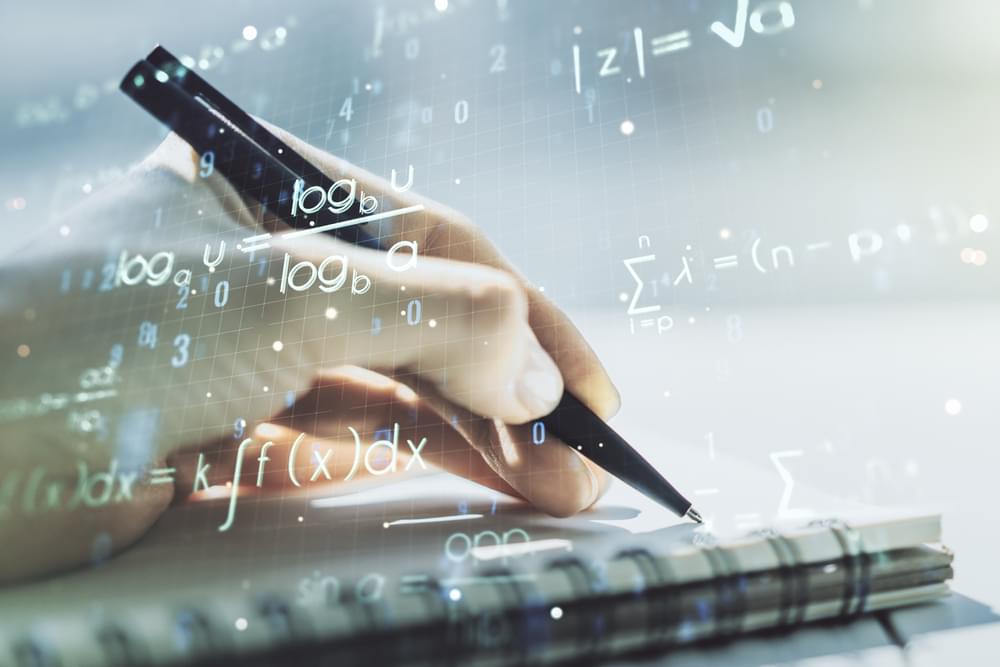
Confirmed: We are very bad at detecting deepfakes.
No se nos da bien detectar los vídeos e imágenes imitando la apariencia de una persona.


While 3D printing has exploded in popularity, many of the plastic materials these printers use to create objects cannot be easily recycled.
The automatically generated parameters can replace about half of the parameters that typically must be tuned by hand. In a series of test prints with unique materials, including several renewable materials, the researchers showed that their method can consistently produce viable parameters.
This research could help to reduce the environmental impact of additive manufacturing, which typically relies on nonrecyclable polymers and resins derived from fossil fuels.

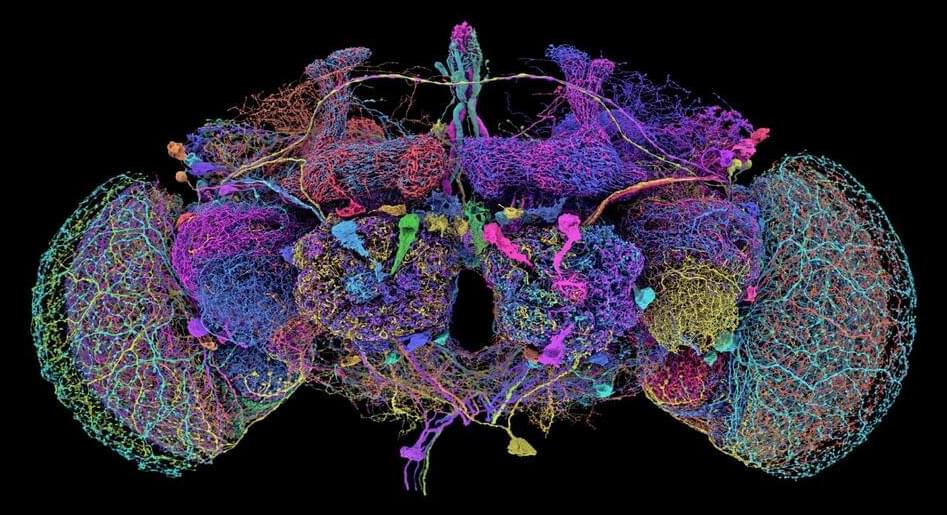
A Princeton-led team of scientists has created the first detailed connectome of an adult fruit fly brain, a complex network with almost 140,000 neurons. This significant step in neuroscience was featured in Nature and involved contributions from various global institutions, highlighting both the complexity of the fly’s brain and the potential insights it offers into human neurological diseases.
Groundbreaking Brain Mapping: A Connectome for the Adult Fruit Fly
Researchers led by Princeton University have constructed the first detailed neuron-by-neuron and synapse-by-synapse roadmap through the brain of an adult fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster), achieving a major milestone in brain research. This study is the flagship article in the October 2 special issue of Nature, which is devoted to the new fruit fly “connectome.”
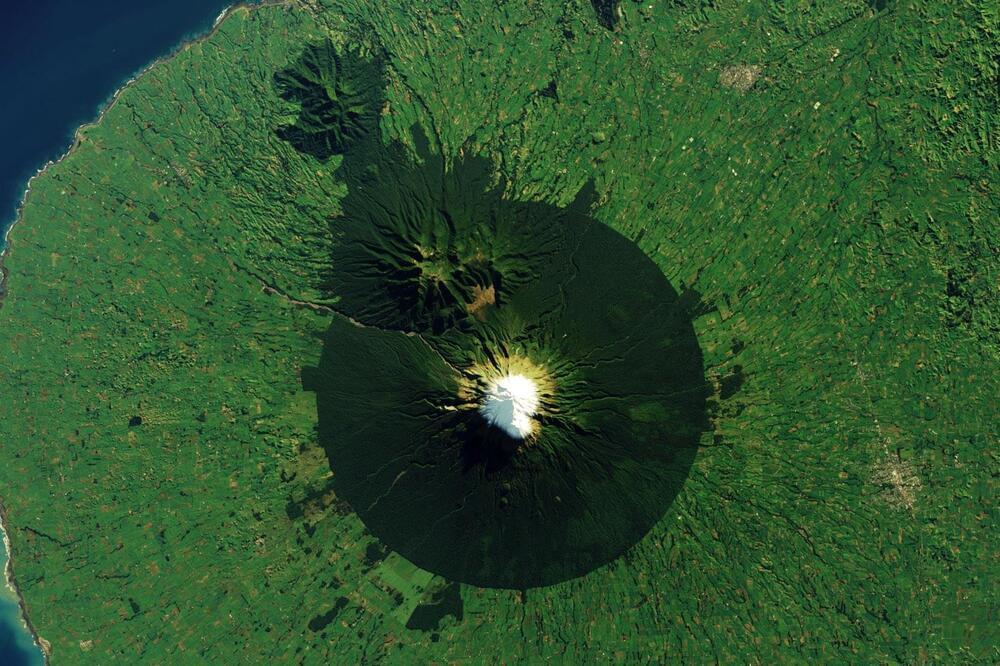

The precise geometry of the protected area encompassing an iconic New Zealand volcano, Mount Taranaki, is unmistakable from space, highlighting its status as New Zealand’s second national park.
This conical, often snow-capped volcano not only captivates with its natural beauty but also serves as a critical area for scientific research due to its unstable geological history and ongoing volcanic threats. In 2017, Mount Taranaki was granted the same legal rights as a person, emphasizing its profound cultural significance to the Indigenous Māori people.
Mount Taranaki

Masafumi Oizumi: Unsupervised alignment of qualia structures: Towards direct communication of experience.
Pre-ASSC (2024, June 30, Sun) Satellite Workshop Registration Form: Structural approaches to consciousness: Qualia Structure and Integrated Information Theory.
— program -
Day: June 30, 2024 (Sun)
Time: 9:00–17:00
Place: Ito Hall, Ito International Research Center, University of Tokyo.
Aims:
In this satellite symposium, hosted by the Qualia Structure, we will discuss the current state of the structural approaches to consciousness from empirical, computational and theoretical perspectives. The satellite will be open to any researcher (but registration is required) who are interested in the structural approach to consciousness. A one day event will be a mixture of lectures and poster presentations.
Registration: Free.
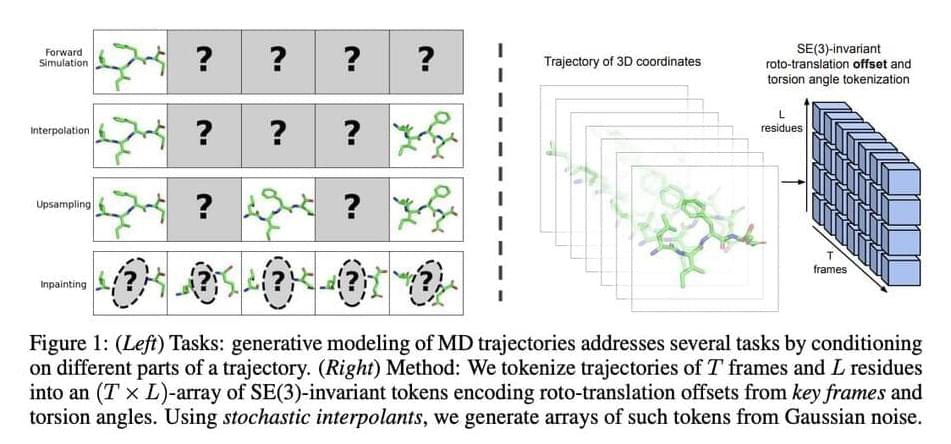
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a popular method for studying molecular systems and microscopic processes at the atomic level. However, MD simulations can be quite computationally expensive due to the intricate temporal and spatial resolutions needed. Due to the computing load, much research has been done on alternate techniques that can speed up simulation without sacrificing accuracy. Creating surrogate models based on deep learning is one such strategy that can effectively replace conventional MD simulations.
In recent research, a team of MIT researchers introduced the use of generative modeling to simulate molecular motions. This framework eliminates the need to compute the molecular forces at each step by using machine learning models that are trained on data obtained by MD simulations to provide believable molecular paths. These generative models can function as adaptable multi-task surrogate models, able to carry out multiple crucial tasks for which MD simulations are generally employed.
These generative models can be trained for a variety of tasks by carefully choosing and conditioning on specific frames of a molecule trajectory. These tasks include the following.
