Scientists and space explorers have been on the hunt to determine where and how much ice is present on the Moon. Water ice would be an important resource at a future lunar base, as it could be used to support humans or be broken down to hydrogen and oxygen, key components of rocket fuel. University of Hawai’i at Manoa researchers are using two innovative approaches to advance the search for ice on the Moon.
ShadowCam scouts for surface ice.
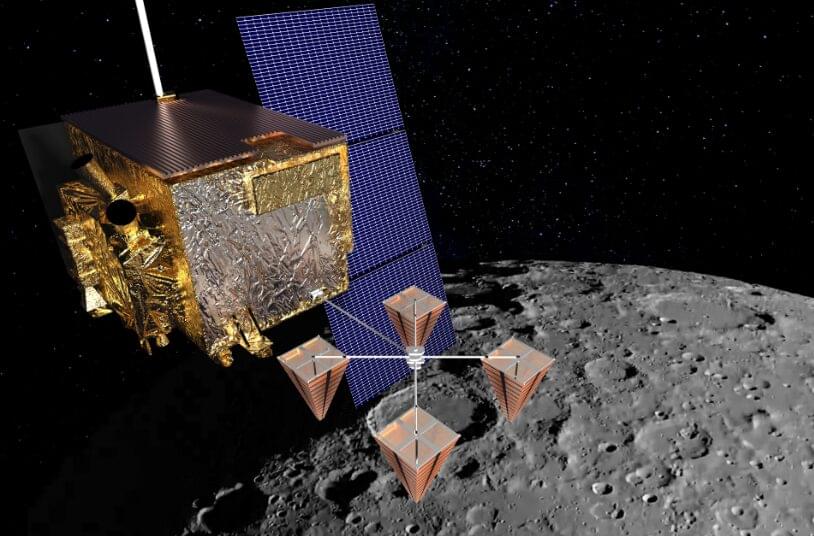
Water ice was previously detected in the permanently shaded regions of the Moon’s north and south poles by Shuai Li, assistant researcher at the Hawai’i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) in the UH Manoa School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST). A new study led by Jordan Ando, planetary sciences graduate student in Li’s laboratory, examined images from a specialized camera, the “ShadowCam,” that was on board the Korea Aerospace Research Institute Korea Lunar Pathfinder Orbiter.