A 2024 study is facing skepticism, so the people behind that study are diving back underwater.
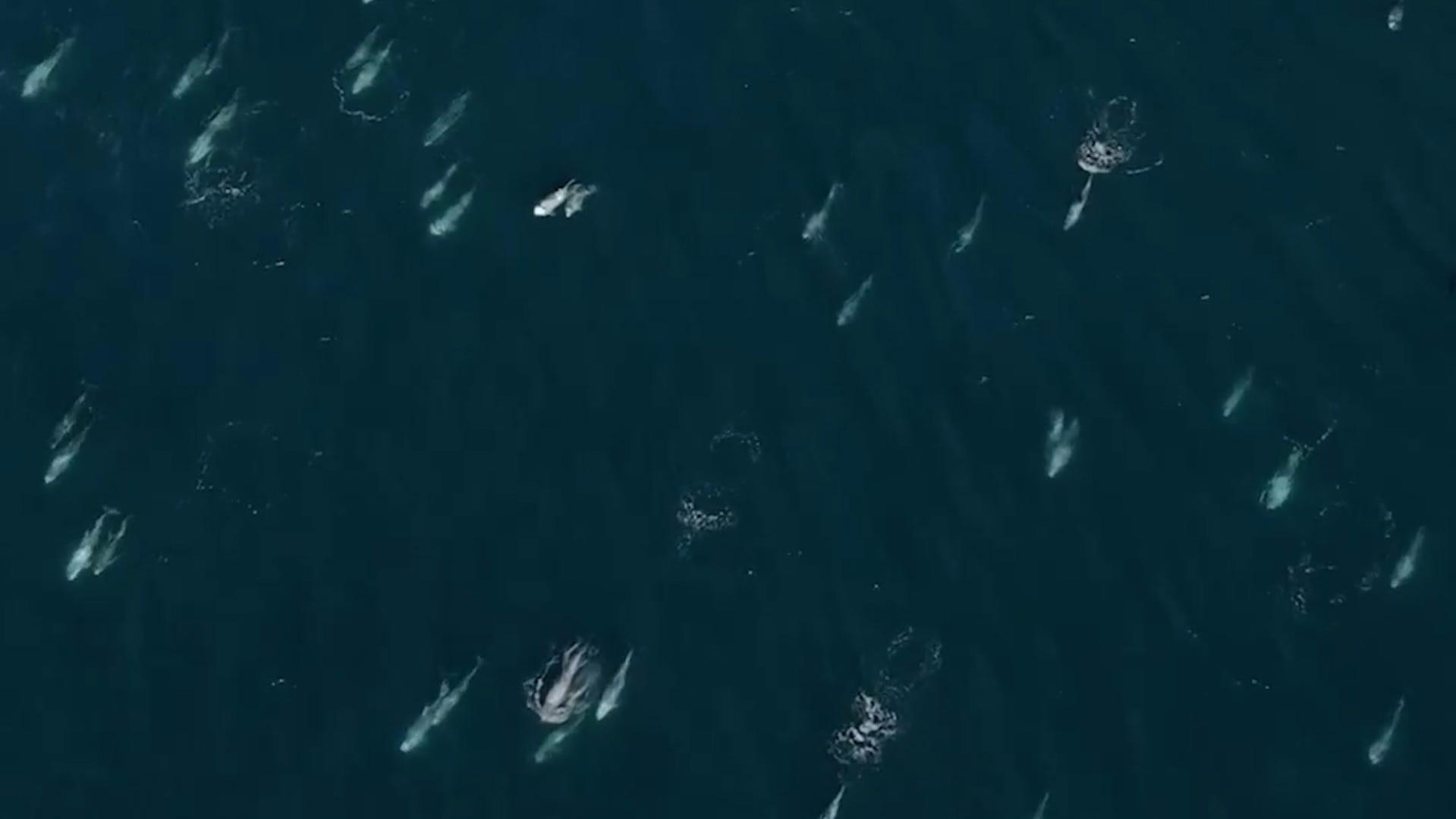




Monterey Bay Whale Watch said on Facebook that their scouting boat spotted the dolphins when it went out to “perform a survey on the coast south of Monterey,” about a 120 miles southwest of San Francisco.
The tour agency said its team counted 33 gray whales, 1,500-plus Risso’s dolphins and three northern right whale dolphins as they undertook the 60-mile roundtrip from Monterey to Point Sur.
Our psychological profiles provide clues to our future risk and severity of cognitive decline that may one day inform tailored prevention strategies, a new study suggests.
“The aim was to elucidate how various combinations of psychological characteristics are related to mental, cognitive and brain health,” explains University of Barcelona psychologist David Bartrés-Faz.
“To date, psychological risk and protective factors have been examined almost exclusively independently: this approach is limiting, as psychological characteristics do not exist in isolation.”
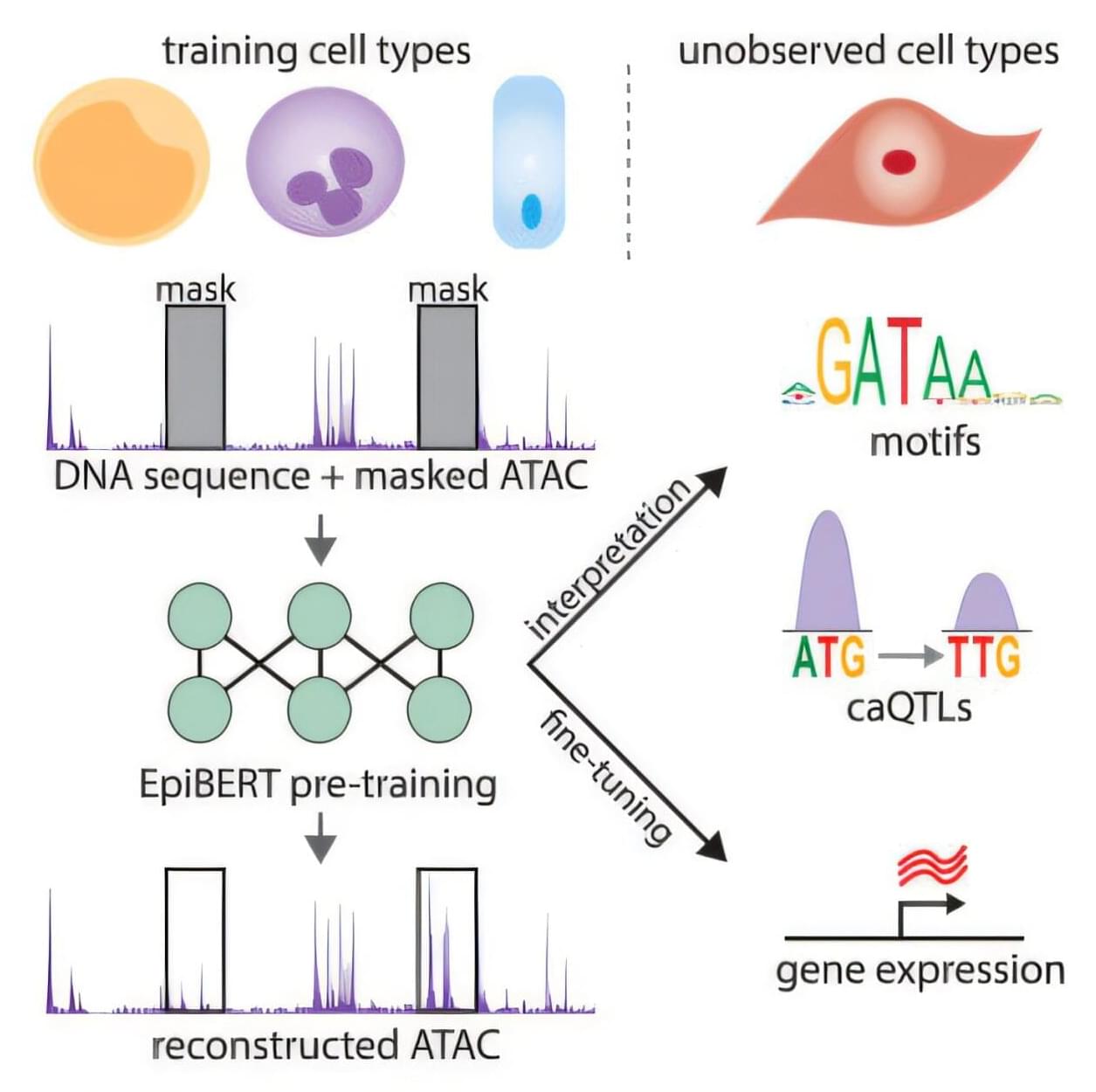
A team of investigators from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Google, and Columbia University have created an artificial intelligence model that can predict which genes are expressed in any type of human cell. The model, called EpiBERT, was inspired by BERT, a deep learning model designed to understand and generate human-like language.
The work appears in Cell Genomics.
Every cell in the body has the same genome sequence, so the difference between two types of cells is not the genes in the genome, but which genes are turned on, when, and how many. Approximately 20% of the genome codes for regulatory elements determine which genes are turned on, but very little is known about where those codes are in the genome, what their instructions look like, or how mutations affect function in a cell.


Shoeb Javed is chief product officer at iGrafx.
Navigating the intricacies of compliance and risk management can seem overwhelming for businesses, especially those operating in heavily regulated industries. The rules are complex and the stakes are high, and the old ways of managing compliance aren’t enough anymore. By using smart tools and clear processes, businesses can handle tasks more efficiently, reduce risks and make audits less stressful.
Many organizations face a daunting array of compliance requirements, both external and internal. Regulatory demands vary across industries such as financial services, healthcare, manufacturing, retail and technology. Businesses may also have to contend with regulations that differ by country and even by region.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
