A team of researchers report colloidal quantum dots (QDs) offer a unique platform for exploring quantum effects.


Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/mattbatwings.
Discord: https://discord.gg/V5KFaF63mV
My socials: https://linktr.ee/mattbatwings.
My texture pack: https://modrinth.com/resourcepack/mattpack.
Original Playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL5LiOvrbVo8nPTtdXAdSmDWzu85zzdgRT
LRR: (Recommended Prerequisite) https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL5LiOvrbVo8keeEWRZVaHfprU4zQTCsV4
ALL WORLD DOWNLOADS can be found on my Planetminecraft: https://www.planetminecraft.com/member/mattbatwings/
Project Repo: https://github.com/mattbatwings/BatPU-2
Final Instruction Set (Spreadsheet): https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1Bj3wHV-JifR2vP4HRYoC…8Nm56W4aI/
Final World Download: https://www.planetminecraft.com/project/new-redstone-computer/
Thumbnail made by @Sloimay.
0:00 Intro.
0:17 Episode 1 — Introduction to Computing.
10:23 Episode 2 — The Arithmetic Logic Unit.
26:29 Episode 3 — The Register File.
39:37 Episode 4 — Machine Code & Assembly.
52:28 Episode 5 — Instruction Memory.
1:06:11 Episode 6 — The Program Counter.
1:16:43 Episode 7 — Jumping, Branching, & Flags.
1:34:27 Episode 8 — The Call Stack.
1:45:24 Episode 9 — Data Memory.
1:56:13 Episode 10 — Input & Output.
2:11:46 Episode 11 — Assembly Programming.
Music (in order):
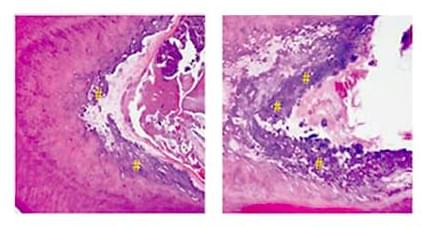
A small dose of low-power laser light activated dental stem cells in rat molars to generate dentin, one of the major components of teeth. The finding may lead to new approaches to develop low-cost, non-invasive therapies for treating dental disease and tooth damage.
Dentists currently use inert materials to repair damaged teeth. Tissue regeneration would be an attractive alternative, because inert materials can fail with time and don’t provide the full function of the tissue. Stimulating regeneration of teeth, however, is a major challenge. Teeth are composed of several parts, including the pulp at the core, dentin in the middle, and enamel on the surface.
Stem cells, found throughout the body, can give rise to specialized cells. Researchers have been able to coax stem cells to transform (differentiate) into many types of cells in the laboratory before infusing them into the body. But these techniques are time consuming and can bring unwanted side effects.

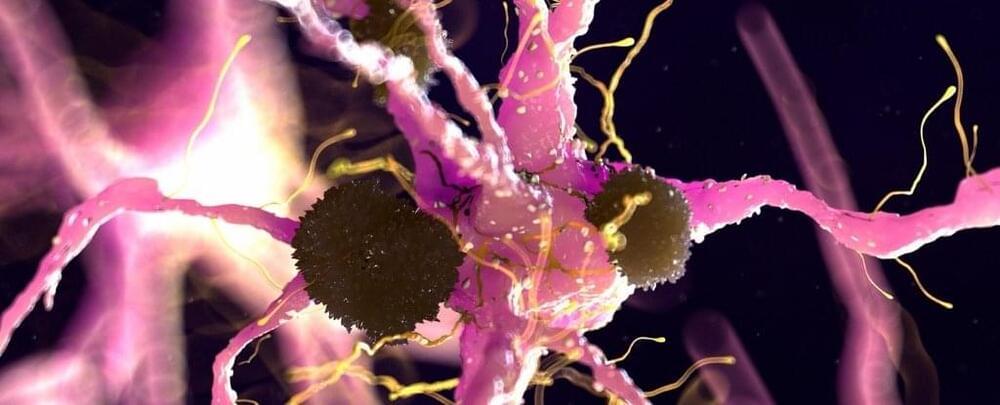
Researchers have discovered how a cell surface protein called Aplp1 can play a role in spreading material responsible for Parkinson’s disease from cell-to-cell in the brain.
Promisingly, an FDA-approved cancer drug that targets another protein called Lag3 – which interacts with Aplp1 – blocks the spread in mice, suggesting a potential therapy may already exist.
In a paper published last year, an international team of scientists describes how the two proteins work together to help harmful alpha-synuclein protein clumps get into brain cells.
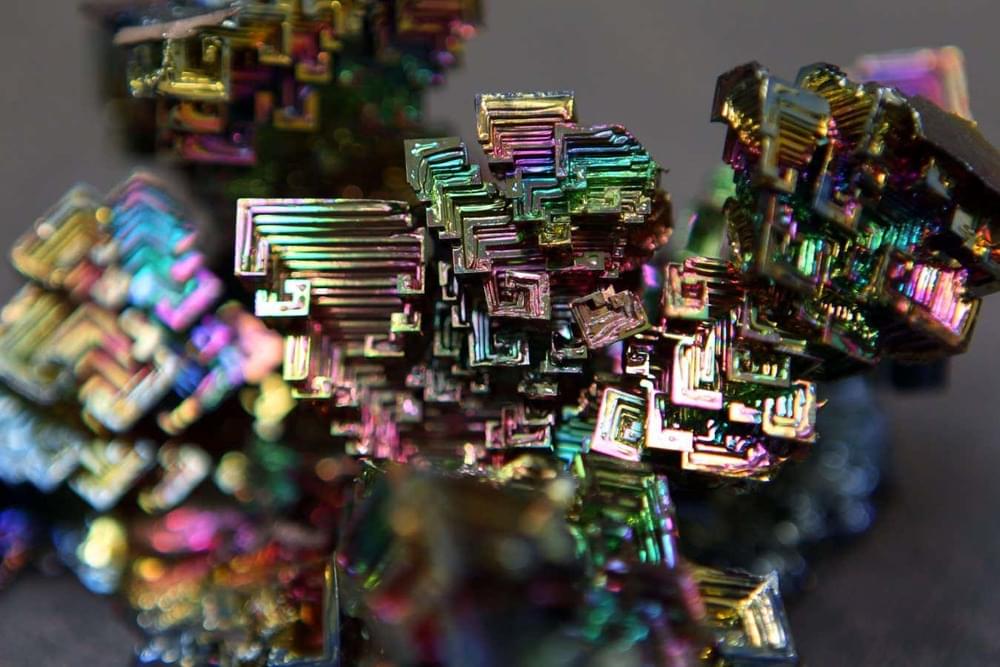


The soft metal bismuth may be a wonder material for electronics – particularly because of one surprising behaviour it displays when exposed to magnetic fields.

The James Webb Space Telescope.
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST or Webb) is an orbiting infrared observatory that will complement and extend the discoveries of the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers longer wavelengths of light, with greatly improved sensitivity, allowing it to see inside dust clouds where stars and planetary systems are forming today as well as looking further back in time to observe the first galaxies that formed in the early universe.

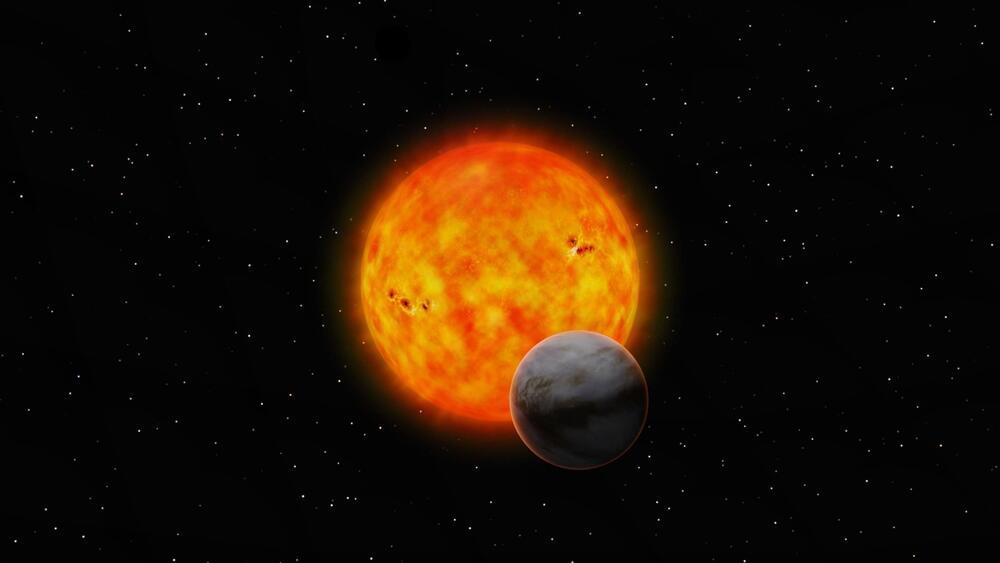
An international team of astronomers reports the discovery of a new compact galaxy group using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA). The new group, designated CGG-z4, hosts two optically dark star-forming galaxies. The finding was detailed in a research paper published Jan. 9 on the pre-print server arXiv.
Galaxy groups are the smallest aggregates of galaxies, typically containing up to 50 members. For astronomers, overdense structures like protoclusters or galaxy groups are prime targets to help them investigate the growth of massive galaxies.
Recent observations performed by a group of astronomers led by Malte Brinch of the Technical University of Denmark, have uncovered the presence of a new galaxy group. They identified the new group with ALMA in the Cosmic Evolution Survey (COSMOS) field.

Researchers developed a durable, bioinspired ZIF-67 MOF membrane that efficiently separates propylene from propane, offering high performance, long-term stability, and industrial scalability.
Polymer-grade propylene (99.5%) is a vital raw material in the chemical industry. Its production inevitably generates propane as a byproduct in the product stream. A critical step in producing polymer-grade propylene is the separation of propylene from propane—a challenging and energy-intensive process due to the molecules’ nearly identical physical and chemical properties.
Molecular sieve membranes offer an energy-efficient and effective solution for this separation. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs.