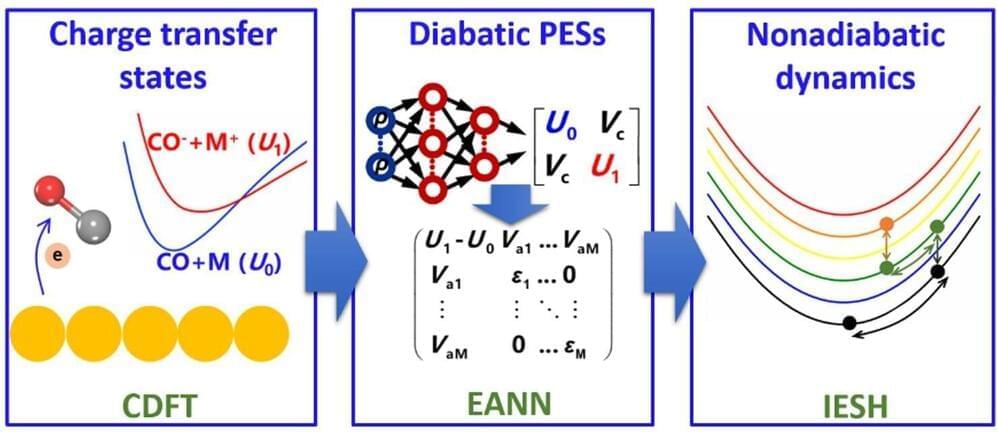
A research team has proposed a novel approach to accurately describe electron transfer mediated nonadiabatic dynamics of molecules at metal surfaces. Their works were published in Physical Review Letters.


PRESS RELEASE — IQM Quantum Computers (IQM), a global leader in designing, building, and selling superconducting quantum computers, today announced that it has reached a milestone of producing 30 full-stack quantum computers in its manufacturing facility in Finland.
In addition, IQM has also completed the delivery and installation of six full-stack quantum computers to customers worldwide. IQM’s previously announced customers include VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, Leibniz Supercomputing Centre (LRZ) in Germany as well as Forschungszentrum Jülich in Germany.
With increasing demand for on-premises quantum computers globally, IQM Quantum Computers Co-CEO Mikko Välimäki highlighted the significance of the manufacturing milestone, stating: “One of the key bottlenecks in quantum computer adoption has been prohibitively high prices. We are the first quantum computer manufacturer with the goal of taking quantum computers to a much wider market with industrialized manufacturing capabilities that help drive the prices lower. Looking ahead, our production line has the capacity to deliver up to 20 full-stack quantum computers a year.”

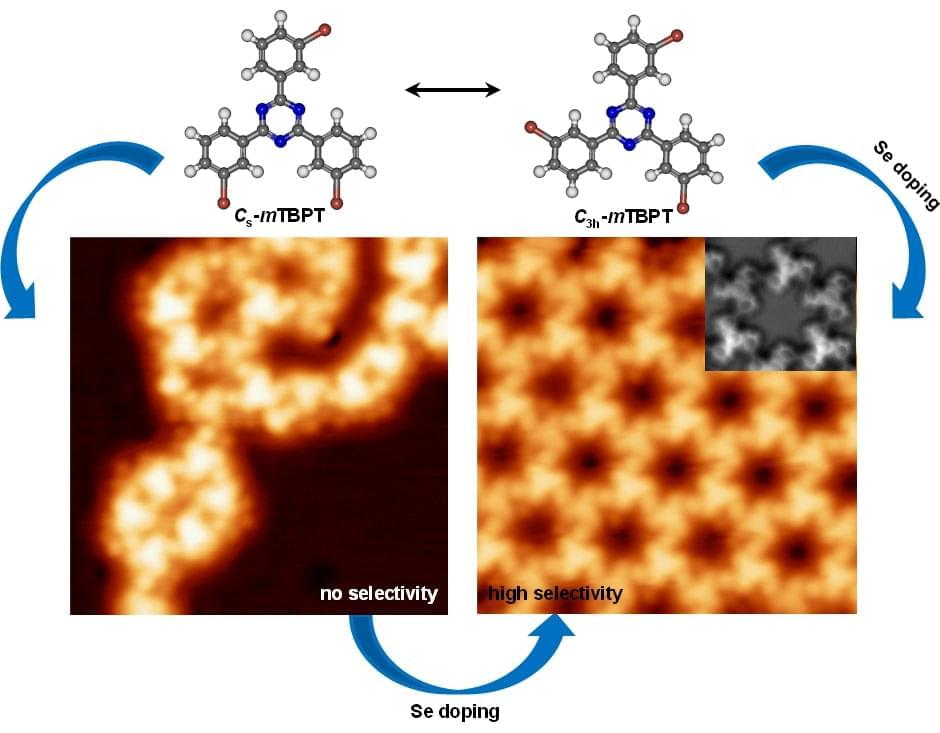
Physicists from the National University of Singapore (NUS) have achieved controlled conformational arrangements in nanostructures using a flexible precursor and selenium doping, enhancing material properties and structural homogeneity. Their method advances on-surface synthesis for the design and development of engineered nanomaterials.
On-surface synthesis has been extensively investigated over the past decades for its ability to create diverse nanostructures. Various complex nanostructures have been achieved through the smart design of precursors, choice of substrates and precise control of experimental parameters such as molecular concentration, electrical stimulation and thermal treatment.
Among these methods, the Ullmann coupling is notable for efficiently linking precursors through dehalogenation and covalent bonding. While most research has focused on conformationally rigid precursors, exploring conformationally flexible precursors offers significant potential for developing complex functional nanomaterials with engineered structures and properties.
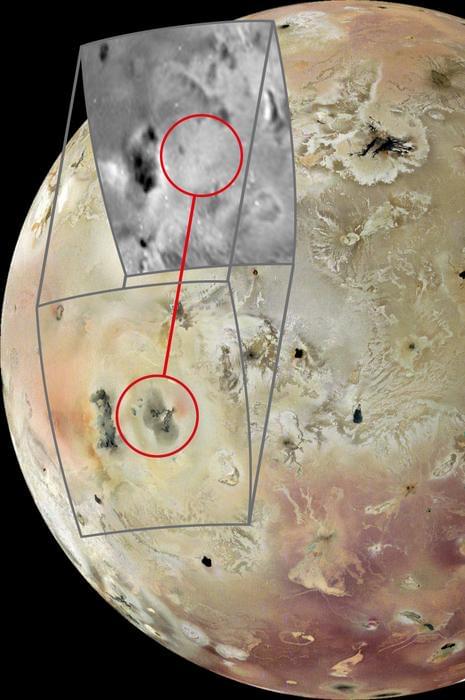
Jupiter’s moon, Io, is the most volcanically active planetary body in the entire solar system as it boasts hundreds of active volcanoes. This number continues to grow as recent study at the Europlanet Science Congress 2024 meeting showed a new active volcano on the small moon taken by NASA’s JunoCam after the spacecraft conducted the first up-close images of Io in more than a quarter of a century.
Not only have Io’s volcanoes been observed to shoot volcanic material hundreds of miles into space, but its lava fields also spread almost as far across its surface due to the much smaller gravity. For example, the volcanic deposits from this new image were observed to encompass an area spanning 180 kilometers by 180 kilometers (112 miles by 112 miles).
“Our recent JunoCam images show many changes on Io, including this large, complicated volcanic feature that appears to have formed from nothing since 1997,” said Dr. Michael Ravine, who is an Advanced Projects Manager at Malin Space Science Systems, Inc, which designed, developed and operates JunoCam for the NASA Juno Project, and is lead author of the study.
Gravity is no longer a mystery to physicists—at least when it comes to large distances. Thanks to science, we can calculate the orbits of planets, predict tides, and send rockets into space with precision. However, the theoretical description of gravity reaches its limits at the level of the smallest particles, the so-called quantum level.


One of the most exciting features in Bluetooth 6.0 is called “Channel Sounding,” which makes it possible to locate lost devices and/or other objects with much more precision than previous versions of Bluetooth. In fact, you’ll be able to locate them down to the centimeter.
And this device detection feature isn’t just for close-range uses — it will be able to work across long distances and be just as effective. If it lives up to the hype, this improvement could significantly improve devices like Apple’s AirTag and apps like Google’s Find My Device.
Bluetooth 6.0’s Channel Sounding could even find its way into more types of devices that need protection against loss, such as remote controls (which somehow tend to disappear without a trace).

Why do we study Mars? What missions have been there? How do we plan to explore this intriguing world in the future? Quench your curiosity with this educational infographic on the Red Planet!
For thousands of years, Mars aka the Red Planet, has fascinated skywatchers from countless civilizations and cultures, leading some to speculate that it was a lush world full of life. However, the exploration of Mars has proven to be quite the contrast, instead exhibiting a dry and inhabitable world utterly devoid of life. Despite this, scientists and engineers from around the world have learned quite a bit from our planetary neighbor with the countless robotic explorers sent there, including flybys, orbiters, landers, and rovers.
Through this, we have gained incredible insight into the ancient history of Mars and whether life might have existed there long ago. In the future, as humanity looks to return the first samples from Mars and land humans on the Red Planet’s surface, we will continue to learn more about this fascinating world and whether it could have, or currently, hosts life as we know it.