India officially becomes the world’s largest open-source contributor, surpassing the United States for the first time, according to GitHub’s Octoverse 2025 report.


https://www.jimruttshow.com/currents-ben-goertzel-2/
Jim talks with Ben Goertzel about the ideas in his recent essay “Three Viable Paths to True AGI.” They discuss the meaning of artificial general intelligence, Steve Wozniak’s basic AGI test, whether common tasks actually require AGI, a conversation with Joscha Bach, why deep neural nets are unsuited for human-level AGI, the challenge of extrapolating world-models, why imaginative improvisation might not be interesting to corporations, the 3 approaches that might have merit (cognition-level, brain-level, and chemistry-level), the OpenCog system Ben is working on, whether it’s a case of “good old-fashioned AI,” where evolution fits into the approach, why deep neural nets aren’t brain simulations & attempts to make them more realistic, a hypothesis about how to improve generalization, neural nets for music & the psychological landscape of AGI research, algorithmic chemistry & the origins of life problem, why AGI deserves more resources than it’s getting, why we may need better parallel architectures, how & how much society should invest in new approaches, the possibility of a cultural shift toward AGI viability, and much more.

Focusing on the futuristic tech that appears in sci-fi without paying attention to the actual point of the story is a big mistake, says Annalee Newitz

Researchers working on China’s fully superconducting Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) have experimentally accessed a theorized “density-free regime” for fusion plasmas, achieving stable operation at densities well beyond conventional limits.
The results, reported in Science Advances, provide new insights into overcoming one of the most persistent physical obstacles on the path toward nuclear fusion ignition.
The study was co-led by Prof. Zhu Ping from Huazhong University of Science and Technology and Associate Prof. Yan Ning from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. By realizing a novel high-density operating scheme on EAST, the team demonstrated that plasma density, long constrained by empirical limits in tokamak operation, can be substantially extended without triggering disruptive instabilities.


On the Same Origin of Spacetime, Matter, and Everything https://lnkd.in/gCs9XBzx What if space, time, matter, gravity, dark matter, and dark energy all come from one thing: quantum entanglement? 1. Reality starts as a quantum state (not spacetime) In EWOG, the universe does **not** begin with space and time. It begins with a single quantum state: |Ψ⟩ ∈ No coordinates No distances No clocks Only quantum information. ➡ Spacetime appears later. 2. Geometry is quantum, not classical Spacetime is not a background — it is made of operators: ĝ_μν, R̂_μν, R̂ What we experience as classical spacetime is just the **average**: g_μν = ⟨ ĝ_μν ⟩ Intuition: Spacetime is a *shadow* cast by quantum entanglement. 3.

Cancer stem cell plasticity and tumor hierarchy👇
✅Hierarchical tumor organization Tumors are organized in a hierarchical manner, with cancer stem cells (CSCs) positioned at the apex. CSCs possess long-term self-renewal capacity and generate diverse progeny, sustaining tumor growth and cellular heterogeneity.
✅Self-renewal and differentiation CSCs can undergo self-renewal to maintain the stem cell pool or differentiate into multiple cancer cell lineages. These differentiated cells form the bulk of the tumor and display varying functional and phenotypic states.
✅Cell plasticity and dedifferentiation Differentiated cancer cells are not irreversibly committed. Through cellular plasticity, they can dedifferentiate back into CSCs, often via processes such as epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), restoring stem-like properties.
✅Interconversion of CSC states Distinct CSC subpopulations can transition between different stemness states. This dynamic interconversion enhances tumor adaptability and contributes to therapy resistance and disease progression.
✅Biological and clinical relevance The combination of hierarchy and plasticity allows tumors to regenerate after treatment and maintain intratumoral diversity. Targeting both CSCs and the mechanisms that enable plasticity is therefore critical for effective cancer therapy.
💡
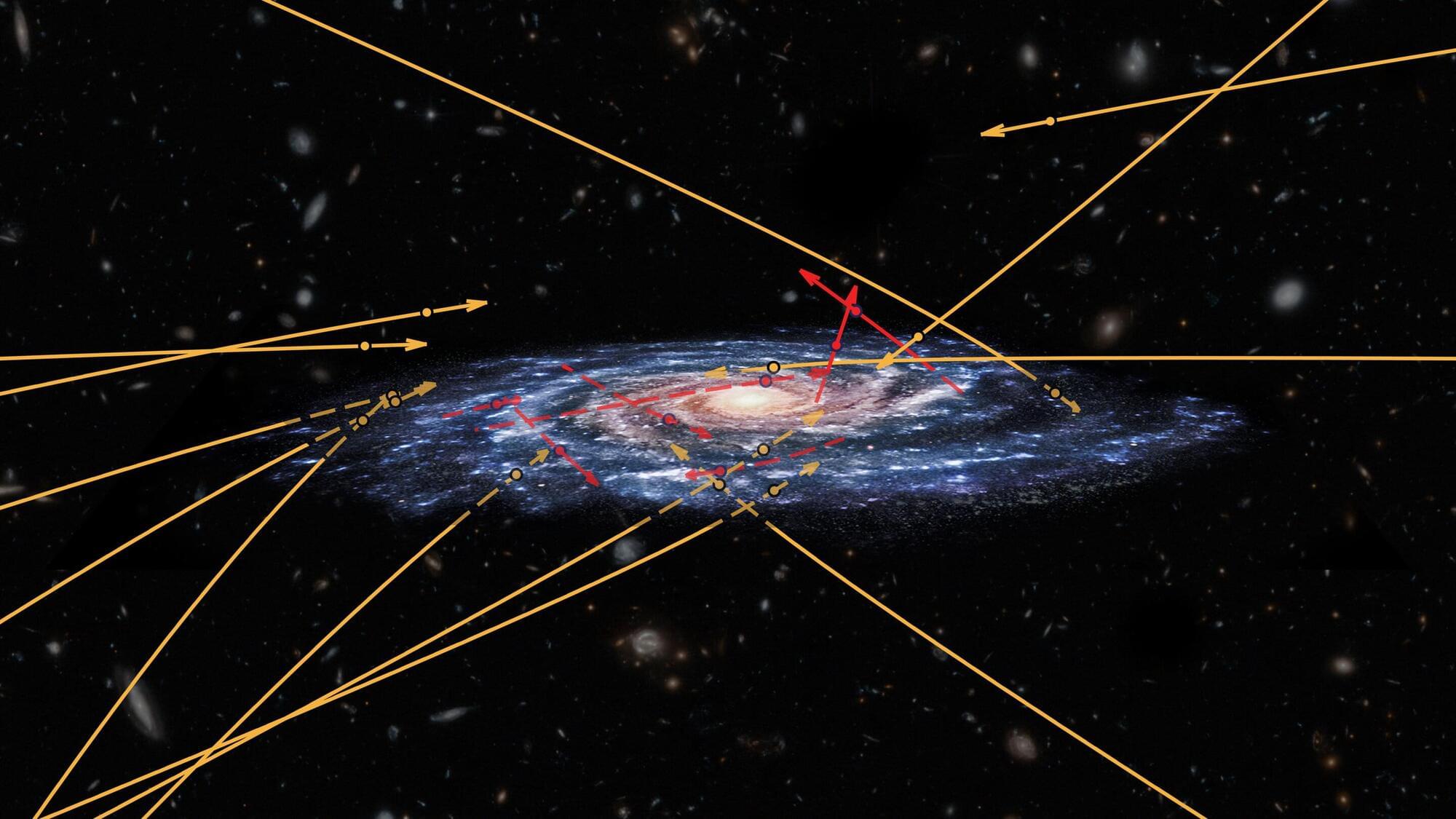
Hypervelocity stars have, since the 1920s, been an important tool that allows astronomers to study the properties of the Milky Way galaxy, such as its gravitational potential and the distribution of matter. Now astronomers from China have made a large-volume search for hypervelocity stars by utilizing a special class of stars known for their distinct, regular, predictable pulsation behavior that makes them useful as distance indicators.
Their research is published in The Astrophysical Journal.
The escape velocity of any planet, star or galaxy is the velocity required for a mass, leaving the object’s surface, to coast completely and exactly out of the planet’s gravitational well, going to infinity. Earth’s escape velocity is 11.2 kilometers per second (km/s).