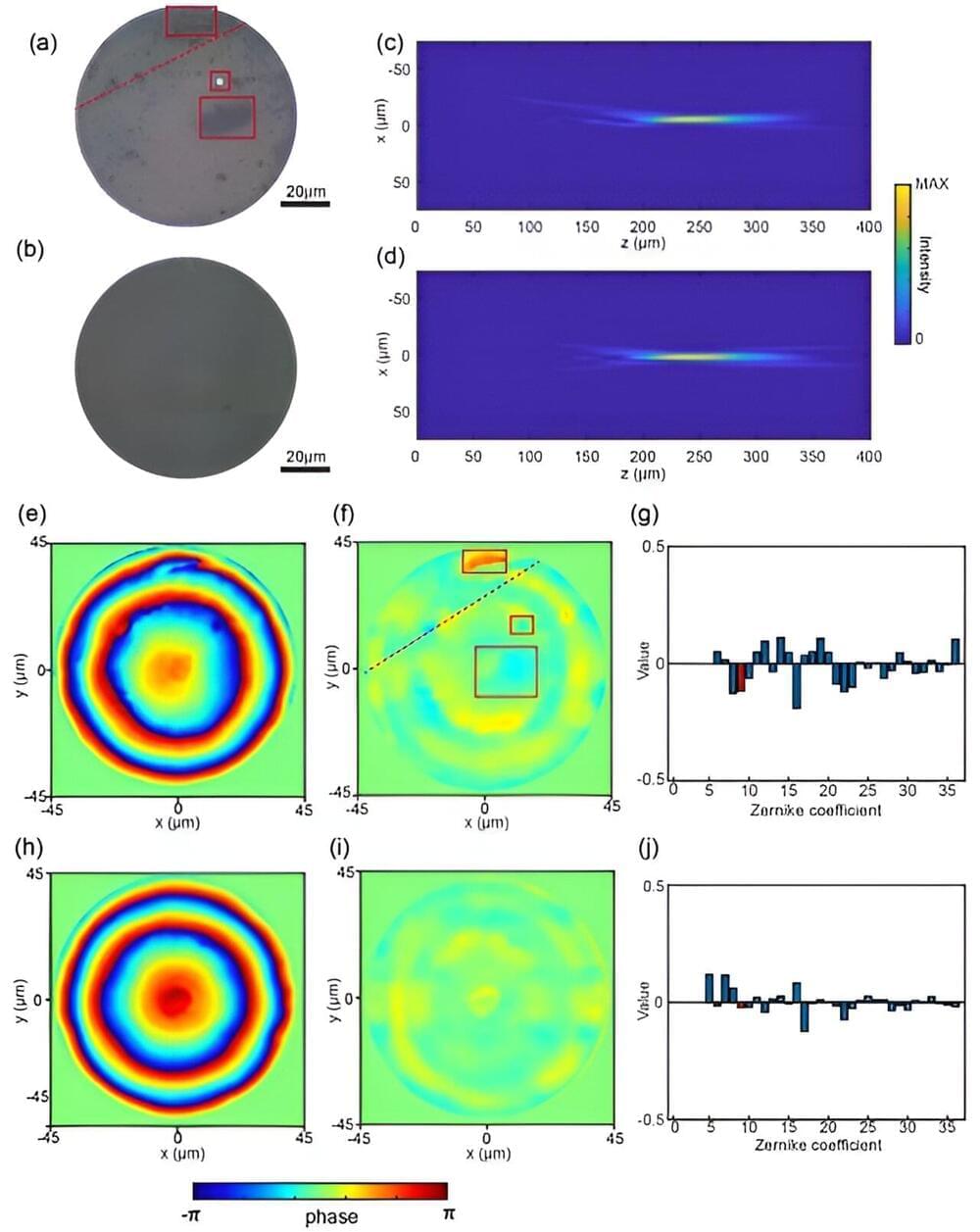
Metalens is a kind of optical metasurface composed of metaatoms for manipulating incoming light’s amplitude, phase, and polarization. Unlike traditional refractive lenses, metalens can modulate the wavefront from plane to spherical at an interface. It has garnered widespread attention due to its novel physical properties and promising potential applications.


What does the inside of a cell really look like? In the past, standard microscopes were limited in how well they could answer this question. Now, researchers from the Universities of Göttingen and Oxford, in collaboration with the University Medical Center Göttingen (UMG), have succeeded in developing a microscope with resolutions better than five nanometers (five billionths of a meter). This is roughly equivalent to the width of a hair split into 10,000 strands. Their new method was published in Nature Photonics.
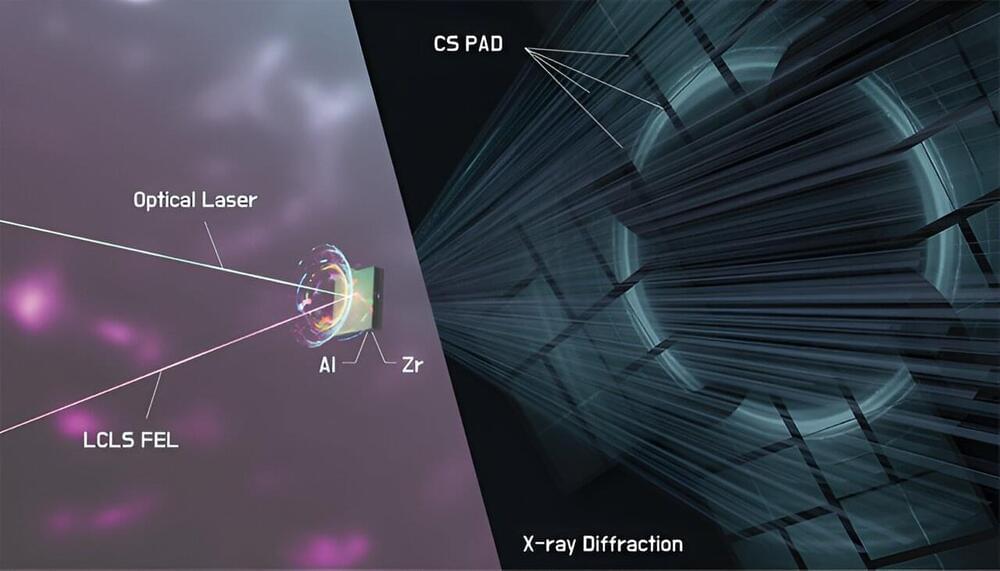
Shock experiments are widely used to understand the mechanical and electronic properties of matter under extreme conditions, like planetary impacts by meteorites. However, after the shock occurs, a clear description of the post-shock thermal state and its impacts on material properties is still lacking.

“Quantum computing is not going to be just slightly better than the previous computer, it’s going to be a huge step forward,” he said.
His company produces the world’s first dedicated quantum decoder chip, which detects and corrects the errors currently holding the technology back.
Building devices “that live up to the technology’s incredible promise requires a massive step change in scale and reliability, and that requires reliable error correction schemes”, explained John Martinis, former quantum computing lead at Google Quantum AI.
