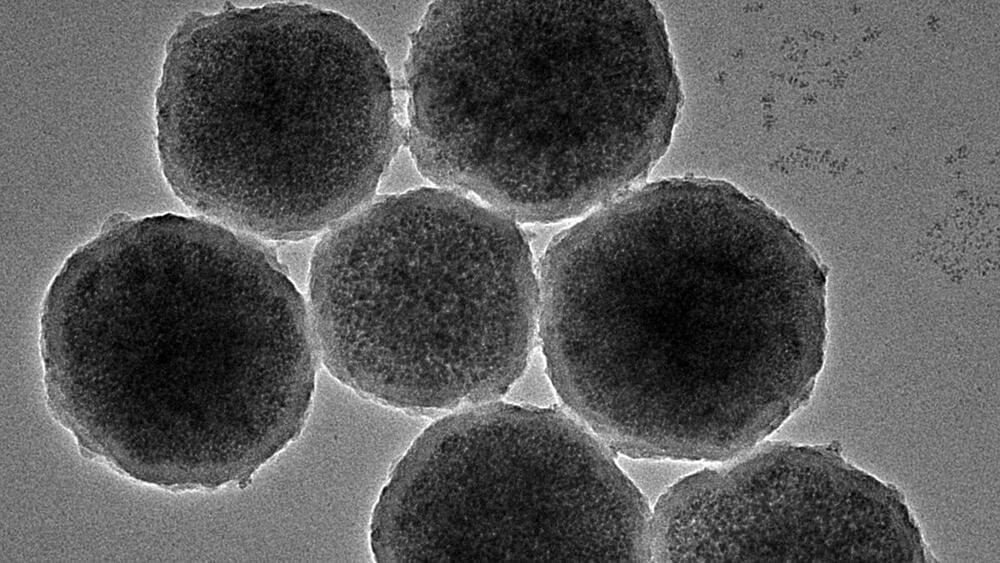
Tiny robots much smaller than blood cells could deliver clot-forming drugs where they’re needed most, a study in rabbits suggests. The tech has yet to be tested in humans.

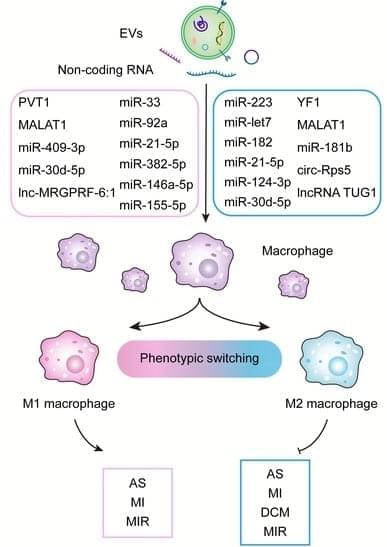
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) or exosomes are nanosized extracellular particles that contain proteins, DNA, non-coding RNA (ncRNA) and other molecules, which are widely present in biofluids throughout the body. As a key mediator of intercellular communication, EVs transfer their cargoes to target cells and activate signaling transduction. Increasing evidence shows that ncRNA is involved in a variety of pathological and physiological processes through various pathways, particularly the inflammatory response. Macrophage, one of the body’s “gatekeepers”, plays a crucial role in inflammatory reactions. Generally, macrophages can be classified as pro-inflammatory type (M1) or anti-inflammatory type (M2) upon their phenotypes, a phenomenon termed macrophage polarization.

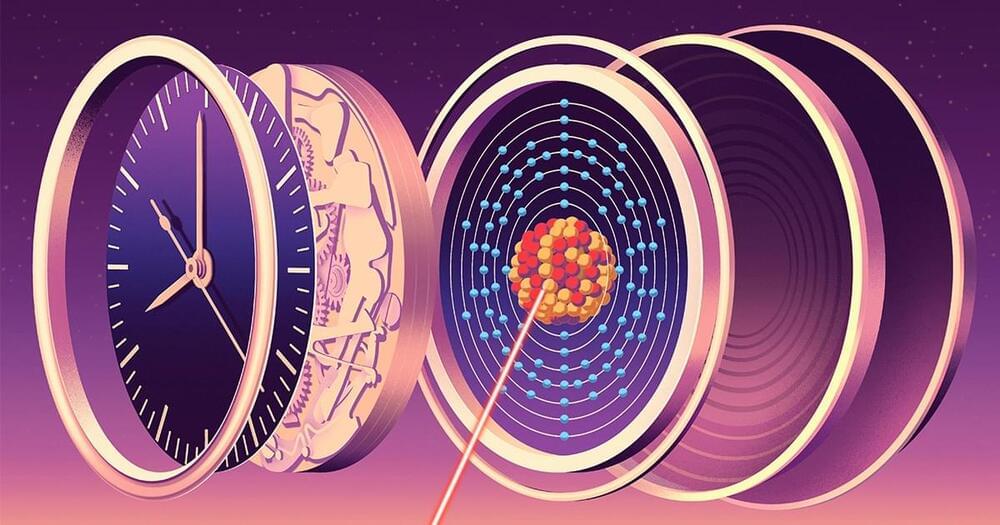
Proposed experiments will search for signs that spacetime is quantum and can exist in a superposition of multiple shapes at once.
By Nick Huggett & Carlo Rovelli
There is a glaring gap in our knowledge of the physical world: none of our well-established theories describe gravity’s quantum nature. Yet physicists expect that this quantum nature is essential for explaining extreme situations such as the very early universe and the deep interior of black holes. The need to understand it is called the problem of “quantum gravity.”

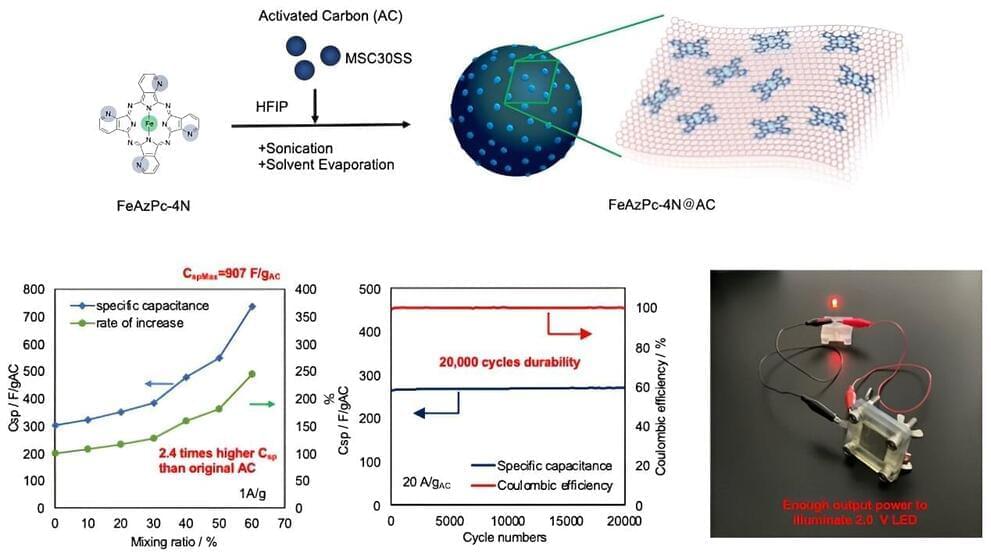
Researchers at Tohoku University have successfully increased the capacity, lifetime durability, and cost-effectiveness of a capacitor in their pursuit of a more power-efficient future. The research is published in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
A capacitor is a device used as part of a circuit that can store and release energy, just like a battery. What makes a capacitor different from a battery is that it takes much less time to charge. For example, your cellphone battery will power your phone instantly, but charging that battery back up to 100% when it dies is far from instantaneous.
While this makes capacitors sound like the superior choice, they have some big drawbacks that need to be overcome. First, their capacity is much smaller than batteries, so they cannot store large amounts of energy at once. Second, they can be quite expensive.
Today, SpaceX took a short break from Starlink flights and launched a national security mission. Who made these satellites? SpaceX with some sensors from Northrop Grumman. It is amazing how many of the satellites that SpaceX launches are made by SpaceX!
It would be hard to make reusable rockets work if you didn’t have a ton of payloads to launch.
SpaceX launched a Falcon 9 rocket with an undisclosed number of satellites on behalf of the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO). The spacecraft, which are believed to be Starshield satellites, make up the third batch of what the NRO calls its “proliferated architecture.”

Some of our closest invertebrate cousins, like this Acorn worm, have the ability to perfectly regenerate any part of their body that’s cut off — including the head and nervous system. Humans have most of the same genes, so scientists are trying to work out whether human regeneration is possible, too.
Regeneration – now that’d be a nice superpower to have. Injure an arm? Chop it off and wait for it to grow back. Dicky knee? Ingrown toenail? Lop off your leg and get two for one!
It sounds ridiculous, but there’s a growing number of scientists that believe body part regeneration is not only possible, but achievable in humans. After all, not only are there plenty of animals that can do it, we can do it ourselves for our skin, nails, and bits of other organs.