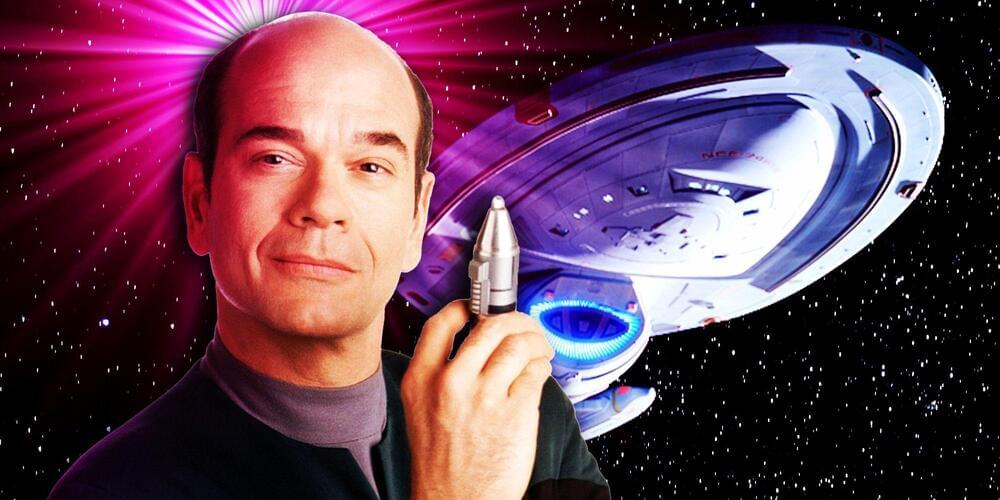
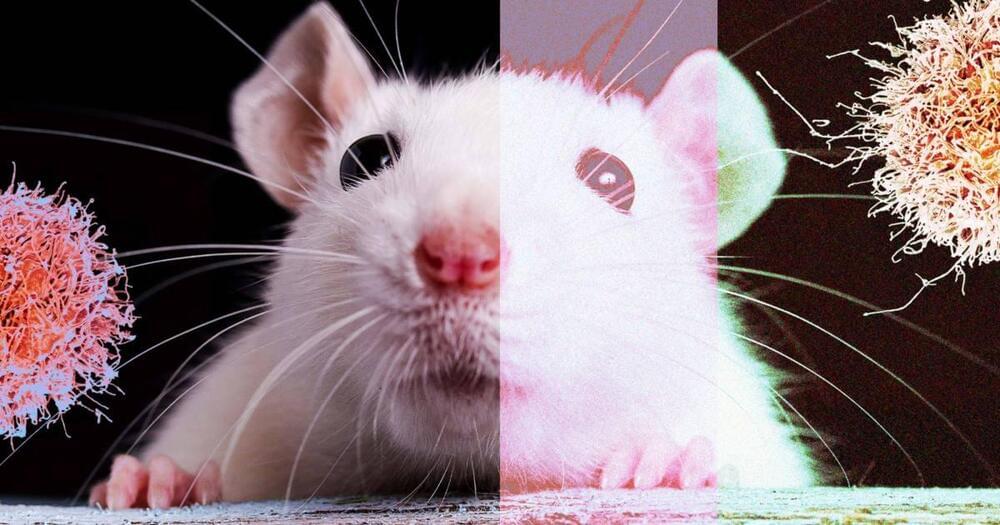
An antibody treatment designed to revitalize an aging immune system delivers “surprising” results in elderly mice.




New data on the rotation around both long and short axes of plastic strands may help researchers track and remove microplastics that pollute the ocean.
Pollution from tiny plastic particles (microplastics) increasingly threatens ocean and river ecosystems, and potentially human health, but researchers don’t have a good understanding of how and where these pollutants are transported by flowing waters. Now a research team has observed 1.2-mm-long, 10-µm-wide strands—similar to the most common type of microplastic particles—as they moved in turbulent flows mimicking those in natural environments [1]. The experiments reveal new aspects of their motion, including the rates at which fibers spin around their long axes. The researchers hope that their results will help engineers design structures that can concentrate plastics for easier removal.
Scientists currently have a limited understanding of where microplastics tend to accumulate in the environment, says fluid dynamics expert Alfredo Soldati of the Vienna University of Technology. Where plastics gather depends on natural fluid flows and on the nature of the plastic objects themselves.
On cosmological scales, dark matter so dominates the gravitational behavior of the Universe that, to first approximation, researchers can ignore the gravitational pull of visible matter when simulating the large-scale distribution of galaxies. Still, determining subtle yet important properties of the Universe, such as variations in the amount of dark energy, requires knowing the exact locations of the subatomic particles (baryons) that make up the Universe’s visible matter, as well as what these particles are doing and how they are interacting with dark matter. Now Tassia Ferreira of the University of Oxford, UK, and her collaborators have identified a statistical correlation between two observable features of the Universe that has the potential to reveal the extent of astronomers’ understanding of how baryons shape the large-scale structure of the cosmos [1].
The uncovered correlation is between variations across the sky of the amount of “cosmic shear” and the intensity of the diffuse background of cosmic x rays. Cosmic shear is the apparent warping of the shapes and positions of distant galaxies by the gravitational pulls of intervening clusters of galaxies and other large concentrations of matter. The x-ray background emanates mostly from hot, thin plasma held in the gravitational potentials of those same intervening structures.
Ferreira and her collaborators found that the cosmic shear and the x-ray background are strongly correlated. This correlation is unsurprising given that both features are manifestations of the same dark-matter structures. But the researchers also found that the baryons’ locations influenced how well various physical models reproduced the correlation. One important factor is the amount of plasma (which is made of baryons) that supermassive black holes expel into intergalactic space.

Our brain measures time by counting experiences, not by following a strict chronological order.
A new study by a team of UNLV researchers suggests that there’s a lot of truth to the trope “time flies when you’re having fun.”
In their study, recently published in the journal Current Biology, the researchers discovered that our perception of time is based on the number of experiences we have, not on an internal clock. Additionally, they found that increasing speed or output during an activity appears to affect how our brains perceive time.

Researchers have been delving into the concept of warp drives, theoretically allowing spaceships to surpass the speed of light, using principles from Einstein’s General Relativity.
Physicists have been exploring the theoretical possibility of spaceships driven by compressing the four-dimensional spacetime for decades. Although this so-called “warp drive” originates from the realm of science fiction, it is based on concrete descriptions in general relativity. A new study takes things a step further – simulating the gravitational waves such a drive might emit if it broke down.
Warp Drive Research

A new quantum sensor developed by researchers from Korea and Germany can measure magnetic fields at the atomic scale with high precision. This technology uses a single molecule for detection, offering superior resolution and the potential for significant advancements in quantum materials and molecular systems analysis.
In a scientific breakthrough, an international research team from Korea’s IBS Center for Quantum Nanoscience (QNS) and Germany’s Forschungszentrum Jülich developed a quantum sensor capable of detecting minute magnetic fields at the atomic length scale. This pioneering work realizes a long-held dream of scientists: an MRI-like tool for quantum materials.
“You have to be small to see small.” —