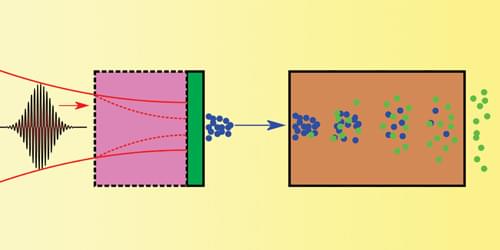
The color centers of diamond are the focus of an increasing number of research studies, due to their potential for developing quantum technologies. Some works have particularly explored the use of negatively-charged group-IV diamond defects, which exhibit an efficient spin-photon interface, as the nodes of quantum networks.
Researchers at Ulm University in Germany recently leveraged a Germanium vacancy (GeV) center in diamond to realize a quantum memory. The resulting quantum memory, presented in a Physical Review Letters paper, was found to exhibit a promising coherence time of more than 20 ms.
“Our research group’s primary focus is the exploration of diamond color centers for quantum applications,” Katharina Senkalla, co-author of the paper, told Phys.org. “The most popular defect of diamond so far has been the nitrogen-vacancy center, but, recently, other color centers have also become a focus of research. These consist of an element from the IV column of the periodic table—Si, Ge, Sn or Pb, and a lattice vacancy (i.e., missing next-neighbor carbon atom).”
 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)