Albedo Space wants to launch satellites that can track the movements of and even image individual people. Obviously, privacy is an issue.
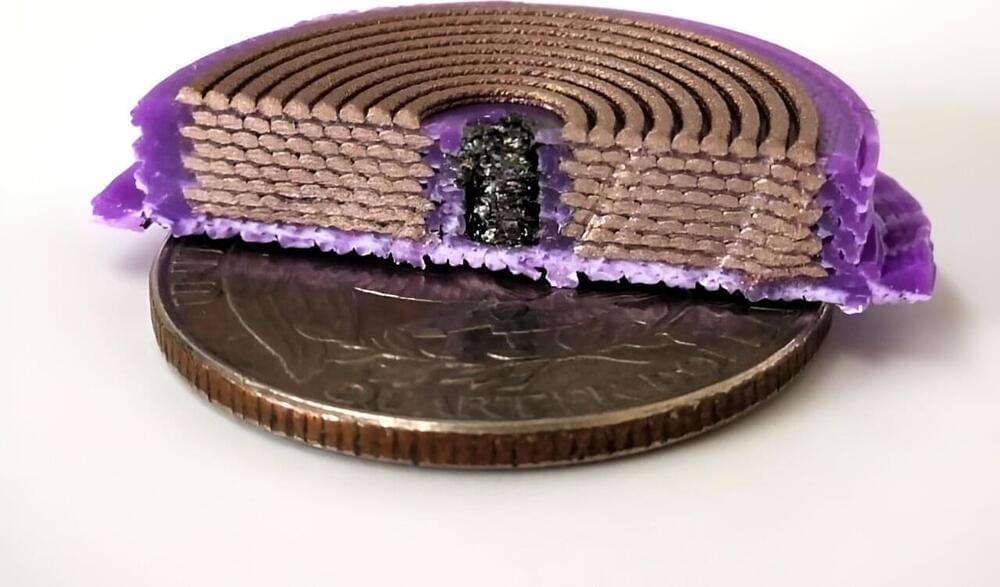
Imagine being able to build an entire dialysis machine using nothing more than a 3D printer.
This could not only reduce costs and eliminate manufacturing waste, but since this machine could be produced outside a factory, people with limited resources or those who live in remote areas may be able to access this medical device more easily.
While multiple hurdles must be overcome to develop electronic devices that are entirely 3D printed, a team at MIT has taken an important step in this direction by demonstrating fully 3D-printed, three-dimensional solenoids.
Scientists working in the Amazon rainforest have discovered a new species of snake, rumored to be the biggest in the world.
A team from the University of Queensland traveled to the Ecuadorian Amazon to search for the previously undocumented northern green anaconda (Eunectes akayima), following an invitation from the Waorani people to observe anacondas “rumoured to be the largest in existence,” according to the scientists.
The team joined the hunters on a 10-day expedition to the Bameno region of Baihuaeri Waorani Territory, before paddling down the river system to “find several anacondas lurking in the shallows, lying in wait for prey,” Professor Bryan Fry, a biologist from the University of Queensland, who led the team, said in a statement.
The agency says applicants must have a master’s degree with STEM qualifications and experience in the field, or a minimum of 1,000 hours piloting an aircraft or the requisite military experience. A bachelor of science degree in a STEM field also may be considered, NASA said.
“What we are looking for in this call is everyday civilians who are very astronaut-like to be research participants for us,” Bell said.
Compensation for participating in the mission is available, according to NASA, but an exact salary will be provided during the candidate screening process.
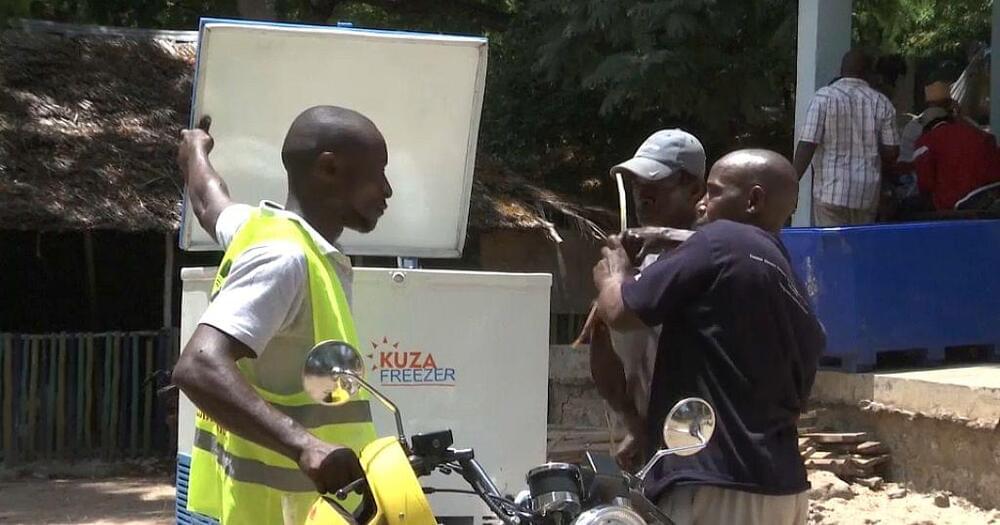
A Kenyan company is proving the saying: “one person’s waste is another person’s treasure,” still rings true.
On a February morning, a group of women on a Mombasa beach pick up plastic waste that will serve to build freezers.
The waste is sold to company Kuza Freezer where employees first break it down into pellets before moulding it into cold storage units.
NASA opened applications for people to live a paid year in its CHAPEA Mars simulation. The job requires an agreeable personality and STEM degree.
Cosmic dust—like dust on Earth—comprises groupings of molecules that have condensed and stuck together in a grain. But the exact nature of dust creation in the universe has long been a mystery. Now, however, an international team of astronomers from China, the United States, Chile, the United Kingdom, Spain, etc., has made a significant discovery by identifying a previously unknown source of dust in the universe: a Type 1a supernova interacting with gas from its surroundings.
The study was published in Nature Astronomy on Feb. 9, and was led by Prof. Wang Lingzhi from the South America Center for Astronomy of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Supernovae have been known to play a role in dust formation, and to date, dust formation has only been seen in core-collapse supernovae—the explosion of massive stars. Since core-collapse supernovae do not occur in elliptical galaxies, the nature of dust creation in such galaxies has remained elusive.
The landscape of artificial intelligence (AI) applications has traditionally been dominated by the use of resource-intensive servers centralized in industrialized nations. However, recent years have witnessed the emergence of small, energy-efficient devices for AI applications, a concept known as tiny machine learning (TinyML).
We’re most familiar with consumer-facing applications such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, but the limited cost and small size of such devices allow them to be deployed in the field. For example, the technology has been used to detect mosquito wingbeats and so help prevent the spread of malaria. It’s also been part of the development of low-power animal collars to support conservation efforts.
Small size, big impact Distinguished by their small size and low cost, TinyML devices operate within constraints reminiscent of the dawn of the personal-computer era—memory is measured in kilobytes and hardware can be had for as little as US$1. This is possible because TinyML doesn’t require a laptop computer or even a mobile phone. Instead, it can instead run on simple microcontrollers that power standard electronic components worldwide. In fact, given that there are already 250 billion microcontrollers deployed globally, devices that support TinyML are already available at scale.
Gemini 1.5 Pro includes a breakthrough in long-context understanding, handling up to 1 million tokens. It can also decipher the content of videos and describe what is happening in a scene.
In the world of large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, so-called “tokens” are the fundamental units of text that these models process, akin to words, punctuation, or parts of words in human language.
Physical effects of learning
Posted in robotics/AI
Interacting many-body physical systems ranging from neural networks in the brain to folding proteins to self-modifying electrical circuits can learn to perform diverse tasks. This learning, both in nature and in engineered systems, can occur through evolutionary selection or through dynamical rules that drive active learning from experience. Here, we show that learning in linear physical networks with weak input signals leaves architectural imprints on the Hessian of a physical system. Compared to a generic organization of the system components, (a) the effective physical dimension of the response to inputs decreases, (b) the response of physical degrees of freedom to random perturbations (or system “susceptibility’‘) increases, and © the low-eigenvalue eigenvectors of the Hessian align with the task.