Widely utilized across various industries such as chemistry, agriculture, and military, this technology relies on strategies like dispersive optics and narrow-band light filters.
However, limitations exist in these approaches. Additionally, the fabrication of large-scale InGaAs detector arrays poses challenges, necessitating the development of new experimental methods and algorithms to advance infrared hyperspectral imaging technology in terms of miniaturization and cost-effectiveness.
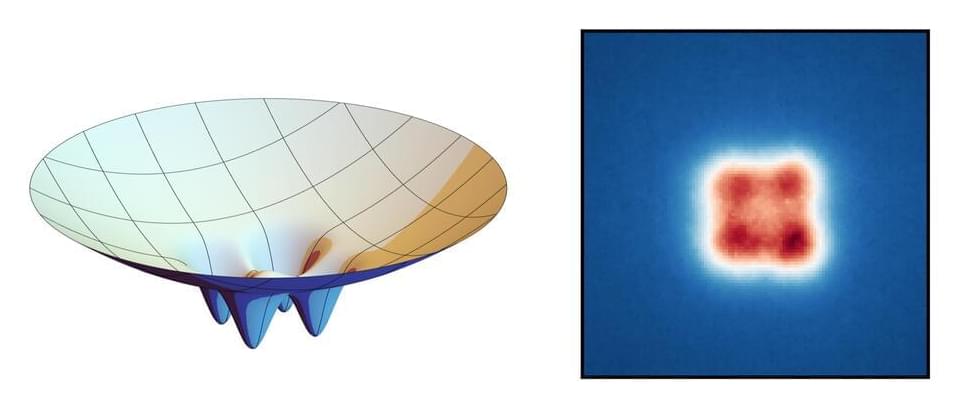
In a paper published in Light Science & Applications, a team led by Professor Baoqing Sun and Yuan Gao from Shandong University introduce a novel method for encoding near-infrared spectral and spatial data.