XR Today reports on the latest extended reality news from around the globe, including virtual reality, augmented reality and mixed reality.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.


An artificial nerve system gives prosthetic devices and robots a sense of touch
Stanford and Seoul National University researchers have developed an artificial sensory nerve system that can activate the twitch reflex in a cockroach and identify letters in the Braille alphabet.
The work, reported May 31 in Science, is a step toward creating artificial skin for prosthetic limbs, to restore sensation to amputees and, perhaps, one day give robots some type of reflex capability.
“We take skin for granted but it’s a complex sensing, signaling and decision-making system,” said Zhenan Bao, a professor of chemical engineering and one of the senior authors. “This artificial sensory nerve system is a step toward making skin-like sensory neural networks for all sorts of applications.”

Asia’s Economies Can Embrace Services to Boost Growth and Productivity
Employment and production typically move from agriculture to manufacturing to services, as part of a natural progression that comes with rising income. In Asia, factories have propelled economies, but a transition to modern services could be a new source of growth and productivity. Our blog explains.
Manufacturing has been the engine of growth in Asia, but a transition to modern, tradable services could be new source of growth and productivity.
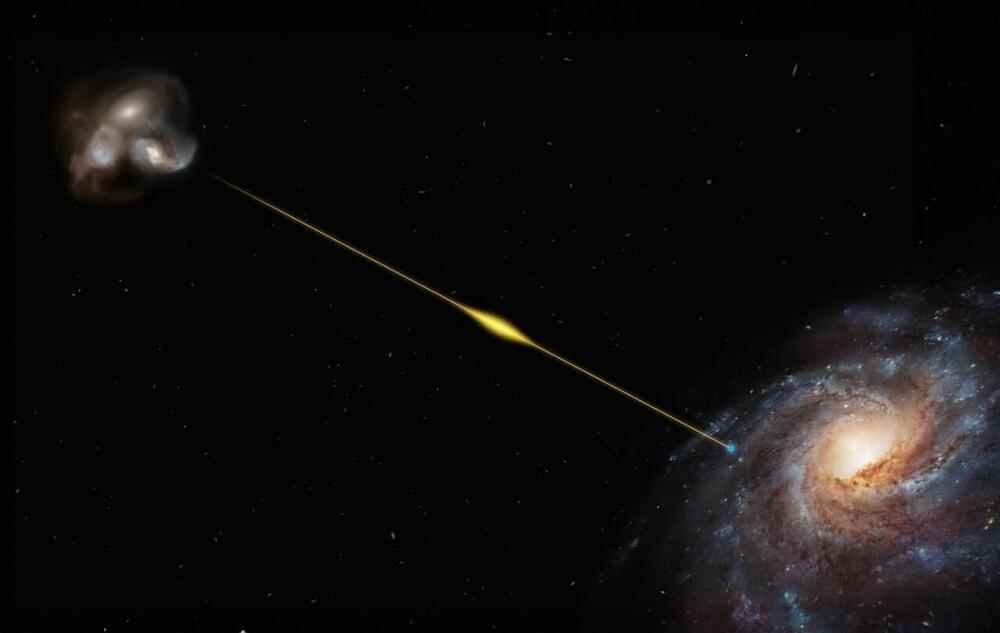

Cosmic Radio Burst from 8 Billion Years Ago Reveals Universe’s Missing Matter
An international team has spotted a remote blast of cosmic radio waves lasting less than a millisecond. This ‘fast radio burst’ (FRB) is the most distant ever detected. Its source was pinned down by the European Southern Observatory’s (ESO) Very Large Telescope (VLT) in a galaxy so far away that its light took eight billion years to reach us. The FRB is also one of the most energetic ever observed; in a tiny fraction of a second it released the equivalent of our Sun’s total emission over 30 years.
The discovery of the burst, named FRB 20220610A, was made in June last year by the ASKAP radio telescope in Australia and it smashed the team’s previous distance record by 50 percent.
“Using ASKAP’s array of dishes, we were able to determine precisely where the burst came from,” says Stuart Ryder, an astronomer from Macquarie University in Australia and the co-lead author of the study published today in Science. “Then we used [ESO’s VLT] in Chile to search for the source galaxy, finding it to be older and further away than any other FRB source found to date and likely within a small group of merging galaxies.”
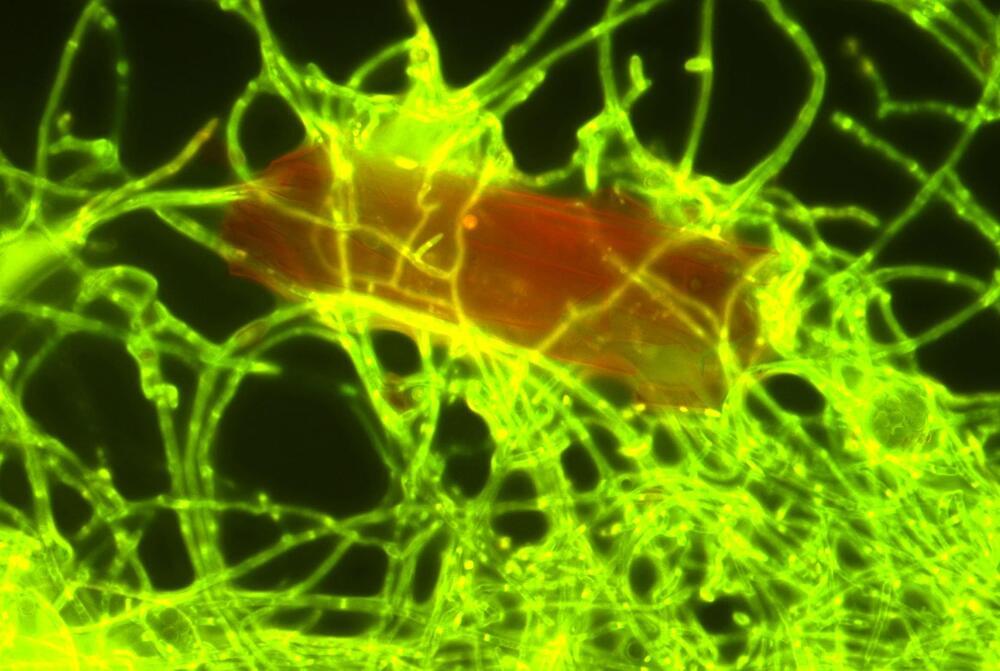
Scientists Discover Marine Fungus That Can Eat Plastic
Researchers found that the fungus Parengyodontium album degrades UV-exposed polyethylene in the ocean, suggesting that similar fungi might also break down plastics in deeper waters.
Researchers, including those from NIOZ, have discovered that a marine fungus can decompose the plastic polyethylene after it has been exposed to UV radiation from sunlight. Their findings, published in the journal Science of the Total Environment, suggest that numerous other fungi capable of degrading plastic likely reside in the deeper regions of the ocean.
The fungus Parengyodontium album lives together with other marine microbes in thin layers on plastic litter in the ocean. Marine microbiologists from the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ) discovered that the fungus is capable of breaking down particles of the plastic polyethylene (PE), the most abundant of all plastics that have ended up in the ocean. The NIOZ researchers cooperated with colleagues from Utrecht University, the Ocean Cleanup Foundation and research institutes in Paris, Copenhagen, and St Gallen, Switzerland. The finding allows the fungus to join a very short list of plastic-degrading marine fungi: only four species have been found to date. A larger number of bacteria were already known to be able to degrade plastic.
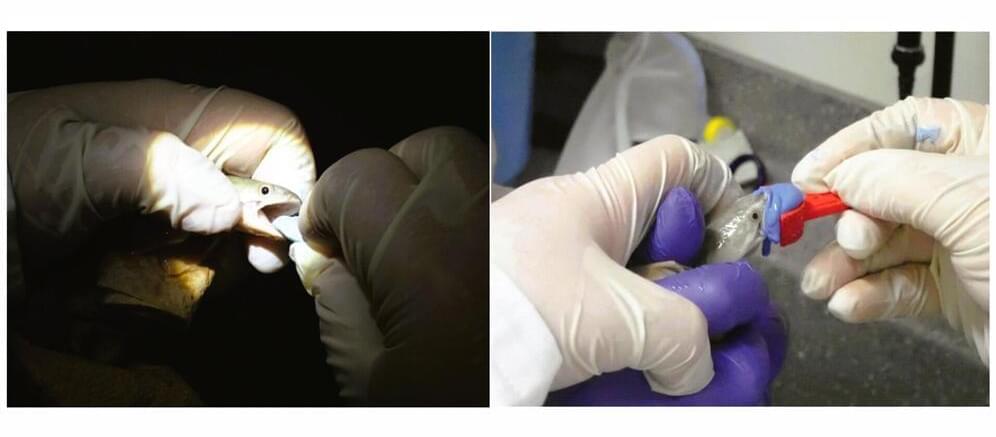
Fish-friendly dentistry: New method makes oral research non-lethal
Can we examine the teeth of living fish and other vertebrates in detail, repeatedly over time, without harming them?
Previously, small animals often had to be euthanized to obtain precise information, but now scientists have found a new way to humanely study detailed dental characteristics of vertebrates. This customizable method can be used for both living animals and museum specimens and has been published in the Journal of Morphology.
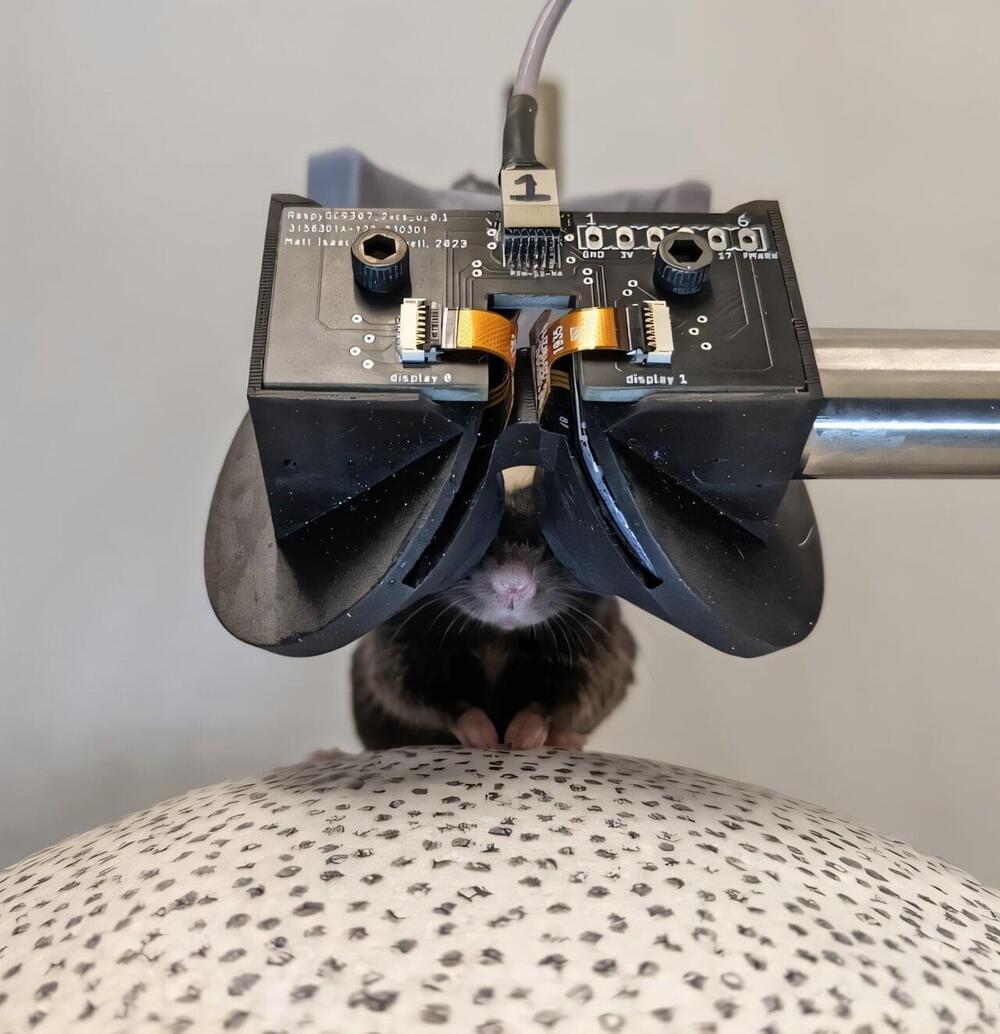

Mice headsets make it easier to study brain response to virtual reality
Virtual reality headsets like the Meta Quest or Apple Vision Pro will be a Christmas gift in more than one home this year.
Now mice are getting in on the action.
Researchers have developed a set of VR goggles for lab mice for use in brain studies, according to a report published recently in the journal Nature Methods.

Rewiring Hope: How Nerve Stimulation Transforms Severe Depression
A groundbreaking clinical trial has revealed that nerve-stimulating therapy can bring significant improvements to people with severe, treatment-resistant depression.
Nearly 500 participants, many unable to work due to their condition, received devices that stimulate the vagus nerve—a critical connection between the brain and body. After a year, those with activated devices reported measurable improvements in symptoms, quality of life, and daily functioning.
Breakthrough in Treatment-Resistant Depression.