New research explores the mechanics behind the “false vacuum” theory, the idea that the universe is in a state of only temporary stability.





The quest to halt or reverse aging has long captivated human imagination. By 2032, could artificial intelligence (AI) make this aspiration a reality? Futurist Ray Kurzweil, renowned for his forward-thinking predictions, believes so. He envisions a future where AI plays a pivotal role in achieving “longevity escape velocity,” a state where life expectancy increases more than one year per year, effectively outpacing aging.


A study from Nagoya University.
Nagoya University, sometimes abbreviated as NU, is a Japanese national research university located in Chikusa-ku, Nagoya. It was the seventh Imperial University in Japan, one of the first five Designated National University and selected as a Top Type university of Top Global University Project by the Japanese government. It is one of the highest ranked higher education institutions in Japan.
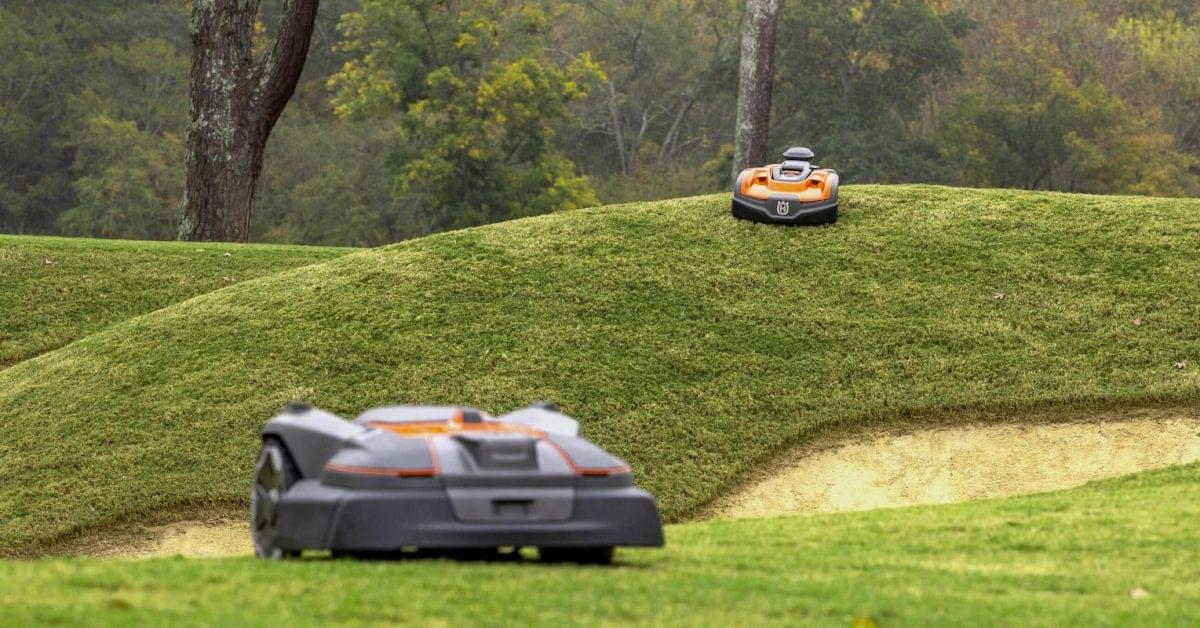

They may look like beefed up Roombas, but the new 535 and AWD 580L EPOS robotic lawn mowers from Husqvarna leverage the brand’s decades of outdoor power products expertise to deliver commercial-grade capability in an innovative package.
Husqvarna dropped the two new commercial robot lawnmowers at the GCSAA Conference and Trade Show in San Diego this weekend with claims that the new 580L EPOS model, specifically, “furthers Husqvarna’s commitment to providing autonomous solutions and revolutionizing turf management for golf courses, sports fields, and facility maintenance.”
If you’re wondering about that “EPOS” acronym, it stands for Exact Positioning Operating System. It’s a Husqvarna-developed, satellite-based positioning system that enables the robot mowers to work within virtual boundaries instead of relying on physical boundary wires like other (significantly less expensive) models.
Year 2016 Symmetrical music creates symmetry in water crystals and also water may also be a computer because it can be used as a computer.
Is water ALIVE?! Here are some mysterious ways water react to our words, pictures, music and even thoughts.
►Subscribe for more videos! http://bit.ly/1Mo6FxX
►Check out my food channel! http://bit.ly/1hsxh41
Get early access to NEXT week’s video on Vessel:
http://vessel.com/beyondscience.
★↓FOLLOW ME ON SOCIAL MEDIA!↓★
Year 2024 face_with_colon_three
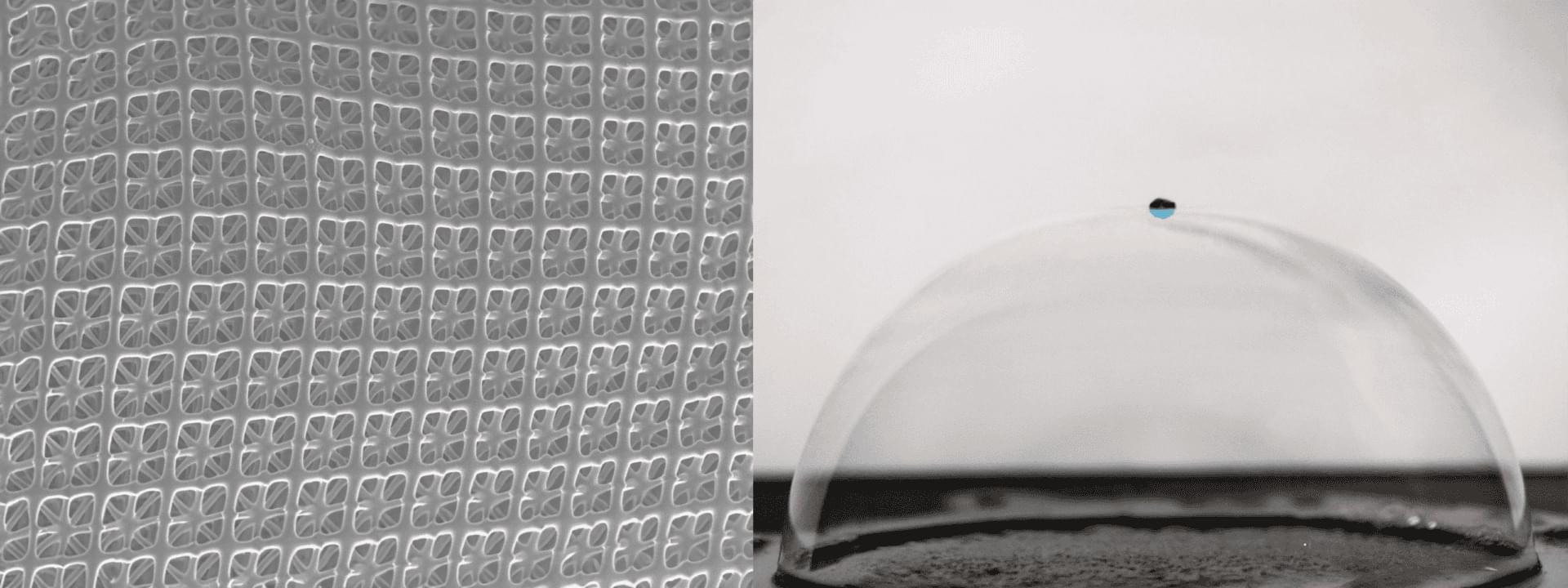
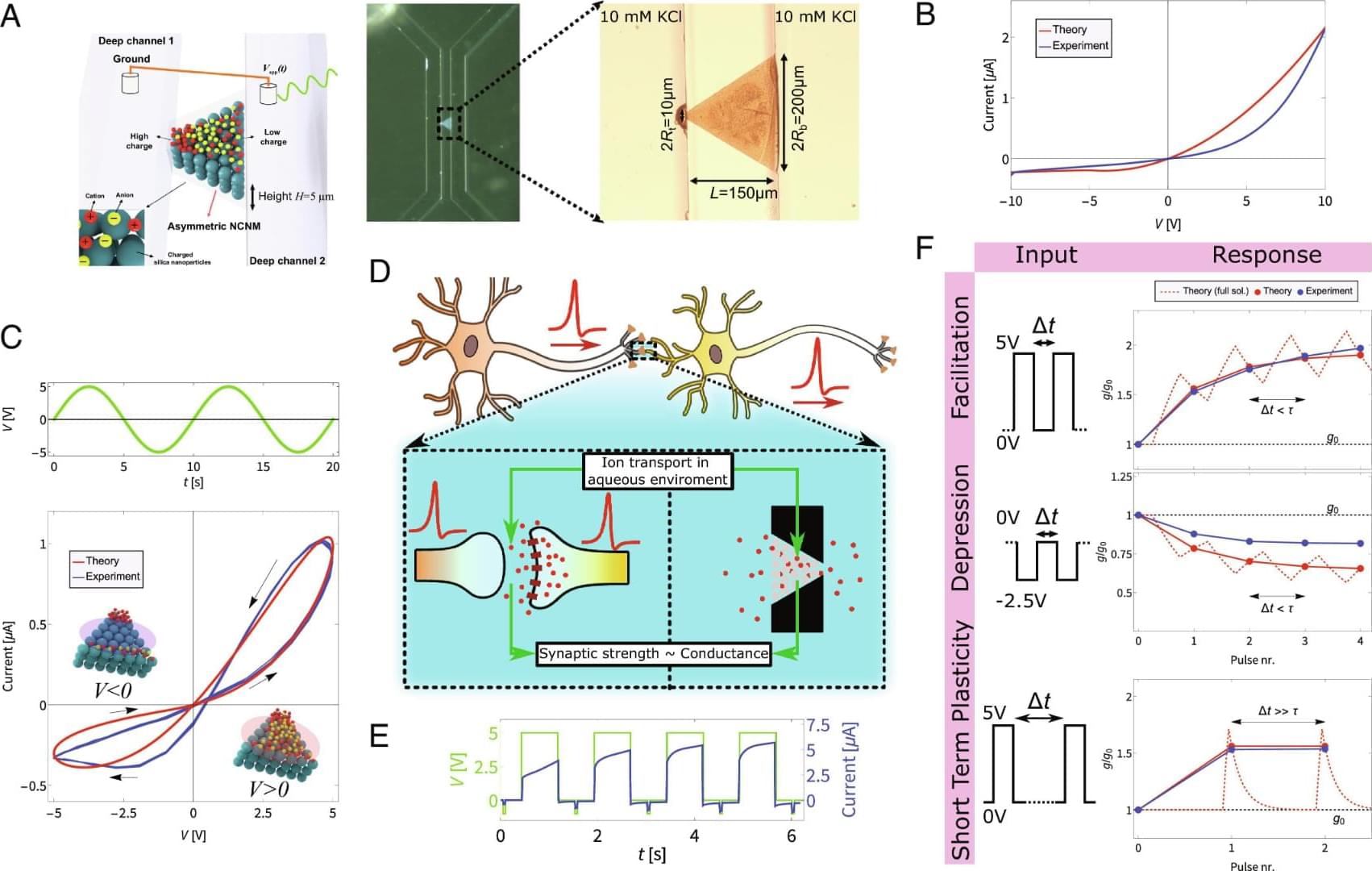
Our memristor is inspired and supported by a comprehensive theory directly derived from the underlying physical equations of diffusive and electric continuum ion transport. We experimentally quantitatively verified the predictions of our theory on multiple occasions, among which the specific and surprising prediction that the memory retention time of the channel depends on the channel diffusion time, despite the channel being constantly voltage-driven. The theory exclusively relies on physical parameters, such as channel dimensions and ion concentrations, and enabled streamlined experimentation by pinpointing the relevant signal timescales, signal voltages, and suitable reservoir computing protocol. Additionally, we identify an inhomogeneous charge density as the key ingredient for iontronic channels to exhibit current rectification (provided they are well described by slab-averaged PNP equations). Consequently, our theory paves the way for targeted advancements in iontronic circuits and facilitates efficient exploration of their diverse applications.
For future prospects, a next step is the integration of multiple devices, where the flexible fabrication methods do offer a clear path toward circuits that couple multiple channels. Additionally, optimizing the device to exhibit strong conductance modulation for lower voltages would be of interest to bring electric potentials found in nature into the scope of possible inputs and reduce the energy consumption for conductance modulation. From a theoretical perspective, the understanding of the (origin of the) inhomogeneous space charge and the surface conductance is still somewhat limited. These contain (physical) parameters that are now partially chosen from a reasonable physical regime to yield good agreement, but do not directly follow from underlying physical equations. We also assume that the inhomogeneous ionic space charge distribution is constant, while it might well be voltage-dependent.